Computed tomography vet: A modern diagnostic method for your pet
introduction
Modern veterinary medicine is constantly developing and offers more and more options for diagnosing illnesses in pets early and accurately. One such method is the computer tomography (CT). In this article you will learn how a CT is used by a veterinarian, what advantages this method offers and which clinical pictures can be examined with it.
What is a CT scanner?
A CT scanner is a state-of-the-art medical device that can use X-rays to create three-dimensional images of an animal's interior. This technique allows veterinarians to obtain detailed information about an animal's anatomy and possible diseases without having to perform invasive procedures.
When is a CT used at the vet?
A CT scanner is used in various situations to make a precise diagnosis and determine the best possible therapy for your pet. Some of the most common areas of application are:
- Neurology : Examination of the brain and spinal cord to identify conditions such as tumors, inflammation, or injury.
- Oncology : Diagnosis of tumors and metastases to determine the exact location, size and extent of cancerous tumors.
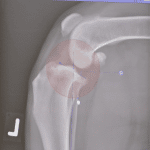
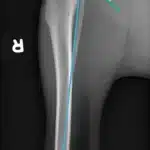
- Orthopedics : Visualization of bones, joints and soft tissues to detect fractures, osteoarthritis or herniated discs.
- Cardiology : Examination of the heart and blood vessels to diagnose heart defects, heart failure, or blood clots.
Advantages of computed tomography in veterinary medicine
Computed tomography offers several advantages over other imaging procedures such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
- Speed : The CT scan typically only takes a few minutes, which is particularly beneficial for animals in pain or anxiety.
- Precision : The three-dimensional images enable a more precise representation of the anatomy and possible diseases, making diagnosis easier.
- Minimally invasive : Since no invasive procedures are required, the animal is not placed under unnecessary stress during the examination.
Process of a CT examination at the vet
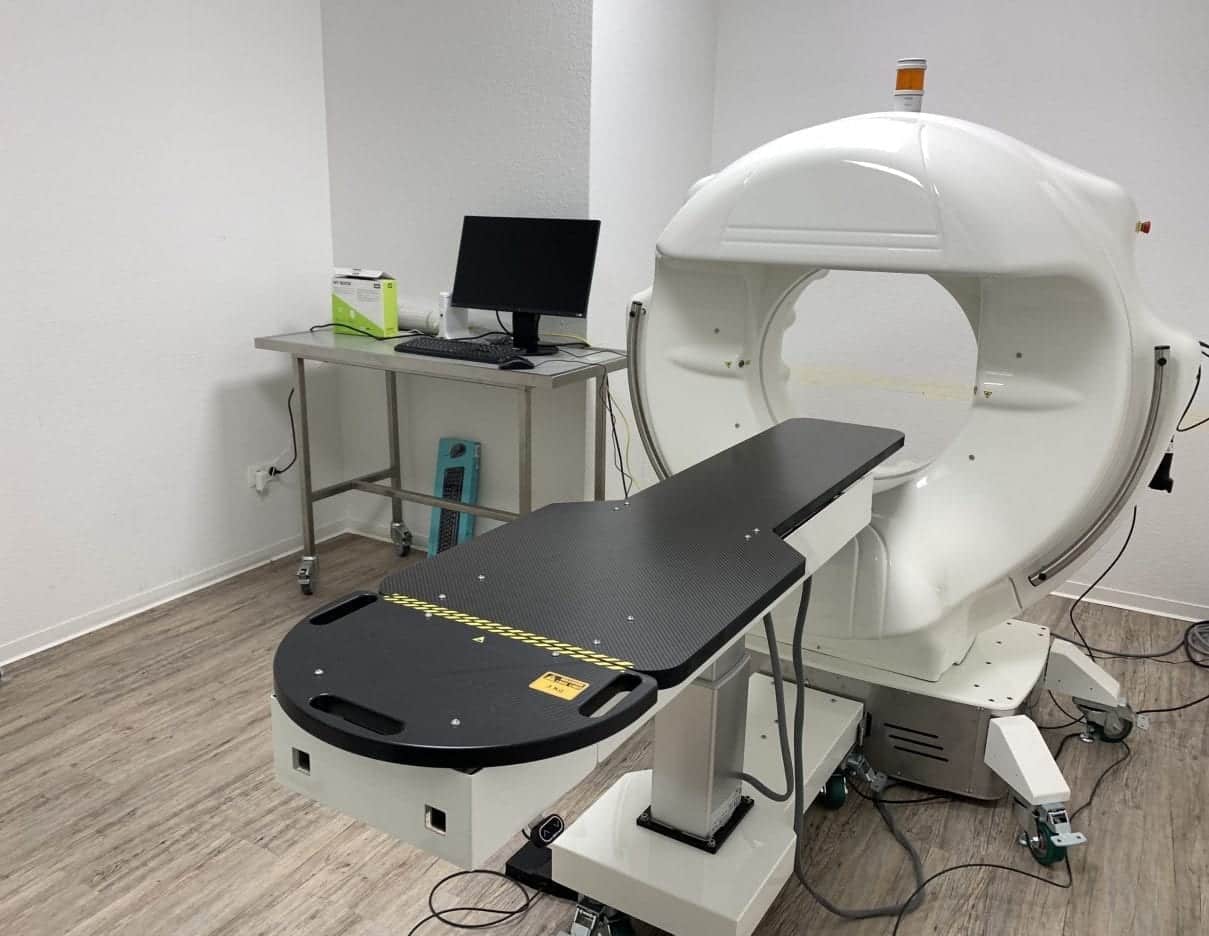
Before the CT scan begins, the animal is usually sedated or placed under general anesthesia to ensure that it remains calm during the scan. The animal is then positioned on a special table and pushed into the CT tube. During the examination, the X-ray tube rotates around the animal and takes multiple X-ray images from different angles. The data obtained is then analyzed by a computer and converted into three-dimensional images.
Once the images are created, they are evaluated by a veterinarian or a specialized radiologist. The results of the examination can then be discussed directly with the animal owner and the necessary treatment options can be initiated.
Possible risks and side effects of computer tomography
Although CT is a relatively safe procedure, there are some possible risks and side effects that pet owners should consider:
- Radiation exposure : As with any x-ray examination, a certain amount of radiation exposure is also present in computer tomography. However, this is usually very low and poses only minimal risk to the animal.
- Anesthesia : Because the CT scan is performed under sedation or general anesthesia, there is some risk of anesthesia-related complications. However, this risk is also low and is minimized by a thorough examination of the animal and its state of health before the examination.
- Allergic reactions : In some cases, a CT scan uses a contrast agent to make certain structures more visible. Some animals may experience allergic reactions to the contrast medium. However, these are rare and usually easy to treat.
Cost of a computer tomography at the vet
The cost of a CT scan can vary depending on the veterinary practice, region and the animal's individual circumstances. As a rule, the prices for a CT examination are between 500 and 1,500 euros. In some cases, additional costs may apply for anesthesia, contrast agent or image evaluation. It is therefore advisable to obtain a cost estimate before the examination and find out about any additional costs.
Our VIMAGO™ Pico computer tomograph
We have a latest generation computer tomograph / digital volume tomograph from VIMAGO. The VIMAGO™ is tailored precisely to the needs of veterinary medicine and is not a discarded former CT as is often found in veterinary practices. This can be seen in the user interface, which displays animals instead of human body regions. Our computer tomograph produces 30x higher resolution images than a normal 16-row computer tomograph and is between 60% -90% lower in radiation than a comparable computer tomograph.
What does this mean for your loved one?
✔ faster and less radiation examination
✔ creates real 3D images, which can then be used, for example, to prepare complicated bone fractures using a 3D printer
Sub-disciplines of veterinary medicine such as orthopedics, cardiology, pulmonology and urology, as well as postoperative controls, benefit from his exceptional skills.
The VIMAGO™ can also do everything that any other CT can do. The VIMAGO™ allows computed tomography imaging of various body regions such as: B. Effectively display the paranasal sinuses and nasal passages, bulla, ear, brain, teeth or spine.
Further advantages of our computer tomograph:
- Size of isotropic voxels ≥ 90x90x90 µm
- allows patients to be scanned in their full length
- Warm-up takes less than 3 minutes
- enables examinations of patients up to 80 kg
- was developed for diagnostic, interventional and intraoperative use
- integrated 2D, MPR and 3D imaging
- diagnostically advantageous soft tissue contrast
- Software enables cutting of the 3D images on all levels in excellent quality
- Export of examination results in standard DICOM format
In addition to our in-house experts, we work closely with internationally trained experts to evaluate the examination results so that you have an optimal examination report in your hands at the end of every CT examination.
Important areas of application for our computer tomograph are:
- Dental x-rays, e.g. FORL in cats - but also dogs, rabbits and guinea pigs can be examined in more detail using computer tomography
- Diagnosis of tumors and metastases
- Setting up bone fractures
- preoperative planning of fracture treatment
- Representation of vessels, bile ducts and gastrointestinal sections with appropriate contrast media
- Placement of probes
- Observation of dynamic processes
- Heart movement
- Swallowing movement (esophagus representation)
- Integrating implant control during surgery (functions similar to a C-arm)
- Biopsies
- Positioning control before the CT examination
In certain areas, our VIMAGO™ is not only equal to a human medical 64-row computer tomograph, but also superior. You can find a comparison here:
Here is an example of a cat dental CT taken with our in-house computer tomograph:
And here is the corresponding 3D printout from our in-house 3D printer:

Conclusion
Computed tomography is an advanced and precise method for diagnosing diseases in pets. It allows veterinarians to obtain detailed information about an animal's anatomy and possible diseases without having to perform invasive procedures. The CT scan is quick, minimally invasive and generally safe. However, pet owners should inform themselves about possible risks, side effects and costs before deciding to undergo a CT scan.