Dog mammary tumor: Everything you need to know
introduction
Dog mammary tumor is a common condition that can affect both female and male dogs. They are usually benign, but can also be malignant. In this article, we will go into detail about the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of dog mammary tumors in order to provide you and your four-legged friend with the best possible care.
(C) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mammary_tumor#/media/File:Mammary_tumor.JPG
Symptoms of dog mammary tumor
Dog mammary tumors can cause various symptoms, depending on the size, location and type of tumor. Here are some of the most common signs that may indicate that your dog may have a dog mammary tumor:
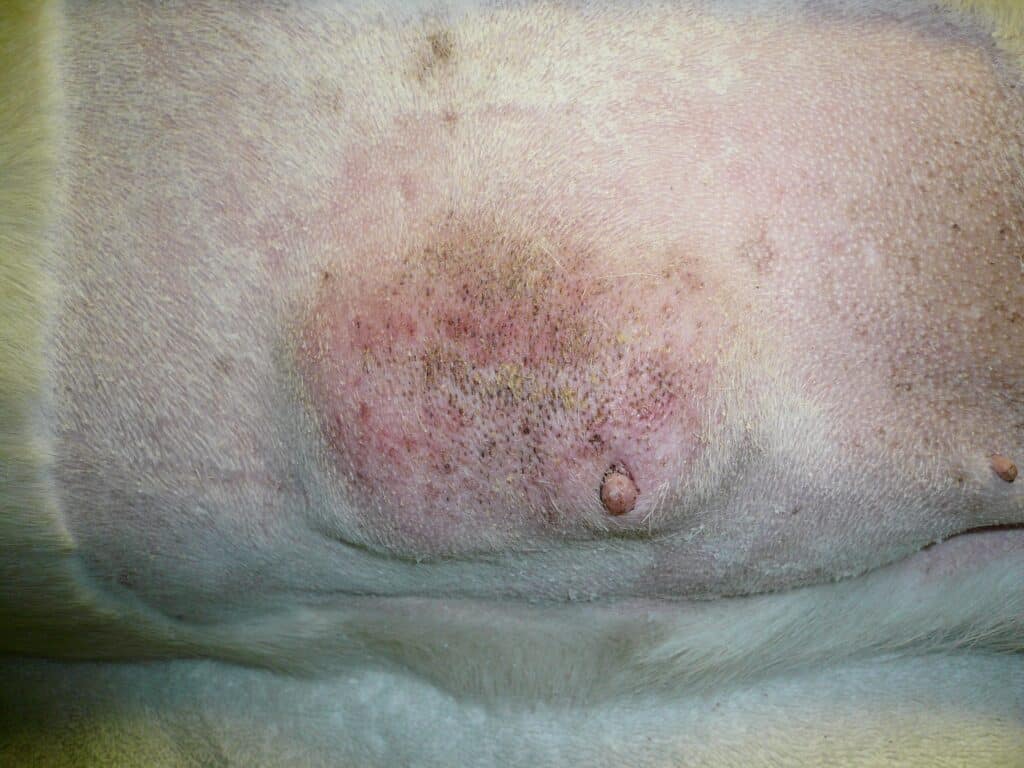
- Breast swelling or lumps : The most noticeable symptom of a mammary tumor in dogs is breast swelling or lumps. These can be of different sizes and shapes and may feel firm or soft.
- Changes in the skin : Skin changes such as redness, scaling or ulcers can indicate a breast tumor.
- Pain or discomfort : If your dog shows pain or discomfort when you touch his chest area, it could be a sign of a mammary tumor.
- Behavioral changes : Dogs with mammary tumors may exhibit behavioral changes such as loss of appetite, lethargy, or increased licking of the affected area.
- Weight loss : Weight loss may occur in advanced breast tumors as the tumor uses energy and nutrients.
Diagnosis of dog mammary tumor
If you notice one or more of the above symptoms in your dog, you should consult a veterinarian immediately. The vet will perform a physical exam and may order a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- Fine needle aspiration : This technique uses a thin needle to remove cells from the tumor. The cells are then examined under a microscope to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
- Biopsy : A biopsy is another way to determine the type of tumor. A small piece of tumor tissue is removed and examined histologically.
- X-rays : X-rays can be used to determine whether the tumor has metastasized to other parts of the body.
- Ultrasound : Ultrasound scans can be helpful in assessing the size and structure of the tumor.
Treatment of mammary tumor dog
Treatment for mammary tumors in dogs depends on several factors, such as the type of tumor, the stage of the disease, and the dog's general health. Below are some of the common treatment methods:
- Surgery : Surgery is the most common and effective treatment method for dog mammary tumors . For benign tumors, it may be enough to simply remove the tumor itself, while for malignant tumors, more extensive surgery may be required to remove surrounding tissue and possibly lymph nodes as well. In some cases, a mastectomy, the complete removal of the breast gland, may be necessary.
- Radiation therapy : Radiation therapy can be used to kill tumor cells and slow tumor growth. This treatment method can be used alone or in combination with surgery. Radiation therapy can be used for localized tumors that are difficult to remove surgically due to their location or size. It can also be used after surgery to destroy remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Chemotherapy : Chemotherapy is another treatment option for dogs with mammary tumors, particularly advanced or metastatic tumors. Chemotherapy drugs can be administered either orally or intravenously and work by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy : Immunotherapy is a relatively new treatment method that aims to boost the dog's immune system to fight against the tumor. This therapy can be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Pain management : Pain management is an important part of treating mammary tumors in dogs. Your veterinarian may prescribe pain medications to ease your dog's discomfort and improve his quality of life.
- Hormone therapy : Hormone therapy can be used for hormone-sensitive tumors to slow or stop tumor growth. Your veterinarian will select the most appropriate therapy based on your dog's tumor type and individual needs.
Surgical treatment of mammary tumor dog
Surgical treatment of dog mammary tumors is one of the most common and effective methods of removing tumors and improving the prognosis for the animal. Depending on the size, location and type of tumor, there are different surgical procedures that veterinarians may use.
Lumpectomy for dog mammary tumor
A lumpectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the tumor and a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue. This procedure is suitable for small, benign tumors that can be easily separated from surrounding structures. Lumpectomy is less invasive than other surgical procedures and allows for a quicker recovery for the dog.
Partial mastectomy for dog mammary tumor
During a partial mastectomy, part of the affected mammary gland is removed along with the tumor. This procedure is suitable for larger or deeper tumors that cannot be easily removed with a lumpectomy. It allows more tumor tissue to be removed and reduces the risk of the tumor forming again.
Radical mastectomy for dog mammary tumor
Radical mastectomy is a more extensive surgical procedure that involves removing all of the mammary glands on one side of the body. This procedure is usually used for aggressive or widespread tumors that cannot be treated by less invasive methods. Radical mastectomy has a higher success rate in completely removing tumor tissue, but can result in longer recovery times and possible complications.
Reconstructive surgery for dog mammary tumor
In some cases, reconstructive surgery may be considered to improve the appearance and function of the mammary glands after removal of mammary tumors. Reconstructive surgery can help increase a dog's confidence and maintain his quality of life.
Dog mammary tumor prevention
Although there is no guarantee that your dog will never develop a mammary tumor, there are some steps you can take to reduce the risk:
- Neutering : Neutering female dogs, especially before their first heat, can significantly reduce the risk of mammary tumors. The hormones estrogen and progesterone, which are produced during the sexual cycle in unspayed female dogs, can promote tumor growth.
- Healthy diet : A balanced and healthy diet is important to strengthen your dog's immune system and reduce the risk of cancer. Make sure your dog gets high-quality food and avoid being overweight, as this can increase the risk of mammary tumors.
- Regular Checkups : Make sure your dog gets regular checkups vet Early detection of mammary tumors can improve treatment outcomes and maintain your dog's quality of life.
- Breast Exams : Perform regular breast exams on your dog to detect early changes such as lumps or swelling. Talk to your veterinarian about how to properly perform these exams.
- Reduce environmental factors : Reduce your dog's exposure to harmful environmental factors such as smoke, pesticides and chemicals, which can potentially increase the risk of cancer.
Frequently asked questions about dog mammary tumors :
How can I tell if my dog has a mammary tumor?
It is important to perform regular breast exams on your dog to detect possible signs of mammary tumors early. Watch for symptoms such as swelling or lumps in the breast, changes in the skin, pain or discomfort in the breast area, changes in behavior, and weight loss. If you notice one or more of these symptoms in your dog, you should consult a veterinarian immediately for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Is a mammary tumor in dogs always malignant?
No, mammary tumors in dogs are not always malignant. In fact, most mammary tumors in dogs are benign, meaning they are noninvasive and do not spread to other parts of the body. However, there are also malignant breast tumors that are more aggressive and have the potential to grow into neighboring tissues and metastasize to distant organs. An accurate diagnosis by the veterinarian is necessary to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant and what treatment is most appropriate.
What factors affect my dog's risk of developing a mammary tumor?
There are several factors that can affect your dog's risk of developing a mammary tumor.
These include: - Genetics: Some dog breeds have a higher susceptibility to mammary tumors, suggesting that genetic factors may play a role.
- Age: Older dogs have a higher risk of developing mammary tumors.
- Neutered status: Female dogs that have not been neutered have a higher risk of mammary tumors than female dogs that have been neutered, especially if neutered before their first heat.
- Hormonal factors: The hormones estrogen and progesterone, which are produced during the sexual cycle in unspayed female dogs, can promote tumor growth.
- Diet and lifestyle: Obesity and an unbalanced diet can increase the risk of breast tumors.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to harmful environmental factors such as smoke, pesticides and chemicals can increase the risk of cancer.
Summary
Dog mammary tumor is a serious disease that should be detected and treated early. By keeping an eye on the above symptoms, making regular vet visits , and taking preventive measures, you can help reduce your dog's risk of mammary tumors and maintain his quality of life. Treatment for breast tumors can vary depending on the type and stage of the tumor and typically includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and pain management.
Preventing mammary tumors in dogs is an important aspect of caring for and protecting your four-legged friend. By spaying female dogs, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exams, and reducing harmful environmental factors, you can help reduce your dog's risk of mammary tumors.
Current research on the topic of dog mammary tumors
Current research on mammary tumors in dogs focuses on various aspects of the disease, such as diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and prevention. Some important topics studied in the scientific literature are:
- Molecular markers : Identification of molecular markers that may aid in the diagnosis and prognosis of mammary tumors in dogs is an active area of research. By understanding the genetic and molecular changes associated with mammary tumor development and progression, researchers can identify new therapeutic targets and develop personalized treatment approaches.
- New therapeutic approaches : The development of new and improved therapeutic approaches for mammary tumors in dogs is another important research focus. This includes research into immunotherapies, targeted therapies and combination therapies aimed at increasing the effectiveness of treatment and minimizing side effects.
- Prevention : Investigating preventive measures that can reduce the risk of mammary tumors in dogs is another important topic in research. This includes studies on the effect of neutering, diet, environmental factors and other aspects of dog health on the risk of mammary tumors.
- Prognostic factors : Research into prognostic factors that can predict the progression and outcome of mammary tumors in dogs is also of interest. This can help optimize treatment decisions and improve the quality of life and survival of affected dogs.
- Comparative oncology : Another area of research is comparative oncology, where studying mammary tumors in dogs can help improve understanding of breast cancer in humans. Because dogs and humans share similar biological and genetic characteristics and live in the same environment, findings from research into canine mammary tumors can potentially be transferred to humans to develop new treatments and prevention strategies.
Overall, current research on mammary tumors in dogs is helping to improve our understanding of the disease and develop new, more effective treatment and prevention approaches that can improve the lives of our four-legged friends.
