Hypoadrenocorticism/Addison's Disease in Dogs: A Comprehensive Guide
introduction
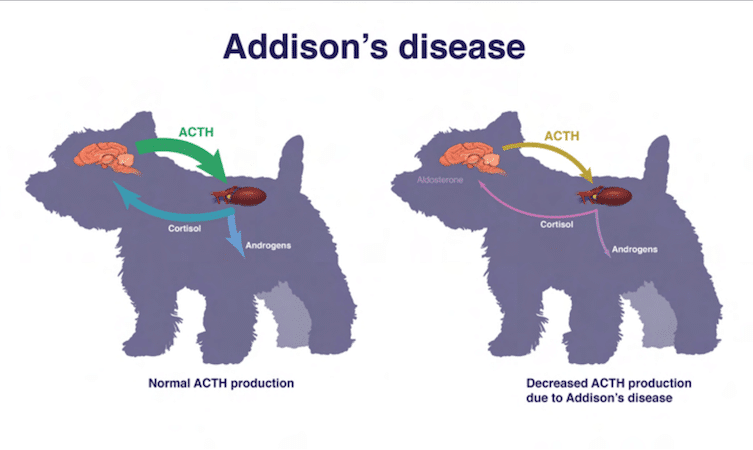
Hypoadrenocorticism, also known as Addison's disease, is a condition that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough vital hormones. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options for Addison's disease in dogs.
(C) https://westiefoundation.org/westie-health-issues
Causes of Addison's Disease in Dogs
The main cause of Addison's disease is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys the cortex of the adrenal glands. This means that the adrenal glands cannot produce enough cortisol and aldosterone, which are essential for metabolism, blood pressure regulation, fluid and electrolyte balance, and the response to stress.
In rare cases, other causes such as injuries, medication side effects, infections or tumors can impair the function of the adrenal cortex and lead to Addison's disease.
Symptoms of Addison's Disease in Dogs
Symptoms of Addison's disease are often non-specific and may resemble those of other diseases. The most common signs are:
- Loss of appetite
- Lethargy and weakness
- Vomiting and diarrhea (possibly bloody)
- weight loss
- Tremors, muscle twitches, or muscle stiffness
- depression
- Dehydration (drying out)
Diagnosis of Addison's disease in dogs
The diagnosis of Addison's disease can be difficult due to the non-specific symptoms. Several blood tests are usually done to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis. A routine blood test that shows changes in electrolyte levels sodium and potassium may indicate Addison's disease.
The ACTH stimulation test is the gold standard for diagnosing Addison's disease. In this test, the dog is given synthetic ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) to stimulate hormone production by the adrenal glands. An inadequate hormonal response indicates Addison's disease.
Treating Addison's Disease in Dogs
Although Addison's disease cannot be cured, the disease can be well controlled with lifelong hormone replacement therapy. Treatment includes administration of medications that replace cortisol and aldosterone, such as glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids.
Careful monitoring and adjustment of medication dosage is required to ensure optimal therapy for the affected dog. In the initial phase of treatment, check-ups are usually carried out at 10 days, 4 weeks, 8 weeks and 12 weeks. Once the dog is well adjusted to the medication, further checks every 4 to 6 months are recommended.
With appropriate treatment, dogs with Addison's disease can achieve a normal life expectancy and quality of life. However, it is important to watch for signs of Addisonian crisis, which can be caused by sudden stressors or inadequate hormone therapy. An Addisonian crisis is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate veterinary care.
Long-term management and care of dogs with Addison's disease
Successful treatment of dogs with Addison's disease requires dedicated long-term management and attentive care from the pet owner. Some aspects that are important when caring for dogs with Addison's disease include:
Adaptation of living conditions
It is important to make the dog's daily routine as stress-free as possible, as stress can worsen the symptoms of Addison's disease. Pet owners should be careful to keep their dog's daily routine consistent and minimize potential stressors, such as loud noises or changes in the environment.
Regular veterinary examinations
Regular visits to the veterinarian are crucial to monitoring the health of a dog with Addison's disease and adjusting medication dosages accordingly. The veterinarian will check the dog's hormone levels and blood electrolyte levels and adjust the medication dosage if necessary.
Nutrition and hydration
A balanced diet tailored to the dog's needs will help improve his overall health and manage Addison's disease. Adequate fluid intake is also important to prevent dehydration, especially in dogs suffering from vomiting or diarrhea. Pet owners should ensure that fresh drinking water is always available.
Movement and social interaction
Moderate exercise and social interaction are important for the dog's physical and emotional well-being. Pet owners should ensure that their dog regularly participates in age- and health-appropriate activities to ensure an optimal living environment.
Education and support for pet owners
Pet owners faced with Addison's disease should become well-informed and up-to-date about the condition in order to provide their dog with the best possible care. Talking to other pet owners who also care for dogs with Addison's disease can provide helpful support and valuable information.
Overall, successfully caring for a dog with Addison's disease requires commitment, knowledge and care on the part of the pet owner. With dedicated long-term management, regular veterinary care, and attentive care, dogs with Addison's disease can live full, healthy lives.
Prevention of Addison's Disease in Dogs
Since the main cause of Addison's disease is an autoimmune disease, there are currently no specific measures to prevent the disease. However, a healthy lifestyle and regular veterinary exams can help reduce your dog's risk of Addison's disease and other diseases.
Summary
Addison's disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough vital hormones, which may be due to an autoimmune disease or other causes. Diagnosis can be difficult due to non-specific symptoms, but the ACTH stimulation test is considered the gold standard for confirming the diagnosis. Treatment for Addison's disease involves lifelong hormone replacement therapy, with careful monitoring and adjustment of medication dosage required. With proper treatment, dogs with Addison's disease can achieve a normal life expectancy and quality of life.
- Hypoadrenocorticism/Addison's Disease in Dogs: A Comprehensive Guide
