Inflammatory bowel disease in dogs - symptoms, treatment and prognosis
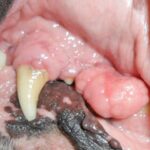
Inflammatory bowel disease is a common cause of diarrhea and abdominal pain in dogs. These diseases can occur both acutely and chronically and have different triggers. This article describes the most common symptoms, treatment options, and prognosis for inflammatory bowel disease in dogs.
Symptoms
A dog with inflammatory bowel disease may exhibit the following symptoms:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- stomach pain
- Greasy or mucous stools
- Flatulence
- weight loss
- Loss of appetite
It's important to note that these symptoms can also indicate other health problems. Therefore, if you suspect inflammatory bowel disease, you should consult a veterinarian.
causes
There are many factors that can trigger inflammatory bowel disease in dogs. This includes:
- Infections caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites
- Nutritional problems, e.g. due to intolerances or intolerant fasting
- stress
- Immune disorders
diagnosis
To diagnose inflammatory bowel disease in a dog, a veterinarian may perform several tests, including:
- Blood tests
- Stool examinations
- X-rays
- Ultrasound examinations
- Endoscopy
Treatment
Treatment for inflammatory bowel disease in dogs depends on the cause. A veterinarian may recommend the following treatment options:
- Antibiotics to treat bacterial infections
- Diet changes to avoid intolerances or intolerances
- Medications to relieve pain and inflammation
- Stress reduction
- Immunotherapy for immune disorders
Does your dog suffer from chronic intestinal disease or an allergy?
Do you often change dog food and/or the vet out of sheer desperation?
The intestines of humans and animals are often referred to as the seat of health. Around 70% of immune cells are found in the intestine alone; their main task is to ward off pathogens that cause illness. At the same time, the immune system must support beneficial bacteria and food antigens . Autoimmune reactions occur when defense cells of the immune system attack and damage healthy and useful cells and tissue parts.
In allergic reactions, the immune system reacts unnecessarily strongly to harmless foreign substances. Intestinal flora and intestinal mucosa should be absolutely intact in order to keep the intestinal environment constant in order to avoid allergies or intolerances or at least keep them under control.
A healthy intestine is absolutely necessary for a strong immune system. In our practice, we have been checking the composition of the microbiome in the intestine for chronic intestinal diseases for a long time and, if necessary, begin targeted therapy immediately.
This examination of the microbiome is carried out via a fecal examination in a special laboratory and is now also carried out for other diseases, e.g. chronic skin diseases / allergies, recurring giardia infections, etc.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Is a chronic disease of the digestive tract that can occur in dogs. This is an inflammation of the mucous membranes in the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to a disruption in normal digestive processes. The causes of IBD in dogs are not yet fully understood, but it is thought that a malfunction of the immune system, a genetic predisposition, or an allergic reaction to certain foods may play a role.
Symptoms of IBD in dogs include diarrhea, vomiting, weight loss, bloating, and emaciation. It is important to see a veterinarian if you suspect IBD, as these symptoms can also indicate other health problems. The veterinarian will perform a thorough physical examination and may perform additional tests, such as blood and stool tests, to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for IBD in dogs can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Changing your diet, using medications that suppress the immune system, or even surgery may be an option. In some cases, a combination of these treatment methods may be necessary.
It is important that owners of dogs with IBD work closely with their veterinarian to ensure the best possible treatment for their pet. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of treatment is necessary because the symptoms of IBD can change and worsen.
In summary, IBD can be a serious condition in dogs, but early diagnosis and adequate treatment can improve the animal's quality of life and keep symptoms under control. It is important that owners work closely with their veterinarian to achieve the best possible outcome for their animal.
IGOR, or Inflammatory Gastroesophageal Reflux
Is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract in dogs that is caused by inflammation of the mucous membranes in the esophageal area. This inflammation can cause the dog to vomit stomach contents back into the esophagus or even sneeze.
The causes of IGOR in dogs are not yet fully understood, but it is thought that a malfunction of the stomach, an allergic reaction to certain foods, or a genetic predisposition may play a role.
Typical symptoms of IGOR in dogs include frequent vomiting, sneezing, coughing and hoarseness. It is important to see a veterinarian if IGOR is suspected, as these symptoms may also indicate other health problems.
Diagnosis of IGOR in dogs is usually made through a thorough physical examination, blood and stool tests, and an endoscopic examination. In some cases, a stomach acid measurement may also be necessary.
Treatment for IGOR in dogs can vary depending on the severity of the disease. A change in diet, the use of medications that neutralize the stomach, or surgery may be an option. In some cases, a combination of these treatment methods may be necessary.
It is important that owners of dogs with IGOR work closely with their veterinarian to ensure the best possible treatment for their pet. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of treatment is necessary as the symptoms of IGOR may change and worsen.
Prognosis for dogs with inflammatory bowel disease
The prognosis for dogs with inflammatory bowel disease depends on the cause, severity, and timely diagnosis and treatment. Many dogs can expect a good prognosis with successful treatment, while others may require longer treatment or have permanent impairment. It is important to have close monitoring and regular checks by a veterinarian to ensure your dog has the best possible prognosis.
Conclusion
Inflammatory bowel disease in dogs is a serious health condition that must be recognized and treated early. By observing the symptoms, carrying out a comprehensive diagnosis and providing appropriate treatment, the dog's well-being can be improved and its quality of life increased. It is important to work closely with a veterinarian to achieve the best possible outcome.
For further help, please contact Dr. Horst-Dieter Krause Small Animal Center Arndt
Here you can prepare for an appointment according to Dr. Already submit documents to Krause: