- Eosinophilic Keratitis in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide
- Development and causes of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
- Symptoms of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
- Diagnosis of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
- Treatment of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
- Prophylaxis and long-term care for eosinophilic keratitis
- Summary of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
Eosinophilic Keratitis in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide
The health of our pets is very important to us. The health of the eyes in particular is essential for their quality of life. Eosinophilic keratitis is a disease that particularly affects cats and is often associated with a previous herpes infection. Below we will examine the clinical picture in detail and provide recommendations for prevention and treatment.
Development and causes of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
Eosinophilic keratitis is a serious eye disease in cats that often occurs as a result of a herpes infection. In order to better understand the complex process behind this disease, it is important to shed light on the various factors and processes that contribute to the development of eosinophilic keratitis.
Herpes infection as a trigger
One of the main triggers of eosinophilic keratitis is a previous infection with the Feline Herpesvirus (FHV-1). This virus is common and can cause acute inflammation in the eyes, known as herpetic keratitis. After such an infection, the cat's immune system may mount an excessive response, leading to eosinophilic keratitis.
Misguided immune response
The central cause of the development of eosinophilic keratitis is a misdirected immune reaction. During acute herpes keratitis, new vessels grow into the cornea to support the healing process. However, these vessels can transport eosinophilic white blood cells into the cornea after infection. Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that usually become active during allergic reactions or parasite infestations. In this case, however, they react to the previous herpes infection and get into the cornea.
Inflammatory process and corneal changes
The eosinophil cells cause inflammation and damage to the cornea. This inflammation can affect the healing of the cornea and lead to visible changes. These include whitish, dot-like deposits (plaque) on the cornea and possibly loose, non-adhering epithelial edges of the top layer of the cornea. As it progresses, a raised pink scar tissue known as pannus may develop, further reducing the transparency of the cornea and disrupting the cat's vision.
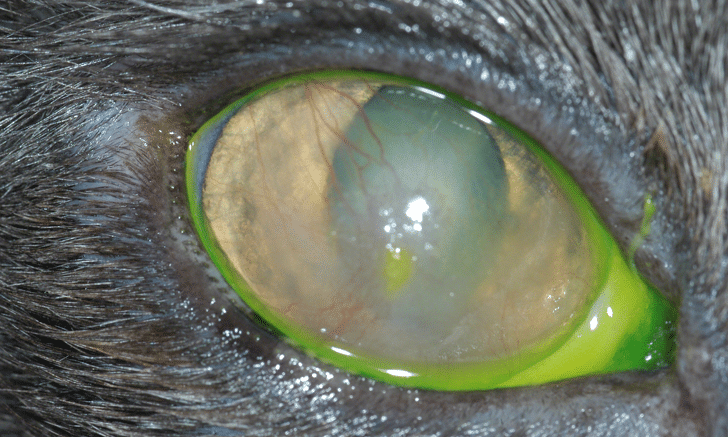
(C) https://www.cliniciansbrief.com/article/image-gallery-eosinophilic-keratitis-cats
Continue
The inflammation and damage to the cornea can cause other problems, such as chronic corneal inflammation and possibly intraocular inflammation. If the inflammation progresses, permanent vision loss may occur, although the inside of the eye may still be healthy.
The exact development and causes of eosinophilic keratitis are complex and are influenced by a variety of factors. However, the previous herpes infection and the subsequent immune reaction play a central role in the development of this serious eye disease in cats.
Symptoms of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
Eosinophilic keratitis can be very worrying for cat owners and especially for the animals affected. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial to enable timely and effective treatment. Here you will find a comprehensive overview of the symptoms that can be associated with eosinophilic keratitis.
Visible changes in the cornea
- Point-like deposits: One of the first and most noticeable symptoms are whitish, point-shaped deposits on the cornea. These deposits are accumulations of eosinophil cells that are formed by the body's immune response to a previous herpes infection.
- Pannus (raised scar tissue): Over time, pink scar tissue (pannus) can form, affecting the transparency of the cornea and therefore reducing the vision in the affected eye.
Discomfort and behavioral changes
- Rubbing the eye: Cats may begin rubbing their eye or rubbing their face against furniture or the floor to relieve the irritation.
- Blinking or squinting the eye: Affected cats may blink more frequently or squint their eye to protect it from light and irritation.
Tearing and eye discharge
- Increased tear flow: Increased tear flow may occur due to the irritation and inflammation.
- Dry eye: Paradoxically, dry eye can also occur when the communication between the nerve fibers of the cornea and the tear gland is impaired by the herpes virus.
Redness and swelling
- Redness: The inflammation can cause significant redness of the eye and surrounding tissues.
- Swelling: Swelling of the eyelid or surrounding tissues may also occur.
reaction to light
- Light sensitivity: Cats with eosinophilic keratitis may be sensitive to bright light and may seek out darker areas to minimize irritation.
Reaction to eye medication
- Adverse Reaction to Eye Medication: In some cases, the use of eye medications may result in increased eye discharge, redness, and other negative reactions, especially if there is intolerance to an active ingredient or the basis of the medication.
Altered vision
- Impaired vision: The clouding of the cornea and inflammation can affect the cat's vision, which can be reflected in altered behavior or mobility.
Symptoms of eosinophilic keratitis can range from mild to severe and can significantly impact affected cats' quality of life. If you notice one or more of these symptoms in your cat, it is advisable to consult a veterinarian for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Dealing with your cat's symptoms and needs with understanding and attentiveness can make a difference in promoting their well-being and improving their quality of life.
Diagnosis of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
Early and accurate diagnosis of eosinophilic keratitis is crucial for successful treatment and the long-term well-being of the affected cat. Here we discuss the different steps and methods used in the diagnosis of this serious eye disease.
History and clinical examination
The first step in diagnosis is a thorough medical history and a clinical examination by a veterinarian . Both the cat's medical history and current symptoms are recorded. Particular attention is paid to previous eye infections, especially herpes infections, and existing eye symptoms.
Eye exam
The eye examination is a central part of the diagnosis. The veterinarian examines the cat's eyes for visible signs of eosinophilic keratitis, such as pinpoint deposits, pannus, and corneal opacities. The reaction of the pupils to light and general eye mobility can also be assessed.
Fluorescein test
The fluorescein test is an important diagnostic tool to check the integrity of the cornea. In this test, a fluorescent dye is applied to the eye, which attaches to defective areas of the cornea and becomes visible under UV light. In this way, injuries or ulcerations to the cornea can be detected and the severity of the disease can be assessed.
Cytological examination
In some cases, a cytological examination of the ocular surface may be performed to identify the type of cells involved in the inflammatory response. This can help distinguish eosinophilic keratitis from other eye diseases.
Cultural investigation
A culture examination for eosinophilic keratitis may also be helpful to rule out or identify bacterial infections that may be present in addition to eosinophilic keratitis.
Further diagnostic tests
Additionally, other diagnostic tests such as a blood test, allergy test, or systemic disease test may be performed to assess the cat's overall health and identify possible comorbidities.
Specialized eye exams
Further special eye examinations can be carried out in specialized veterinary practices or by eye specialists. These include, for example, slit lamp biomicroscopy, tonometry to measure intraocular pressure or gonioscopy to assess the chamber angle.
Diagnosis of eosinophilic keratitis requires careful examination and possibly a series of tests. Through a thorough diagnosis, an individual treatment plan can be created that is tailored to the specific needs of the affected cat and offers the best chance of successful treatment.
Treatment of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
Eosinophilic keratitis is a serious condition whose treatment requires careful consideration and tailoring to the specific needs of the affected cat. Below we provide a comprehensive overview of the therapeutic approaches that can be used in the treatment of this eye disease.
Local therapy
Corticosteroids:
Topical application of corticosteroid eye preparations is a common treatment for eosinophilic keratitis. These medications can help reduce inflammation and ease discomfort for the cat. However, corticosteroids must be used with caution as they can worsen symptoms if used incorrectly, particularly in the presence of a concomitant herpes infection.
Nourishing eye drops and ointments:
To protect and care for the cornea, nourishing eye drops or ointments can be administered. These preparations can help keep the calluses moist, support the healing process, and relieve discomfort.
Systemic therapy
Antiviral drugs:
If a concomitant herpes infection is present, antiviral medications may be given to combat the infection and prevent further damage.
Immunomodulators:
In some cases, immunomodulators may be helpful in modulating and controlling the excessive immune response that leads to eosinophilic keratitis.
Supportive therapy
Tear substitutes:
If you have dry eyes, tear substitutes can help replace the missing tear film and thus protect the cornea from further damage.
Dietary supplements:
Dietary supplements containing omega-3 fatty acids and other anti-inflammatory substances can provide support and help promote overall eye health.
Further measures
Regular check-ups:
Regular monitoring by a veterinarian is crucial to assess treatment progress and adjust therapy if necessary.
Specialized eye care:
In severe cases or if treatment does not work as desired, a referral to a veterinarian specializing in ophthalmology may be advisable for specialized treatment.
Important information for treatment
The treatment of eosinophilic keratitis requires patience and close cooperation between the veterinarian and the cat owner. Early intervention, consistent treatment and good communication can go a long way to improving the prognosis and promoting the well-being of the affected cat. If symptoms worsen or persist, a veterinarian should be consulted in order to adjust therapy and take further diagnostic measures. This ensures that your cat receives the best possible care and that its quality of life can be maintained at a high level.
Prophylaxis and long-term care for eosinophilic keratitis
Eosinophilic keratitis in cats requires not only comprehensive therapy, but also careful prophylaxis and long-term care to prevent recurrence of the disease and maintain the cat's quality of life. The most important measures and considerations for prophylaxis and long-term care are discussed below.
Vaccinations
Regular vaccinations against cat flu and cat flu can help minimize the risk of herpes infections, which are a common cause of eosinophilic keratitis. It is advisable to discuss and follow a vaccination schedule with your veterinarian.
Eye care
Regular eye care is crucial to promote eye health and detect potential problems early. This includes:
- Check eyes daily for redness, swelling, discharge, or other abnormalities.
- Cleaning the eyes with a soft, damp cloth to remove crusts or discharge.
- Using veterinarian-recommended eye drops or ointments to care for the cornea and prevent dryness.
Stress management
Stress can affect the immune system and increase the risk of eye problems. It is important to create a calm and stable environment for your cat. This includes:
- Providing a safe and peaceful retreat.
- Avoiding abrupt changes in your cat's environment or routine.
- Providing appropriate mental and physical stimulation.
Nutrition management
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients and omega-3 fatty acids can promote eye health and support the immune system. It is advisable to follow your veterinarian's nutritional guidelines and recommendations.
Regular vet visits
Regular vet visits are important to monitor your cat's eye health and detect potential problems early. During these visits, the veterinarian can evaluate the effectiveness of ongoing treatment and make adjustments if necessary.
Long-term medication management
In some cases, long-term medication management may be necessary to control symptoms and prevent recurrence of eosinophilic keratitis. Adherence to the medication schedule and regular monitoring of eye health are critical to the success of long-term care.
Education and support
As a cat owner, it is important to educate yourself about eosinophilic keratitis and its long-term care. Working with your veterinarian and having access to supportive resources can help you provide the best possible care for your cat.
Prophylaxis and long-term care for eosinophilic keratitis is an ongoing process that requires commitment and attention. By following the guidelines above and working closely with your veterinarian, you can help promote your cat's eye health and improve his quality of life.
Summary of eosinophilic keratitis in cats
Eosinophilic keratitis is a serious eye disease in cats that typically occurs after a herpes infection. The development of eosinophilic keratitis is due to a derailed immune reaction in which eosinophilic cells invade the cornea. The symptoms of eosinophilic keratitis include punctate deposits on the cornea, pannus formation, redness and possibly altered vision.
Diagnosis of eosinophilic keratitis includes a thorough clinical examination, eye examination and specific tests such as fluorescein test and cytological examinations. Eosinophilic keratitis can be treated locally with eye preparations containing corticosteroids and nourishing eye drops or systemically with antiviral medications and immunomodulators.
Prevention of eosinophilic keratitis includes regular vaccinations, eye care, and stress management. Long-term care for eosinophilic keratitis includes regular veterinary visits, possibly long-term medication management, and appropriate nutrition.
Eosinophilic keratitis requires careful attention and treatment to maintain the cat's eye health and improve its quality of life. Close collaboration with the veterinarian and comprehensive education about eosinophilic keratitis are critical to the successful treatment and prevention of this serious eye disease. Eosinophilic keratitis is challenging but can be managed effectively with well-designed therapy and long-term care.
Eosinophilic keratitis is an example of how dedicated and informed care can make the difference in a cat's life and highlights the importance of early diagnosis and treatment for eye problems in cats.
Classification of eosinophilic keratitis into other corneal diseases in cats
Corneal diseases in cats can have different causes and manifestations. They represent a broad spectrum of eye diseases, of which eosinophilic keratitis is a specific form. Here is a classification of eosinophilic keratitis in the context of other corneal diseases in cats:
- Herpetic keratitis:
- Caused by Feline Herpesvirus-1 (FHV-1), often leads to corneal ulcers and inflammation.
- Bacterial keratitis:
- Bacterial infections can lead to inflammatory processes and corneal ulcers.
- Fungal keratitis:
- Fungal infections can also cause inflammation and corneal ulcers.
- Eosinophilic keratitis:
- An immune-mediated reaction, often following a herpes infection, leads to inflammation and corneal opacity.
- Corneal dystrophy:
- A non-inflammatory, often hereditary disease that leads to deposits in the cornea.
- Corneal degeneration:
- Often age-related, leads to calcification and lipid deposits in the cornea.
- Traumatic keratitis:
- Caused by physical injury, foreign objects or chemical irritants.
- Ulcerative keratitis:
- Inflammatory processes lead to corneal ulcers.
Eosinophilic keratitis differs from other corneal diseases in its specific immune-mediated inflammatory response, which often occurs after a herpes infection. The correct diagnosis and differentiation of eosinophilic keratitis and other corneal diseases is crucial for choosing the right therapy and the prognosis. If corneal disease is suspected, a veterinarian should always be consulted to receive an accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Early detection and treatment of eosinophilic keratitis can slow the progression of the disease and preserve the cat's vision. Treatment options include topical steroids, immunomodulatory medications, and in some cases surgery. It is important to carefully follow the veterinarian's treatment recommendations and have regular check-ups to monitor the success of the therapy. Regularly cleaning the eyes and avoiding irritants can also help improve the cat's well-being and minimize possible complications.
Proper care and regular monitoring of your cat's eyes can help detect and treat potential problems early. This includes regularly cleaning the eyelids to remove dirt and tear stone buildup. Also avoid contact with potential irritants such as smoke or chemicals that could irritate the eyes. Make sure your cat is fed a balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants to support overall eye health. If you see any signs of discomfort or changes in the eyes, you should immediately consult a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
