- Inflammatory Bowel Disease - IBD in Cats
- Introduction to IBD in Cats
- Causes of IBD in Cats: A Comprehensive Overview
- Symptoms of IBD in Cats: A Detailed Guide
- Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of IBD in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide
- Differentiated Treatment of IBD in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide
- Preventative Measures for IBD in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Inflammatory Bowel Disease - IBD in Cats
- Summary of IBD in cats
Inflammatory Bowel Disease - IBD in Cats
Introduction to IBD in Cats
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in cats is a group of diseases characterized by chronic inflammation of the intestinal wall. This condition can cause serious symptoms such as persistent diarrhea, vomiting and weight loss. It is important to develop an understanding of IBD in order to effectively support and treat your cat.
Causes of IBD in Cats: A Comprehensive Overview
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in cats is a complex condition whose exact causes are often difficult to determine. It is believed that several factors work together to cause and maintain inflammation of the intestinal wall. Here we look at the different factors that can contribute to the development of IBD in cats.
Genetic predisposition
Some cats may be genetically more susceptible to IBD. Although the genetic basis is not fully understood, studies show that certain breeds or family lines may have a higher prevalence of the disease. This suggests that genetic components may play a role.
Immune system reactions
IBD is essentially a condition in which the cat's immune system overreacts. Normally, the immune system serves to protect the body from pathogens. However, in cats with IBD, the immune system mistakenly attacks the cells of the intestinal wall, causing inflammation and its associated symptoms.
Nutritional factors
Diet can play a significant role in the development of IBD. Some cats may be allergic or intolerant to certain components of their diet, such as certain proteins, additives or preservatives. These reactions can trigger or worsen inflammation in the digestive tract.
Infections
Infections caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites can also cause inflammation of the intestines. Although a single infection usually does not cause IBD, repeated or chronic infections can increase a cat's risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease.
Environmental factors
Stress and environmental changes can affect the immune system and cause IBD symptoms to worsen. Stress can be triggered by many factors, including changes in the household, conflicts with other pets, or changes in routine.
Age and chronic inflammation
While IBD can occur in cats of any age, it is more commonly diagnosed in middle-aged to older cats. It is believed that years of exposure to various triggers can lead to chronic inflammation, ultimately resulting in IBD.
Although the exact causes of IBD in cats are often multifaceted and complex, it is important to understand the possible contributing factors in order to develop effective treatment and management strategies. If you suspect that your cat may have IBD, it is crucial to have him examined veterinarian Through a combination of dietary adjustments, medical treatment, and living situation changes, many cats with IBD can live comfortable and happy lives.
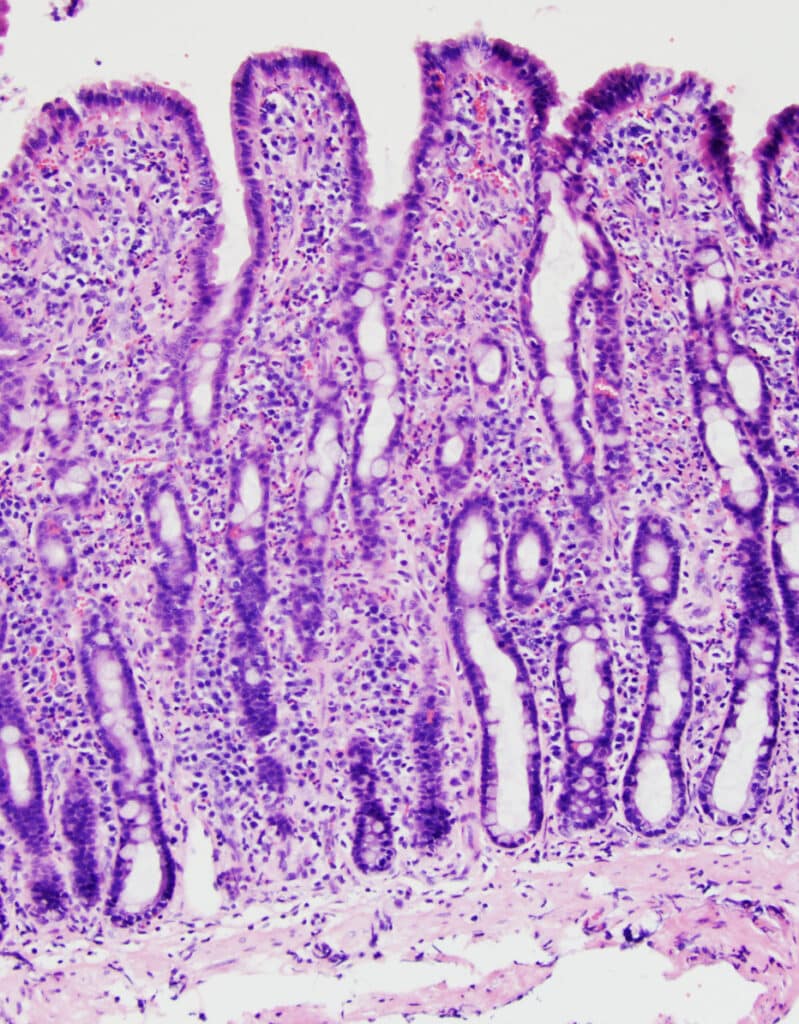
Symptoms of IBD in Cats: A Detailed Guide
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can cause a range of unpleasant and worrying symptoms in cats. It's important to understand how these symptoms may manifest themselves in order to provide your cat with the best possible care and attention. Here is a comprehensive explanation of the symptoms of IBD in cats.
Indigestion
The most obvious signs of IBD in cats involve the digestive tract. This includes:
- Chronic diarrhea : This can range from loose to watery stools and is common. In some cases, the stool may contain blood or mucus.
- Vomiting : Cats with IBD may vomit regularly, which can contain both food and bile. Vomiting can occur immediately after eating or at any time.
- Bloating and abdominal pain : Your cat may have a bloated stomach or show signs of discomfort when his stomach is touched.
Weight loss and appetite changes
Another common symptom of IBD is unexplained weight loss. This can occur despite normal eating habits or be accompanied by a reduced appetite:
- Weight loss : Even if your cat eats as usual, he may lose weight due to nutrient absorption problems.
- Changes in appetite : Cats with IBD may show less interest in eating or even refuse food entirely. In some cases, they may also have an increased appetite as their body tries to compensate for the lack of nutrients.
Lack of energy and behavioral changes
Cats suffering from IBD may also show changes in their behavior and energy levels:
- Lethargy : You may notice that your cat is less active than usual, becomes more withdrawn, and generally shows less interest in play or interaction.
- Hiding : Some cats in discomfort or pain tend to hide or seek out quiet, secluded places.
Coat condition
The condition of the coat can also be an indicator of a cat's health:
- Shaggy, dull coat : A cat that is unwell or suffering from nutritional deficiencies may stop grooming, resulting in an unkempt coat.
Symptoms of IBD in cats can vary and are sometimes difficult to recognize because cats often try to hide discomfort. If you notice any changes in your cat's behavior, eating habits, weight, or digestive patterns, it is important to take it seriously and see a veterinarian . Early diagnosis and treatment can help improve your cat's well-being and maintain his quality of life. Remember that every cat is unique and can show symptoms in different ways. Your attention and care can make a big difference in your cat's life.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of IBD in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide
Diagnosing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in cats can be challenging because symptoms are often similar to other diseases. A thorough diagnosis is crucial to ensure the best possible treatment. Here you can learn more about the process of diagnosis and differential diagnosis in cats with suspected IBD.
Step 1: History and clinical examination
The first step is to collect a detailed medical history of your cat. Your veterinarian will ask questions about symptoms, when they appeared, dietary habits, and previous health problems. A thorough physical exam will help evaluate your cat's overall health and identify possible signs of IBD.
Step 2: Laboratory tests
Blood tests can help assess your cat's health and rule out other diseases. Typical tests include a complete blood count, biochemical profile, and testing for specific infections. Fecal examinations are also performed to rule out parasites or bacterial infections.
Step 3: Imaging procedures
Abdominal ultrasound scans can be helpful in detecting changes in the intestinal wall and surrounding organs. In some cases, an x-ray may also be necessary to rule out other causes for the symptoms.
Step 4: Endoscopy and biopsy
Endoscopy is a crucial step in diagnosing IBD. A small camera endoscope is used to look directly at the gastrointestinal tract and take tissue samples (biopsies). These samples are then examined microscopically to identify inflammatory changes and rule out other diseases such as cancer.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of IBD involves considering other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. This includes:
- Infectious diseases : Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can cause symptoms similar to those of IBD.
- Food allergies or intolerances : These can cause gastrointestinal symptoms similar to IBD.
- Parasitic diseases : Worms or protozoa can cause digestive disorders.
- Neoplastic diseases : Colorectal cancer can cause symptoms similar to those of IBD and must be ruled out.
- Metabolic and systemic diseases : Problems with the liver, kidneys, or thyroid can also cause digestive problems.
Diagnosis of IBD in cats requires a combination of a thorough history, clinical examination, laboratory tests, imaging tests, and, if necessary, endoscopy with biopsy. Differential diagnosis is crucial to rule out other medical conditions and ensure your cat receives appropriate treatment. If you have concerns about your cat's health, contact your veterinarian, who can create an individualized diagnosis and treatment plan.
Differentiated Treatment of IBD in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide
Treatment for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in cats depends on the underlying causes, the severity of symptoms, and the cat's overall health. Here is a comprehensive guide to differentiated treatment of IBD based on various causes.
Treatment for nutritional causes
If IBD is due to a food allergy or intolerance, changing your diet is the first step:
- Hypoallergenic diet : Your veterinarian may suggest a specific hypoallergenic diet to find out what foods your cat reacts to.
- Limited Ingredients : Foods with limited and easily identifiable ingredients can help avoid allergens.
- Highly Digestible Diet : Easily digestible foods can reduce the burden on the digestive system and aid recovery.
Treatment for immune-related causes
If IBD is caused by an excessive immune system response, the following approaches may help:
- Corticosteroids : These medications can reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response. They are often used in the initial phase of treatment.
- Immunomodulators : In cases where steroids are not effective or long-term use is concerning, medications such as cyclosporine may be used.
Treatment for infectious causes
If an infection is causing IBD symptoms, targeted treatment of the infection is crucial:
- Antibiotics : Specific antibiotics may be necessary for bacterial infections.
- Antiparasitic medications : If parasites such as Giardia are diagnosed, appropriate treatments are administered.
Treatment of stress-related factors
Stress can worsen the symptoms of IBD. Therefore, stress factors should be minimized:
- Stress management : Maintain a calm and stable environment. Play and interaction can help reduce stress.
- Pharmacological support : In some cases, anti-anxiety medications may be useful to minimize stress in your cat.
Additional treatment options
Additional measures may be taken depending on your cat's needs and your veterinarian's advice:
- Probiotics and prebiotics : These can help restore the balance of intestinal flora and promote intestinal health.
- Supplements : Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12, and other supplements may be helpful for certain cats.
Long-term management
IBD is a chronic condition that may require lifelong management:
- Regular monitoring : Regular visits to the vet are important to monitor your cat's health and adjust treatment if necessary.
- Diet diary : Keeping a diet diary can help track your cat's reactions to different foods and identify triggers.
Treating IBD in cats often requires a multifactorial approach that addresses the specific causes and symptoms of the condition. Working closely with your veterinarian is crucial to developing the best treatment strategy for your cat and ensuring its long-term well-being. Every cat is unique, and what works for one cat may not work for another. Patience and care are keys to success in managing IBD.
Preventative Measures for IBD in Cats: A Comprehensive Guide
Although there is no guaranteed method to completely prevent inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in cats, there are several strategies that can help minimize the risk of developing these conditions. Here are some comprehensive preventative measures you can take to promote your cat's gut health and reduce the risk of IBD.
Balanced and high-quality nutrition
A healthy diet is crucial to your cat's overall health and can help reduce the risk of digestive problems:
- High-quality food : Choose a high-quality cat food that contains all the necessary nutrients in balanced amounts.
- Age and health status : Adapt the diet to your cat's age, health status and lifestyle.
- Avoid allergies : If your cat is allergic to certain foods, avoid them to prevent inflammation in the digestive tract.
Regular veterinary examinations
Regular check-ups at the vet can help identify and treat potential health problems early:
- Annual Check-ups : Take your cat to the vet for annual health exams.
- Early diagnosis : Discuss any concerns or changes in your cat's behavior and health with your veterinarian.
Stress management
Stress can affect gut health and contribute to inflammation. It is important to create a calm and stable environment for your cat:
- Safe environment : Make sure your cat has a quiet place to retreat.
- Routine : Stick to a regular feeding and care routine to minimize stress.
- Play and Interaction : Regular play and cuddling can help reduce stress and promote your cat's well-being.
Good hygiene practices
Maintaining a clean environment can help reduce the risk of infections that can lead to digestive problems:
- Clean food and water bowls : Wash your cat's bowls daily with hot water and soap.
- Clean litter box : Clean the litter box regularly to prevent the spread of pathogens.
Adequate exercise
Regular exercise supports digestion and helps prevent obesity, which can increase the risk of IBD:
- Active Play : Encourage active play to support your cat's physical health and well-being.
- Stimulation : Offer toys and climbing structures to encourage physical activity and mental stimulation.
Prevention of parasites
Regular deworming and parasite control are important to protect digestive health:
- Regular deworming : Follow your veterinarian's recommendations for deworming your cat.
- Flea protection : Maintain effective flea protection to prevent parasite transmission.
While there is no sure-fire way to completely prevent IBD in cats, the above preventive measures can help minimize the risk and promote your cat's overall health and well-being. A combination of a healthy diet, regular veterinary care, stress management, good hygiene, adequate exercise and parasite prevention can make a big difference. Remember that the best prevention is careful observation and care to ensure your cat lives a long, healthy and happy life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Inflammatory Bowel Disease - IBD in Cats
What are the typical symptoms of IBD in cats?
Symptoms of IBD in cats can vary but typically include chronic diarrhea, vomiting, weight loss, and a decreased appetite. Some cats also show signs of lethargy or a dull, shaggy coat. It is important to note that these symptoms can also occur with other medical conditions, so a thorough veterinary examination is required to diagnose IBD.
How is IBD diagnosed in cats?
Diagnosis of IBD in cats usually involves a combination of clinical examination, blood tests, fecal examinations, ultrasound, and endoscopic procedures with biopsy of the intestinal wall. These tests help rule out other causes of symptoms and confirm the inflammation in the intestinal wall that is characteristic of IBD.
What treatment options are there for IBD in cats?
Treating IBD in cats is often a lifelong process and may include dietary changes, medication, and supplements if necessary. Diet management is a key aspect, which may include switching to hypoallergenic or easily digestible foods. Medical treatments may include anti-inflammatory medications and immunomodulators. Regular follow-up visits are also important to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments if necessary.
Can IBD in cats be cured?
IBD is a chronic disease that currently has no cure. Treatment aims to control symptoms and improve your cat's quality of life. Many cats with IBD can lead relatively normal and comfortable lives with appropriate treatment and management strategies. It is important to work closely with your veterinarian to develop the best treatment strategy for your cat.
How can I help my cat with IBD maintain a healthy weight?
Weight management is an important aspect of treating IBD in cats. A balanced diet tailored specifically to your cat's needs can help maintain the right weight. Your veterinarian may recommend a special diet that is easy to digest and provides necessary nutrients without irritating the intestines. Regular monitoring of weight and adjustments to food portions may be necessary to maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, regular, gentle exercise can help control weight and promote overall health.
Summary of IBD in cats
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in cats is a complex and often chronic condition that can significantly impact the quality of life of our furry friends. The exact cause of IBD in cats is not always clear, but a combination of genetic, immunological and environmental factors are thought to play a role. To effectively treat IBD in cats, it is important to develop a deep understanding of the symptoms and triggers.
Symptoms of IBD in cats can vary, but typically include chronic diarrhea, vomiting, weight loss, and a general decline in enjoyment of life. Because these symptoms can also occur with other medical conditions, an accurate diagnosis for IBD in cats is crucial. Veterinarians use a combination of history, clinical exams, laboratory tests, and imaging tests to diagnose IBD in cats.
Treating IBD in cats often requires a multifactorial approach. Diet management plays a crucial role in the treatment of IBD in cats, with many animals benefiting from a hypoallergenic or easily digestible diet. Medications, including anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating medications, can also be used to treat IBD in cats.
The importance of regular veterinary exams cannot be overstated when it comes to IBD in cats. These regular checks help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments if necessary. Because IBD in cats is a chronic condition, lifelong treatment and care may be required.
Preventative measures can also help reduce the risk of IBD in cats. This includes providing a balanced diet, minimizing stress and ensuring good overall health care. Although there is no guarantee that a cat will never develop IBD, these measures can help reduce the overall risk.
It is also important to recognize that IBD in cats affects not only the affected animals, but also their owners. Supporting cat owners through education and resources is critical to improving the well-being of cats with IBD. Creating a supportive community and access to reliable information can make a big difference.
In summary, IBD in cats is a serious condition that requires careful and comprehensive treatment. By working with a veterinarian, using a holistic treatment approach, and creating a supportive environment, owners can help improve the well-being of their cat with IBD. With proper care and attention, cats with IBD can live comfortable and happy lives.
