- Pulmonary Stenosis in Dogs: A Comprehensive Review
- Introduction
- What is pulmonary stenosis?
- Causes of Pulmonary Stenosis in Dogs
- Symptoms of pulmonary stenosis in dogs
- Diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis in dogs
- Differential diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis in dogs
- Treatment options for pulmonary stenosis in dogs
- Preventive measures and follow-up care for pulmonary stenosis in dogs
- FAQs About Pulmonary Stenosis in Dogs:
- Summary Pulmonary stenosis in dogs
Pulmonary Stenosis in Dogs: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction
Pulmonary stenosis is a significant heart defect in dogs that requires specialized consideration and treatment. In this article, we discuss aspects of pulmonary stenosis in detail, from definition to symptoms to diagnostic methods and treatment options.
What is pulmonary stenosis?
definition
Pulmonary stenosis refers to a narrowing in the pulmonary valve area of the heart. This restriction impedes blood flow from the right ventricle of the heart to the pulmonary artery, leading to various cardiovascular problems.
Causes of Pulmonary Stenosis in Dogs
Pulmonary stenosis is a disease that requires special attention in veterinary medicine. To understand the complexity of this heart defect, it is important to consider the diverse causes and risk factors.
Genetic predisposition
Pulmonary stenosis often occurs due to genetic factors. Certain dog breeds are genetically predisposed to this specific heart defect.
Breeds with increased risk
- Brachycephalic Breeds : These include short-nosed breeds such as the Pug, French Bulldog and Chihuahua. These breeds show a higher incidence rate of pulmonary stenosis.
- Beagle : This breed has a significant predisposition to polygenetic autosomal dominant inheritance, which can lead to pulmonary stenosis.
- Terrier and Cocker Spaniel : These breeds also show an increased susceptibility to this heart defect.
Development time
Pulmonary stenosis is usually a congenital condition that is present at birth. However, symptoms can change as the dog grows and develops and often only become apparent in young adulthood.
Influence of age
- Young Dogs : The diagnosis is often made in young dogs because symptoms become more noticeable as they grow.
- Older dogs : In older dogs, pulmonary stenosis can occur in conjunction with other age-related heart problems, making diagnosis and treatment more complex.
Pulmonary stenosis is a serious condition influenced by a combination of genetic factors and racial predispositions. Early detection and regular monitoring are crucial to enabling affected dogs to live as normal and healthy a life as possible. Especially in breeds with a known predisposition, pet owners should pay close attention to signs of this disease and have regular veterinary checks carried out.
(C) https://www.marvistavet.com/pulmonic-stenosis.pml
Symptoms of pulmonary stenosis in dogs
Symptoms of pulmonary stenosis in dogs can vary depending on the severity of the disease and the individual animal. It is important to recognize these signs to ensure timely and effective treatment.
Mild to moderate cases
In mild to moderate cases, dogs often show no or minimal symptoms. This can make early detection of the disease difficult.
- No symptoms : Many dogs with a mild form of pulmonary stenosis have no obvious symptoms and lead normal lives.
- Mild fatigue : Some dogs may experience mild fatigue with increased physical exertion.
Severe cases
If pulmonary stenosis is severe, symptoms become more obvious and require immediate veterinary attention.
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea) : One of the most common symptoms is difficult breathing, especially after physical exertion.
- Exercise Weakness : Dogs with severe pulmonary stenosis often show significant weakness during physical activity.
- Syncope (fainting) : In some cases, fainting may occur, especially after intense exercise.
- Development of ascites : In some severe cases, ascites, a buildup of fluid in the abdomen, may develop.
- Altered heart murmur : A distinctive heart murmur can often be detected veterinarian
More information
- Behavioral changes : Changes in behaviors such as lethargy or decreased interest in activities can also be signs of heart disease.
- Pale mucous membranes : Poor circulation can lead to pale mucous membranes.
Symptoms of pulmonary stenosis in dogs range from barely noticeable signs in mild cases to severe and life-threatening symptoms. A regular veterinary examination is crucial to detect and treat this condition early. Dog owners should pay attention to behavioral changes and physical symptoms, especially in breeds predisposed to pulmonary stenosis.
Diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis in dogs
Diagnosing pulmonary stenosis in dogs requires a careful and comprehensive examination by an experienced veterinarian . Here we explain the different steps and methods used to diagnose this heart disease.
Initial examination and anamnesis
Diagnosis often begins with a thorough initial examination and a detailed medical history.
- Interview with the owner : The veterinarian will ask specific questions about the dog's behavior, activity, and previous health.
- Physical examination : A general physical examination can provide initial clues, especially listening to the heart.
Heart murmur
The presence of a heart murmur can be an initial indication of pulmonary stenosis.
- Listening to the heart : A characteristic heart murmur, usually a systolic murmur, may indicate pulmonary stenosis.
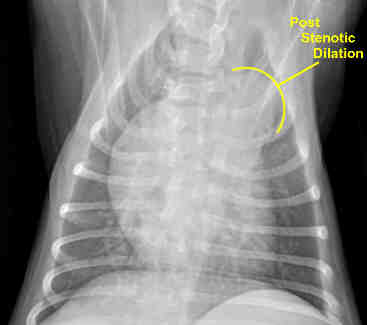
Imaging diagnostics
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in the diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis.
- X-ray examination : A chest X-ray can show changes in the heart and large vessels.
- Echocardiogram (heart ultrasound) : This is the most important diagnostic tool. It allows visual assessment of the structure and function of the pulmonary valve as well as measurement of blood flow and pressure gradient across the valve.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) : An EKG can provide additional information about the heart's rhythm and the heart's electrical activity.
Further investigations
In some cases, additional tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
- Blood tests : Although blood tests do not provide direct information about pulmonary stenosis, they can help evaluate the dog's overall health.
- Specialized cardiological examinations : In complex cases, a referral to a specialized veterinary cardiologist may make sense.
Diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis requires a combination of a thorough history, physical examination, and specialized diagnostic imaging. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for the effective treatment and management of this condition. Dog owners should not hesitate to have their dog examined by a veterinarian or specialist if they suspect heart disease.
Differential diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis in dogs
When diagnosing pulmonary stenosis, it is important to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. This process is called differential diagnosis.
Differentiation from other heart defects
Pulmonary stenosis must be differentiated from other heart defects that may present with similar symptoms.
- Aortic stenosis : Another common heart defect that also causes a heart murmur but requires different treatment.
- Tricuspid valve dysplasia : A malformation of the tricuspid valve that can also cause a heart murmur.
Rule out other causes of symptoms
It is also important to rule out other non-cardiac causes of symptoms such as shortness of breath or weakness.
- Respiratory diseases : Conditions such as bronchitis or pneumonia can cause symptoms similar to dyspnea.
- General weakness : Other systemic diseases such as anemia or metabolic disorders can also cause weakness and lethargy.
Differential diagnosis is a crucial step in ensuring that the correct diagnosis is made and appropriate treatment is initiated. By carefully examining and ruling out other possible causes, the veterinarian can best address the specific needs of the individual dog.
Treatment options for pulmonary stenosis in dogs
Treatment for pulmonary stenosis in dogs depends on the severity of the disease and the individual needs of the dog. There are various approaches, from drug treatment to surgical procedures.
Conservative treatment
Mild to moderate cases
- Monitoring : Regular check-ups are important to monitor the progress of the disease.
- Adapted activities : It may be recommended to limit the dog's physical exertion so as not to overload the heart.
Medical therapy
- Beta blockers : These can be used to reduce heart rate and improve blood flow.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs : Special medications may be necessary for cardiac arrhythmias.
Surgical treatment
Balloon valvuloplasty
- Procedure : This method uses a balloon catheter to expand the narrowed pulmonary valve. This improves blood flow and reduces pressure on the right heart.
- Follow-up care : Regular follow-up visits are required after the procedure to monitor the success of the treatment.
Open surgical correction
- In rare cases : Open heart surgery may be necessary in certain dogs to correct the narrowing.
- More intensive aftercare : This method requires a longer recovery time and more intensive aftercare.
Supportive treatment
Heart-healthy diet
- Diet : A heart-healthy diet can help support the cardiovascular system and improve the dog's overall well-being.
Regular checks
- Ongoing monitoring : Regardless of the treatment chosen, regular veterinary exams are crucial to monitor the dog's condition and adjust treatment if necessary.
Treating pulmonary stenosis in dogs requires an individualized approach tailored to the severity of the disease and the needs of the individual dog. From medication to special diets to surgical procedures, there are a number of options that can improve the dog's well-being and increase his quality of life. Regular veterinary checks are essential to monitor the progression of the disease and adjust treatment accordingly.
Preventive measures and follow-up care for pulmonary stenosis in dogs
Although pulmonary stenosis often has a genetic cause and therefore cannot be completely prevented, there are measures that can minimize the risk and improve an affected dog's quality of life.
Preventive measures
Genetic counseling and responsible breeding
- Breeder advice : Breeders should consider genetic testing and counseling to reduce the risk of inheriting pulmonary stenosis.
- Selection of parents : Avoid breeding dogs that are known carriers of the defect.
early detection
- Regular veterinary checks : Early detection can help slow the progression of the disease and optimize treatment.
Follow-up care after diagnosis
Regular monitoring
- Continuous veterinary examinations : Regular cardiac ultrasound examinations are important to monitor the condition of the heart.
- Adjustment of activities : The dog's physical activity should be adjusted according to its health status.
Medication
- Adherence to Medication Schedule : It is critical that all prescribed medications are administered according to the veterinarian's instructions.
Nutrition management
- Heart-healthy diet : A balanced, nutrient-dense diet can help support the cardiovascular system.
- Weight control : Being overweight can put additional stress on the heart, so good weight control is important.
Aftercare after a surgical procedure
Postoperative care
- Rest and recovery : After a surgical procedure, a quiet environment is essential for the dog's recovery.
- Follow-up visits : Regular check-ups after surgery are necessary to monitor the healing process.
Long-term monitoring
- Lifelong monitoring : Even after a successful operation, ongoing monitoring is important to detect possible future complications early.
Preventive measures and careful follow-up care are crucial to minimize the risk of pulmonary stenosis and improve the quality of life of affected dogs. Regular veterinary examinations, appropriate diet and exercise, and careful adherence to treatment plans go a long way toward supporting the dog's health and well-being.
FAQs About Pulmonary Stenosis in Dogs:
1. What is Pulmonary Stenosis in Dogs?
Pulmonic stenosis is a heart disease characterized by narrowing of the pulmonary valve. This leads to impaired blood flow from the heart to the lungs, which puts strain on the heart and can cause various symptoms.
2. What symptoms indicate pulmonary stenosis in dogs?
Symptoms of pulmonary stenosis in dogs can vary. Mild cases may not show any symptoms, while more severe cases may present with shortness of breath, weakness on exertion, fainting, or even ascites (a buildup of fluid in the abdomen). A characteristic heart murmur can often be detected during a veterinary examination.
3. How is pulmonary stenosis in dogs diagnosed?
Diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis in dogs is made through a combination of physical examination, listening to the heart, x-rays, echocardiogram (heart ultrasound), and, if necessary, EKG. These tests help determine the narrowing of the pulmonary valve and the severity of the disease.
4. What treatment options are available for pulmonary stenosis in dogs?
Treatment for pulmonary stenosis in dogs depends on the severity of the disease. Mild cases may only require regular monitoring, while more severe cases may require medications such as beta-blockers or surgical procedures such as balloon valvuloplasty to expand the pulmonary valve.
5. Can dogs with pulmonary stenosis live a normal life?
Many dogs with pulmonary stenosis can lead relatively normal and active lives, especially with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. However, regular veterinary checks and an adapted lifestyle are important to maintain the dog's health and quality of life.
Summary Pulmonary stenosis in dogs
When considering pulmonary stenosis in dogs, it is important to understand all aspects of this heart disease. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs is a congenital malformation that affects blood flow from the heart to the lungs. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs occurs due to a narrowing in the pulmonary valve area.
Diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis in dogs is made through a combination of history, physical examination, and special diagnostic procedures. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs can occur at different rates in different breeds, with an increased prevalence in certain breeds such as beagles and brachycephalic breeds. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs requires careful and regular monitoring by the veterinarian. Symptoms of pulmonary stenosis in dogs can vary, from subtle signs to severe clinical signs.
Treatment for pulmonary stenosis in dogs depends on the severity of the disease and includes both medical and surgical options. When it comes to pulmonary stenosis in dogs, early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs, especially in severe cases, can have a significant impact on the dog's quality of life. When it comes to pulmonary stenosis in dogs, genetic counseling is of great importance for breeders in order to minimize the risk of inheritance.
Pulmonary stenosis in dogs often requires lifelong monitoring and treatment. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs can, in some cases, lead to complications that require specialized treatment. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs is a condition that requires close collaboration between the pet owner and the treating veterinarian. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs should not be seen as a barrier to a fulfilling life, as many dogs can lead happy lives with proper treatment and care. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs can be well managed with regular veterinary examinations and appropriate treatment.
When it comes to pulmonary stenosis in dogs, a balanced diet and appropriate physical activity are important. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs requires a deep understanding of the disease and its treatment options. Canine pulmonary stenosis is an example of how genetic factors can affect pet health. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs shows the importance of responsible pet care and regular veterinary care. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs highlights the importance of animal health in general.
Canine pulmonary stenosis is an area where research and veterinary advances can make a big difference. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs is an issue that requires attention and awareness in the animal community. Canine pulmonary stenosis is a condition that requires comprehensive care and a deep understanding of the animal's needs. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs is a challenge that both veterinarians and pet owners must overcome together.
Canine pulmonary stenosis is a health condition that highlights the importance of prevention and early detection. Pulmonary stenosis in dogs provides an example of the complexity and diversity of veterinary diseases. In conclusion, pulmonary stenosis in dogs is an important consideration in veterinary medicine.
