Acral lick dermatitis in dogs: A review
- Acral lick dermatitis in dogs: A review
- Introduction
- Understanding Acral Lick Dermatitis
- Possible causes
- Diagnosis of leak granulomas
- Therapeutic measures
- Treatment options in detail - acral lick dermatitis
- Frequently asked questions about acral lick dermatitis
- Summary of acral lick dermatitis
Introduction
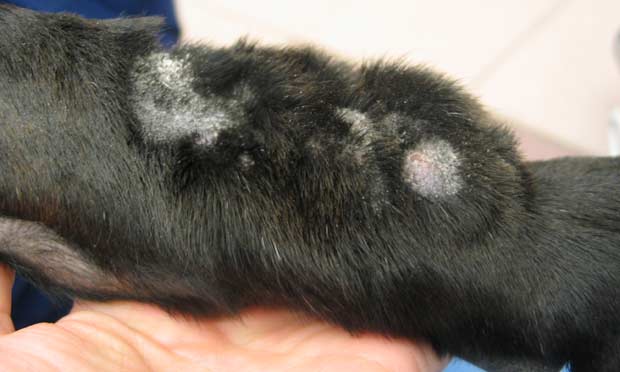
Acral lick dermatitis, also known as lick granuloma, is a commonly observed skin disease in dogs. Characterized by repeated and intense licking of a specific area - most commonly the lower portion of the limbs, this condition poses a significant challenge to both veterinarians and pet owners.
Understanding Acral Lick Dermatitis
Acral lick dermatitis occurs due to continuous and concentrated licking of a specific part of the body. This excessive licking results in hairless, thickened areas of skin that may turn black. In some cases, continuous irritation can cause the condition to maintain itself even when the original triggering factor is no longer present.
Possible causes
Numerous factors can contribute to the development of a leak granuloma. Some of the most famous are:
- Itchy skin conditions such as allergies
- Painful processes in joints or bones
- Boredom in very energetic dogs
- Stress in nervous dogs
- Compulsive licking as a manifestation of a behavioral disorder
Diagnosis of leak granulomas
The diagnosis of acral lick dermatitis is usually based on a combination of clinical examination, skin scraping, and cytologic examination. Localized demodicosis (a disease caused by demodex mites) can be ruled out using skin scrapings. A cytological examination can help identify a secondary infection with bacteria or yeast. In certain cases, skin biopsies, bacterial cultures, or x-rays may provide additional information.
Therapeutic measures
If a secondary infection is present, initial treatment is aimed at eliminating it. Since leak granulomas are often accompanied by profound inflammatory reactions, the treatment process can take several weeks or months. At the same time, the search for the underlying causes is initiated. Various treatment options are available, including:
- Antibiotics in tablet or ointment form to treat the infection
- Anti-inflammatory medications as tablets, ointments or injections to relieve itching
- Special preparations to prevent licking
- Neck braces or bandages
- Medications to modify behavior
- Behavioral measures such as increased walking frequency and playtime, getting another dog or behavioral therapy
Every dog is individual and therefore requires an individually tailored therapy plan. However, in most dogs the disease can be successfully controlled.
The diagram above visualizes the process of the disease, from possible causes to diagnosis and treatment. This understanding is crucial for the effective management of acral lick dermatitis and for successful therapy. It is important to remember that each animal is individual and therefore requires individual therapy.
Treatment options in detail - acral lick dermatitis
Special preparations to prevent licking in dogs (acral lick dermatitis)
Uncontrolled licking can cause a number of health problems in dogs, including acral lick dermatitis. Here are some special preparations that can be used to stop this behavior.
Bitter preparations
These products contain a flavor that most dogs find unpleasant. They are applied to the area the dog is licking in the hope that the bitter taste will deter the dog from continuing to lick. Examples include products like “Bitter Apple Spray” or “Bitter YUCK! No Chew Spray”.
Medical wound dressings
There are various medical wound dressings that are specifically designed to deter dogs from licking a wound or other area on their body. These products often also contain ingredients that promote healing.
Leak protection collar
Anti-lick collars, often referred to as "collars" or "funnels," are physical barriers that prevent the dog from reaching and licking the affected area. There are different models, from traditional plastic funnels to more comfortable inflatable or soft collars.
Special paw socks
In some cases, special paw socks or boots can help stop paw licking. They serve as a physical barrier between the dog's paw and tongue and can also help promote healing of a wound or dermatitis.
It is important to note that these products are temporary solutions at best and do not address the underlying cause of the leaking behavior. They should always be used in conjunction with other therapeutic measures, including medication and behavior modification, to achieve long-term improvement. The use of these preparations should always be under the supervision of a qualified veterinarian .
(C) https://www.cliniciansbrief.com/article/canine-acral-lick-dermatitis
Behavior Modifying Drugs in Dogs - Acral Lick Dermatitis
In some cases, particularly behavioral problems such as compulsive licking leading to acral lick dermatitis, behavior modifying medications may be used. These medications affect dog behavior by acting on the central nervous system and changing brain chemistry.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs, such as fluoxetine, increase the amount of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain, which can improve mood and reduce anxiety. They are often the first choice for dogs with behavioral problems because they are generally well tolerated and have fewer side effects than some other medications.
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA)
TCAs, such as clomipramine, work similarly to SSRIs, but they also affect other neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine. They can be helpful for dogs with severe behavioral problems, especially when other treatments have not been effective.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam, have a calming effect and can be used in dogs with acute anxiety or panic disorders. They work very quickly, but are only suitable for short-term use as they have a high addictive potential.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI)
MAOIs, such as selegiline, are typically used to treat cognitive dysfunction in older dogs, but may also be helpful for certain behavioral problems.
The use of behavior-modifying medications should always be done in combination with other therapeutic measures, such as behavioral therapy and environmental adjustments. It is important to note that these medications do not treat the problem themselves, but simply relieve symptoms and increase the effectiveness of other treatment strategies. In addition, the use of these medications should always be under the supervision of a qualified veterinarian who will carefully weigh the risks and benefits and monitor therapy accordingly.
Behavioral measures in dogs to treat acral lick dermatitis
In addition to drug treatments, various behavioral measures can also be taken to relieve the symptoms of acral lick dermatitis and improve the dog's well-being. Some of these measures are explained in more detail below.
Increased physical activity
More exercise, whether through longer or more frequent walks, can help the dog burn off excess energy and reduce stress. This can be particularly helpful if boredom or under-stimulation have been identified as triggers for the licking behavior. Additionally, the increased physical activity can also help improve the dog's overall health and well-being.
Mental stimulation
Mental stimulation is just as important as physical exercise. This can be achieved by learning new tricks, working on obedience exercises, or using interactive toys that encourage the dog to solve problems. This measure can also help combat boredom and reduce stress.
Environmental changes
Changes in the dog's environment, such as providing a quiet, safe place for the dog to retreat to or removing stressors, can also help. These measures can help reduce anxiety and provide a sense of security.
Behavioral therapy
Behavioral therapy with a certified behavioral therapist can be very useful, especially for more complex or deep-rooted behavioral problems. This may include implementing a desensitization and counterconditioning program aimed at changing the dog's response to the trigger of the licking behavior.
Purchasing another dog
In some cases, it may make sense to get another dog to stimulate and keep the affected dog company. However, this measure should be carefully considered and only considered if the owner is able to meet the needs of both dogs.
The behavioral measures must be tailored to each individual dog and should always be carried out in consultation with a veterinarian or a qualified behavioral therapist. It is important to take a holistic approach to not only treat the symptoms of acral lick dermatitis, but also to improve the dog's overall well-being and quality of life.
Frequently asked questions about acral lick dermatitis
What is acral lick dermatitis?
Acral lick dermatitis, also known as lick granuloma, is a skin condition that occurs primarily in dogs. It is characterized by constant licking of a specific area, usually the limbs, resulting in hairless, thickened and discolored patches of skin.
What are the causes of acral lick dermatitis?
There are many factors that can contribute to the development of a lick granuloma. These can be itchy skin conditions such as allergies, painful processes on joints or bones, boredom in energetic dogs, stress in nervous dogs and compulsive licking as a behavioral disorder.
How is acral lick dermatitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis can be made by physical examination, skin scrapings to rule out local demodicosis, cytologic studies to determine the presence of secondary infection, and in some cases, skin biopsies, bacterial cultures, or radiographs.
How is acral lick dermatitis treated?
Treatment of acral lick dermatitis may require a combination of approaches, including treatment of an existing secondary infection, use of medications to influence behavior, and behavioral measures such as increased walking and playing with the animal. In some cases, behavioral therapy may also be necessary.
Can special preparations prevent licking?
Yes, there are various products on the market that can help prevent licking. These include bitter sprays, medical wound dressings, leak protection collars and special paw socks. However, it is important to note that these products are only short-term solutions and do not address the underlying cause of the leaking behavior.
Summary of acral lick dermatitis
Acral lick dermatitis is a common skin condition in dogs characterized by incessant licking at a specific area. Acral lick dermatitis can be triggered by various factors, including skin allergies, pain in joints or bones, stress, and behavioral problems. Therefore, the diagnosis of acral lick dermatitis requires a comprehensive examination and, if necessary, testing by an experienced veterinarian.
Treatment of acral lick dermatitis may involve a number of approaches, including treatment of secondary infections, drug therapy, and behavioral interventions. It is important to understand that acral lick dermatitis can be a long-term condition that requires consistent treatment.
Special preparations to prevent licking may be helpful in treating acral lick dermatitis. Although they are not a permanent solution, they can temporarily interrupt the licking behavior and help heal the affected skin areas.
Finally, it is important to emphasize that acral lick dermatitis is a serious health problem that can cause significant distress to the affected dog. Therefore, it is of great importance to take acral lick dermatitis seriously and seek professional veterinary help as soon as the first symptoms appear.
