- Introduction to coccidia rabbits
- Causes of coccidia infection in rabbits
- Diagnosis of coccidia rabbits by type of coccidia
- Treatment of coccidia rabbits according to the type of coccidia
- What can I as an owner do against coccidia in rabbits?
- Here are five comprehensive FAQs that address important questions about coccidia in rabbits:
- Summary Coccidia Rabbits
Introduction to coccidia rabbits
Coccidia (lat. Coccidia/Coccidiasina) are one of the most common parasitosis in rabbits and pose a serious and often fatal threat, especially to young animals. This article offers you a detailed insight into the symptoms, diagnosis, therapy and prophylaxis of this complex disease.
Causes of coccidia infection in rabbits
transmission
The coccidia, more precisely the Meileia spp., are primarily ingested orally. Spread occurs particularly in large communities of rabbits. A central aspect here is the contamination of the environment by the mother animals, which excrete the coccidia stages.
Specific species of coccidia
Specific species of coccidia occur in rabbits, which belong to the genus Meileia spp. belong. Particularly pathogenic are the species that colonize the intestine, such as Meileia intestinalis and Meileia flavescens, and Meileia stiedai, which causes hepatic coccidiosis.
The development stages of coccidia
The development of coccidia is complex. After ingestion, the parasites multiply in the intestinal mucosa. They are then excreted as oocysts and develop into infectious stages. These stages remain infectious for months in warm, humid environments.
Symptoms and diagnosis of coccidia infection in rabbits
Intestinal coccidiosis
Intestinal coccidiosis causes symptoms in rabbits such as diarrhea, weight loss and increased gas production. Sudden deaths can also occur.
Liver coccidiosis
Liver coccidiosis can cause symptoms such as reluctance to eat, constipation, weight loss, jaundice and ascites.
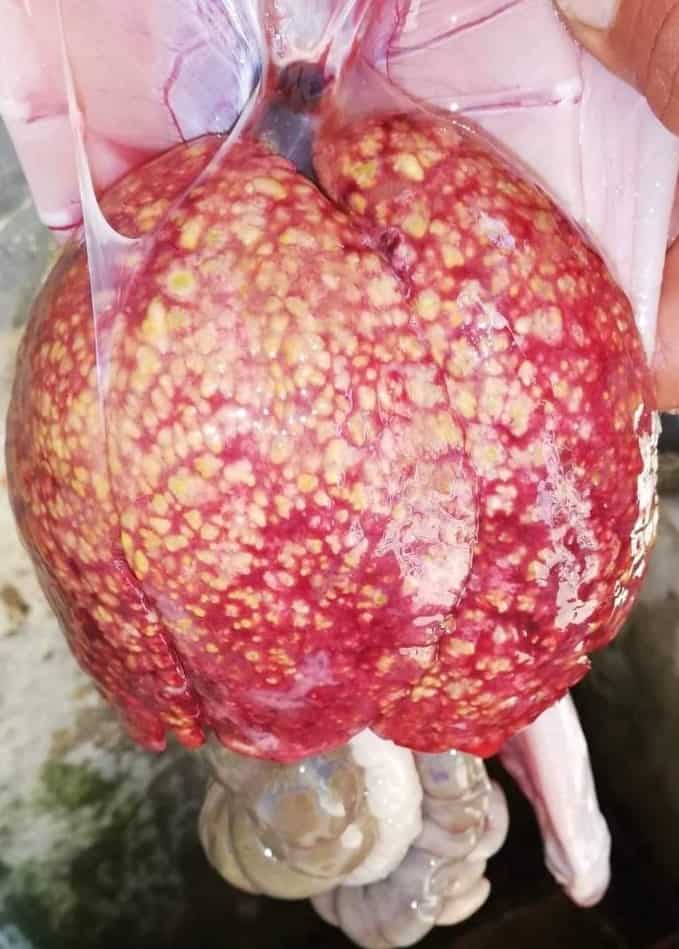
(C) https://www.veterinariadigital.com/en/post_blog/hepatic-coccidiosis-rabbits/
Diagnosis of coccidia rabbits by type of coccidia
Diagnosis and treatment may vary depending on the type of coccidia. Here is a detailed overview of the most common types of coccidia that affect rabbits and how they are diagnosed.
Intestinal coccidiosis
Intestinal coccidiosis causes symptoms in rabbits such as diarrhea, weight loss and increased gas production. Sudden deaths can also occur.
Liver coccidiosis
Liver coccidiosis can cause symptoms such as reluctance to eat, constipation, weight loss, jaundice and ascites.
1. Elmeria spp.
diagnosis
Eimeria species are the most common coccidia in rabbits. Diagnosis is usually made through a microscopic examination of fecal samples. There are many different species of Meileia that can affect rabbits, so accurate diagnosis can be complex.
Distinction
Distinguishing between the different species of Eimeria is done through detailed microscopic examination, looking at the shape, size and other characteristics of the oocysts (the eggs of the coccidia).
2. Isospora spp.
diagnosis
Isospora species are also common, but are generally less harmful than Eimeria species. Diagnosis is made similarly through microscopic examination of fecal samples.
Distinction
The distinction between Isospora species is again made by observing the oocyst shape. Isospora coccidia are typically smaller than Meileia and have other distinctive features.
3. Hepatozoon cuniculi
diagnosis
This particular parasite affects the liver of rabbits. Diagnosis is more difficult and may require a combination of blood tests, liver ultrasound and even biopsy.
Distinction
Distinguishing Hepatozoon cuniculi from other coccidia requires specialized diagnostic techniques because this parasite is not found in feces but in the animal's liver.
Treatment of coccidia rabbits according to the type of coccidia
1. Treatment of Meileia spp.
Medication: Toltrazuril or sulfonamides are often used when infested with Meileia. These drugs work by inhibiting the reproduction of coccidia.
Supportive measures: Supportive measures may include a balanced diet and good hygiene to control the growth of the parasites.
2. Treatment of Isospora spp.
Medication: Similar to Eimeria, toltrazuril or sulfonamides can be used to treat Isospora.
Hygiene: Cleaning the rabbit's environment is crucial to controlling isospora. The droppings should be removed regularly and the housing areas should be cleaned well.
3. Treatment of Hepatozoon cuniculi
Medication: Treatment of Hepatozoon cuniculi may be more complicated and may require special medications that specifically target the liver.
Supportive therapy: Because the liver is affected, supportive therapy may be necessary to maintain normal liver function. This may include a special diet, hydration, and other medical support.
General information on treatment
Visit to the vet: Self-treatment of coccidia is not recommended as the diagnosis can be complex and requires precise identification of the coccidia species. Your veterinarian will know the best treatment options for your specific rabbit.
Duration of treatment: The duration of treatment can vary and depends on the type of coccidia and the severity of the infestation. It is crucial to complete all treatment prescribed by the veterinarian, even if symptoms resolve sooner.
Prevention: After treatment, prevention is equally important. Good hygiene, regular check-ups and possibly preventative medication can help prevent future infections.
In summary, treating coccidia is a serious matter that requires the advice and assistance of a veterinarian. The best treatment depends on the specific type of coccidia and is complemented by good hygiene and prevention.
What can I as an owner do against coccidia in rabbits?
Here are some comprehensive pointers that can help you keep your rabbit healthy:
prevention
1. Cleanliness and hygiene:
- Clean the stable regularly and remove feces daily to prevent the parasites from multiplying.
- Disinfect feeding bowls and water bottles to avoid contamination.
2. Proper Nutrition:
- A balanced diet strengthens your rabbit's immune system and helps it fight against parasites such as coccidia.
3. Quarantine for new animals:
- When adding new rabbits to your population, keep them separate at first to ensure they do not bring coccidia or other diseases with them.
recognition
4. Pay attention to symptoms:
- Symptoms such as diarrhea, loss of appetite or weight loss may indicate coccidia. If you notice such signs, contact your veterinarian.
Treatment
5. Veterinary assistance:
- If you suspect your rabbit has coccidia, see a veterinarian immediately. Only a professional can make an accurate diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment.
6. Follow the Veterinarian's Instructions:
- If your rabbit is being treated with medication, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and duration to ensure complete healing.
Long-term care
7. Regular checks:
- Regular veterinary exams can help detect and treat coccidia early before it becomes a serious problem.
8. Education:
- The more you know about coccidia and other potential health problems, the better you can protect your rabbit.
Interim conclusion
Preventing and controlling coccidia in rabbits requires a combination of good hygiene, proper nutrition, early detection and expert veterinary care. By remaining vigilant and caring for your rabbit's health and well-being, you can help minimize the risk of coccidia infection.
Your commitment to your rabbit is admirable and I am sure you will do everything you can to keep him happy and healthy. If you have any further questions or concerns, please feel free to contact me!
Here are five comprehensive FAQs that address important questions about coccidia in rabbits:
What is rabbit coccidia and how does it infect my rabbit?
Coccidia are microscopic parasites that can colonize in the intestines of rabbits. Infection often occurs through contaminated food or water that has come into contact with infected feces. Rabbits can also touch infected animals or surfaces and then ingest the parasites while grooming. The coccidia multiply in the intestines and can cause diarrhea, loss of appetite and other symptoms.
What symptoms do rabbits show when infected with coccidia?
A coccidia infection can cause a variety of symptoms.
These include: - Diarrhea or loose stools
- Loss of appetite or reduced food intake
- Weight loss or poor weight gain
- Bloated abdomen
- General weakness or lethargy
If an infection is suspected, it is important to seek immediate veterinary care as an untreated infection can cause serious health problems.
How can I prevent coccidia infection in my rabbit?
Prevention is the key to avoiding coccidia infections.
Here are some steps you can take: - Keep the living area clean and hygienic.
- Avoid contact with infected animals.
- Offer a balanced diet to strengthen the immune system.
- Conduct regular veterinary examinations.
These measures significantly reduce the risk of infection.
How is coccidia infection diagnosed and treated in rabbits?
Diagnosis of a coccidia infection is usually made through a stool examination by a veterinarian . Treatment may include various medications to combat the parasites. It is important to follow the veterinarian's instructions carefully, as incomplete treatment can make the parasites resistant. Additional support such as hydration or special nutrition may also be required.
Can people become infected with coccidia from their rabbits?
Most species of coccidia that infect rabbits are not infectious to humans. However, it is still advisable to practice good hygiene measures such as washing your hands thoroughly after handling rabbits or their feces. This helps minimize the risk of transmitting other diseases or infections.
These FAQs are intended to give you a better understanding of coccidia in rabbits. If you need more information or have specific questions about your animal, do not hesitate to consult a veterinarian or professional.
Summary Coccidia Rabbits
Rabbit coccidia is a serious matter for many rabbit owners. They are microscopic parasites that colonize in the digestive tract of animals and can cause a variety of health problems. Infection with coccidia rabbits often occurs in environments where hygiene standards are not maintained.
Symptoms of rabbit coccidia infection may include diarrhea, weight loss, loss of appetite, and general weakness. Treating coccidia in rabbits usually requires an accurate diagnosis by a veterinarian who will examine a stool sample. After that, the veterinarian will prescribe appropriate treatment with anti-coccidia medications for rabbits.
Preventing rabbit coccidia is crucial to protecting your pet's health. This includes steps such as regularly cleaning the living area, avoiding contact with infected animals, and offering a balanced diet to strengthen the immune system against coccidia rabbits.
Because coccidia poses a serious health threat to rabbits, it is important to be aware of how it is transmitted and how to treat it effectively. Most rabbit coccidia are not contagious to humans, but good hygiene is still important to minimize the risk of transmitting other diseases.
Research on rabbit coccidia has advanced in recent years, and there are a growing number of treatment options and preventive measures. Nevertheless, the best defense against coccidia in rabbits remains prevention through proper care and attention.
In summary, dealing with rabbit coccidia is a serious matter that requires the awareness and attention of rabbit owners. By understanding, preventing and appropriately treating rabbit coccidia, you can help ensure your rabbit lives a healthy and happy life. Visiting a veterinarian is crucial if you notice signs of rabbit coccidia infection, as early diagnosis and treatment can make all the difference.
