- Cornea Nigra in Cats: Detection and Treatment
- Introduction
- What is Cornea Nigra?
- Which breeds are particularly affected?
- Symptoms that a patient owner can recognize
- Diagnosis of the cornea nigra
- Differential diagnosis
- What happens if the cornea nigra is not treated?
- Treatment of the cornea nigra
- Can cornea nigra be prevented?
- FAQs about Cornea Nigra
- Summary Cornea Nigra
Cornea Nigra in Cats: Detection and Treatment
Introduction
In cats, eye health is crucial. One of the most serious eye diseases is cornea nigra, also known as corneal sequestration. This condition, which primarily affects pedigree cats, can lead to serious complications if left untreated. In this article you will learn everything about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment options for cornea nigra.
What is Cornea Nigra?
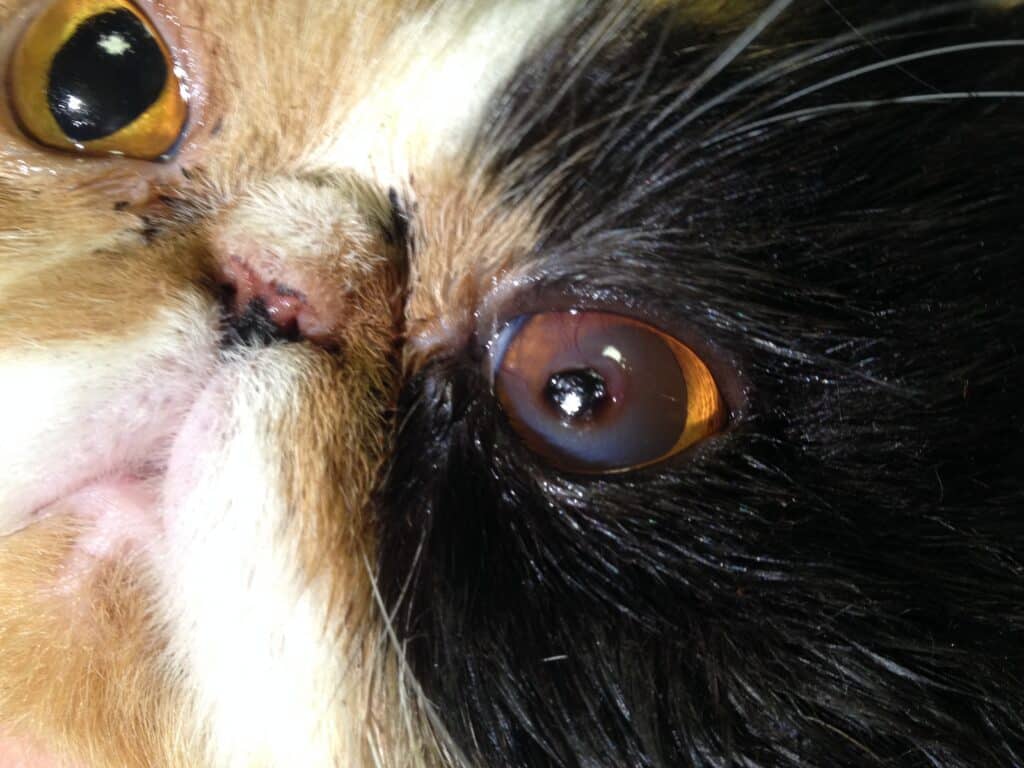
Cornea Nigra is a disease of the cornea in cats in which a black, necrotic area forms. This condition is common in pedigree cats such as Persian, Siamese, Maine Coon, and Carthusian cats, but can also occur in other cats.
Cornea nigra, a serious eye disease in cats, is characterized by characteristic changes to the cornea of the eye. This description is intended to help you better understand the visual signs of the cornea nigra:
- Initial stage: The first signs of cornea nigra are often subtle. They usually begin with a slight discoloration of the cornea. This discoloration may appear as a type of brownish spot or shade that contrasts with the normally clear and transparent texture of the cornea.
- Advanced stages: Over time, the affected area becomes increasingly dark. It can develop from a light brown to a deeper, almost black tone. This is a clear sign that the tissue in this area is becoming necrotic, i.e. dying.
- Change in texture: In addition to the color change, a change in the texture of the cornea can also occur. The affected area may develop a rough or uneven surface that is different from the rest of the smooth corneal tissue.
- Reaction to light: In advanced stages of cornea nigra, the eye's reaction to light may be impaired. The affected cat's pupil may respond to light differently or more slowly than normal.
- Side effects: In addition to the direct changes to the cornea, other symptoms such as redness of the eye, increased tear flow or squinting of the eye can also occur. These signs indicate discomfort or pain that may be associated with the cornea nigra.
It is important that cat owners act quickly and consult a veterinarian if they suspect cornea nigra. Early diagnosis and treatment can help maintain eye health and protect the cat's vision.
Which breeds are particularly affected?
When it comes to cornea nigra, an eye disease in cats, there are certain breeds that are more susceptible. The following list gives you an overview of the cat breeds that are particularly often affected by this disease:
- Persian Cats: Due to their flat face shape and associated eye structure, Persian cats are particularly susceptible to cornea nigra. Their large, bulging eyes are more easily irritated and are more prone to corneal problems.
- Siamese cats: Siamese cats also show an increased tendency to develop cornea nigra. Your genetic predisposition and eye structure favor the occurrence of this specific corneal disease.
- Maine Coon Cats: This large and robust breed is also known to be predisposed to cornea nigra. Their large eyes, similar to Persian cats, can make them more susceptible to eye diseases.
- Carthusian (Chartreux): This breed is also known to be somewhat susceptible to cornea nigra. Their deep eyes and specific eye structure can lead to an increased risk of corneal problems.
It is important to emphasize that although these breeds have a higher predisposition, cornea nigra can occur in basically any cat. Regardless of breed, it is crucial to have regular eye exams and consult a veterinarian immediately at the first sign of illness. Early detection and treatment can prevent serious complications and ensure your cat's health and well-being.
(C) https://oogdierenarts.nl/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/gew1-belle-foto-1-preoperatief.jpg
Symptoms that a patient owner can recognize
As a cat owner, it is important to know the symptoms of cornea nigra so that you can take timely action if your beloved pet is affected. Here is a detailed description of the signs you should look out for:
- Changes in the cornea: One of the first signs of cornea nigra is a visible discoloration of the cornea. This may appear as a brownish or dark spot and is significantly different from the normally clear and transparent cornea.
- Eye redness: Redness around the eye can be an indication of irritation or inflammation, which is often associated with cornea nigra.
- Increased tear flow: Increased tear flow or the presence of tears may be a sign of eye irritation or pain.
- Altered blinking or squinting of the eyes: Cats with eye pain tend to close or blink the affected eye more frequently. You may also observe that your cat tries to avoid the light.
- Change in behavior: A change in your cat's behavior, such as increased eye rubbing or general restlessness, may indicate an eye problem.
- Vision Impairment: In advanced cases of cornea nigra, your cat's vision may be impaired. Pay attention to whether your cat has difficulty locating objects or reacts to light.
- Signs of Pain: Cats in pain may be less active, lose their appetite, or hide.
It is crucial that you seek immediate veterinary care at the first sign of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent disease progression and maintain your cat's well-being. Remember that your attention and care play a huge role in your four-legged friend's health and happiness.
Diagnosis of the cornea nigra
If you suspect that your cat may be suffering from cornea nigra, it is important to see a veterinarian . The process of diagnosis is critical to ensuring the best treatment for your pet. Here I will explain in detail how the diagnosis of suspected cornea nigra typically works:
- History: First, your veterinarian will take a detailed history. You will be asked about the symptoms you have observed as well as your cat's general health and behavior.
- Clinical Examination: The veterinarian will perform a thorough eye examination. He pays particular attention to changes in the cornea, redness, tearing and other signs that could indicate cornea nigra.
- Slit lamp examination: A special examination using a slit lamp allows the veterinarian to take a detailed look at your cat's eye structure. This examination helps identify changes in the cornea.
- Fluorescein staining test: A fluorescein staining test can be used by the veterinarian to determine if there are injuries or ulcers on the cornea. This test also helps assess the depth and severity of corneal damage.
- Imaging tests: In some cases, additional imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans may be necessary to examine the cornea and surrounding structures of the eye in more detail.
- Further tests: Depending on the results of previous examinations, further tests may be necessary to determine the exact cause of the cornea nigra. These include, among other things, blood tests and microbiological examinations.
- Final Diagnosis: Based on the results of these examinations, your veterinarian will make a diagnosis. If the suspicion of cornea nigra is confirmed, an individual treatment plan will be drawn up for your cat.
It is important to emphasize that an early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to your cat's successful treatment and recovery. So don't hesitate to consult a veterinarian at the first signs of an eye disease. Your attention and care can make a big difference in your cat's life.
Differential diagnosis
When differentially diagnosing cornea nigra, it is important to rule out other eye diseases in cats that may show similar symptoms. The veterinarian will consider various possibilities and perform appropriate tests to determine the exact cause of your cat's symptoms. Here I will explain to you which other diseases are taken into account in differential diagnosis:
- Corneal ulcers: These are common eye problems in cats and often manifest as redness, tearing and sensitivity to light. A fluorescein test can help differentiate corneal ulcers from cornea nigra.
- Pink eye (conjunctivitis): This is an inflammation of the conjunctiva that can cause redness, swelling, and discharge. It can be caused by allergies, infections or mechanical irritations.
- Keratitis: An inflammation of the cornea that can be caused by various causes such as infections, injuries or autoimmune diseases. Symptoms are similar to those of cornea nigra, including redness and tearing.
- Uveitis: An inflammation of the uvea, the middle part of the eye, that can cause pain, redness, and a change in pupil size. Uveitis can also cause clouding of the cornea.
- Glaucoma: Increased pressure in the eye that can cause pain, redness, and ultimately vision loss. Glaucoma requires quick action and specialized treatment.
- Foreign body or injury: Foreign bodies or injury to the eye can cause symptoms similar to those of the cornea nigra, such as redness, tearing, and pain.
For an accurate diagnosis, your veterinarian will perform a thorough examination and may order special tests. It is important that you as a cat owner remain vigilant and contact a veterinarian immediately if you suspect eye problems. Early and accurate diagnosis is critical to your cat's health and well-being.
What happens if the cornea nigra is not treated?
If cornea nigra in a cat is not treated, several serious complications can occur. It is important to understand the potential risks and consequences to emphasize the importance of early and appropriate treatment:
- Advanced corneal damage: Without treatment, the necrotic area on the cornea may continue to spread, leading to a significant worsening of the condition.
- Pain and discomfort: The cat may experience persistent and possibly intense pain as the cornea is one of the most sensitive structures in the eye.
- Increased risk of infection: Untreated cornea nigra can make the eye more susceptible to bacterial or viral infections, which can worsen symptoms.
- Loss of vision: In severe cases, the disease can cause clouding or scarring of the cornea, which can result in permanent impairment or even complete loss of vision.
- Corneal perforation: In extreme cases, corneal perforation may occur, a condition that requires immediate medical attention to save the eye.
- General health decline: Pain and stress caused by the disease can affect the cat's general well-being, which can manifest as behavioral changes, loss of appetite and general lethargy.
- Chronic Problems: Untreated cases of cornea nigra can lead to chronic eye problems that require lifelong monitoring and treatment.
It is therefore of the utmost importance that you contact a veterinarian immediately at the first signs of eye disease in your cat. Early diagnosis and treatment can not only relieve your cat's suffering, but also prevent serious long-term damage and preserve your four-legged friend's quality of life. Your care and attention are crucial to your cat's health and happiness.
Treatment of the cornea nigra
The treatment of cornea nigra in cats depends on the severity of the disease and the individual needs of the animal. Here is a comprehensive overview of the different treatment options:
- Medical therapy:
- Antibiotics and anti-inflammatories: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments may be prescribed to fight infections and relieve inflammation.
- Painkillers: Pain-relieving medications can be used to improve the cat's well-being.
- Tear substitutes: If your eyes are dry, artificial tears can be given to moisten and protect the cornea.
- Surgical interventions:
- Removal of necrotic tissue: In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the dead tissue.
- Corneal transplant: If the damage is profound, a corneal transplant may be necessary to preserve the structure and function of the eye.
- Postoperative care:
- Regular check-ups: After a surgical procedure, regular follow-up visits to the vet are necessary to monitor the healing process.
- Continuing medical treatment: Continued use of eye medications may be necessary after surgery to promote healing and prevent complications.
- Supportive measures:
- Eye protection: It may be necessary to put a protective collar on the cat to prevent it from scratching or rubbing its eye.
- Home environment adjustment: Avoid bright light and provide a quiet, comfortable retreat to reduce stress for the cat.
- Long-term monitoring:
- Regular eye exams: Even after recovery, regular eye exams are important to ensure there are no recurrences.
- Preventive action:
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet contributes to general health and therefore also to eye health.
- Regular eye care: Regular eye cleaning and care can help prevent future problems.
Treating cornea nigra requires close collaboration between you as a cat owner and your veterinarian. Early diagnosis and consistent treatment are crucial to your cat's successful recovery. Remember that your care and attention play a huge role in ensuring your four-legged friend has a happy and healthy life.
Can cornea nigra be prevented?
Yes, there are certainly steps you as a cat owner can take to reduce the risk of cornea nigra in your cat. While not all cases can be prevented, especially when genetic factors play a role, preventive steps will help promote your cat's overall eye health:
- Regular eye exams: One of the most important things you can do is to have your cat's eyes checked regularly by a veterinarian. Early detection of problems is the key to preventing more serious illnesses.
- Watch for early signs: Be alert for signs of eye disease, such as redness, tearing, changes in eye color or behavior, and seek immediate veterinary care if suspected.
- Good hygiene practices: Keep your cat's eye area clean. Gently cleaning your eyes with a soft, damp cloth can help remove contaminants and irritants.
- Adequate nutrition: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports your cat's overall health, including eye health.
- Avoiding Stress and Injuries: A safe and quiet home helps reduce stress, which can worsen eye problems. Be careful not to put your cat in situations where it could injure its eyes.
- Specific care for pedigree cats: For breeds that are more susceptible to cornea nigra, such as Persian cats or Siamese cats, you should be particularly vigilant and develop special care routines if necessary.
- Control of environmental factors: Reduce exposure to factors that can cause eye irritation, such as smoke, strong detergents, or drafts.
By taking these preventative measures, you can help minimize your cat's risk of cornea nigra. Remember that your cat's health and well-being depends largely on your attention and care.
FAQs about Cornea Nigra
What is Cornea Nigra and how to recognize it in cats?
Cornea nigra is a serious eye disease in cats characterized by darkening of the cornea. Typical signs of cornea nigra include a visible brownish to black discoloration on the cornea, redness in the eye, increased tear flow and changes in blinking or squinting of the eyes. In advanced cases, vision impairment may occur.
Which cat breeds are particularly susceptible to cornea nigra?
Breed susceptibility : Pedigree cats such as Persian cats, Siamese cats, Maine Coon cats and Carthusian cats are particularly susceptible to Cornea Nigra. These breeds have a higher risk of developing cornea nigra due to their genetic makeup and specific eye structure. However, cornea nigra can generally occur in all cat breeds.
How is it diagnosed?
Diagnosis : Cornea Nigra is diagnosed through a detailed eye examination by the veterinarian . Additional tests such as the fluorescein stain test can help confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or special eye scans may also be necessary to determine the depth and severity of the disease.
What treatment options are there?
Treatment : Treatment for cornea nigra depends on the severity of the condition. It ranges from drug therapies with eye ointments and drops to surgical procedures in which the necrotic tissue is removed or a corneal transplant is performed. Post-operative care is also important to promote a quick recovery.
Can cornea nigra be prevented and how?
Prevention : Complete prevention of cornea nigra is often difficult, especially when genetic factors play a role. However, regular eye care, a balanced diet, and avoiding environmental factors that can irritate the eyes can reduce the risk. Regular check-ups with the vet are also important to detect early signs of the disease.
Summary Cornea Nigra
Cornea nigra is a serious eye disease in cats that is particularly common in certain breeds such as Persian and Siamese cats. Cornea nigra causes the cornea to darken, which can affect the cat's vision. Early detection of the cornea nigra is crucial for successful treatment. Symptoms of cornea nigra include discoloration of the cornea, redness, and increased tearing. If cornea nigra is suspected, a veterinarian should be consulted immediately.
Diagnosis of cornea nigra is made through a thorough eye examination and special tests such as the fluorescein stain test. Treatment for cornea nigra depends on the severity and can range from drug therapies to surgical procedures. Untreated cornea nigra can lead to serious complications such as corneal rupture and vision loss. Postoperative care after cornea nigra treatment is important for the cat's recovery.
Preventative measures for cornea nigra include regular eye exams, good hygiene, and a balanced diet. Particular attention is required for pedigree cats that are more susceptible to cornea nigra. Early detection and treatment of the cornea nigra can prevent long-term damage and maintain the cat's quality of life. Cornea Nigra requires a conscious commitment on the part of cat owners to ensure the well-being of their pets.
