- Diseases in Guinea Pigs: Prevention and Treatment of Common Diseases
- Introduction
- Diet-related health problems
- Gastrointestinal Diseases in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
- Skin and Coat Problems in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
- Parasite Infestation in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
- Reproductive Health Issues in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
- Respiratory Problems in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
- Urinary Problems in Guinea Pigs: A Detailed Guide
- Pododermatitis - one of the often overlooked diseases in guinea pigs
- Overview of diseases in guinea pigs
- FAQ: Diseases in guinea pigs
- Which breeds of guinea pigs are particularly susceptible to which of the diseases mentioned?
- Summary of diseases in guinea pigs
Diseases in Guinea Pigs: Prevention and Treatment of Common Diseases
Introduction
Guinea pigs are popular pets that delight many people with their lively nature. However, like all animals, guinea pigs are susceptible to certain health problems (guinea pig diseases). To help them live a long and healthy life, it is important to know the signs and preventative measures of the most common diseases.
Diet-related health problems
Importance of a balanced diet for illnesses in guinea pigs
A balanced diet is crucial to your guinea pig's health. High-quality hay should make up the majority of their diet, supplemented by fresh vegetables and special guinea pig food.
Prevention of indigestion
- Feed your guinea pig fiber-rich food such as hay.
- Avoid sudden changes in diet.
- Make sure fresh water is always available.
Gastrointestinal Diseases in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
introduction
Stomach and intestinal diseases are not uncommon in guinea pigs and can have various causes. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial to your little friend's health.
Symptoms of stomach and intestinal diseases
Symptoms can be varied and include:
- Loss of appetite or reduced food intake.
- Changed stool consistency, e.g. diarrhea or hard, dry stool.
- Bloated stomach.
- weight loss.
- Behavioral changes such as lethargy or irritability.
Diagnosis
Various steps are necessary to diagnose a gastrointestinal disease:
- History : The veterinarian will first conduct a thorough history to record dietary habits, behavioral changes, and previous health problems.
- Physical examination : This includes checking the abdominal area for pain reactions and swelling.
- Fecal examination : It helps to identify infections or parasites.
- Blood tests : These can help detect systemic diseases.
- Imaging tests : X-rays or ultrasound may be necessary to identify blockages or other abnormalities.
Differential diagnosis
It is important to rule out other medical conditions that may cause similar symptoms, such as:
- Dental problems that affect feed intake.
- Infections or systemic diseases.
- Urinary tract disorders, especially with symptoms such as weight loss and behavioral changes.
Treatment options
Treatment depends on the exact diagnosis:
- Change in diet : If you have digestive problems, it may be necessary to switch to easily digestible food such as fresh vegetables and high-quality hay.
- Hydration : Important, especially if you have diarrhea, to avoid dehydration.
- Medication : Antibiotics or antiparasitics may be necessary if a bacterial infection or parasites are the cause.
- Pain management : Pain-relieving medications can improve the animal's well-being.
- Supportive care : In severe cases, supportive care, such as feeding with a syringe, may be necessary.
The health of your guinea pig's digestive system is essential to his overall well-being. Watch for signs of illness and seek veterinary attention early if you have any concerns. Many problems can be avoided or treated early through preventative measures such as a balanced diet and regular health checks. Your careful attention can help your guinea pig live a long and healthy life.
Skin and Coat Problems in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Skin and coat problems are relatively common in guinea pigs and can have various causes. It is important to recognize these early and treat them appropriately to ensure the well-being of your little friend.
Symptoms of skin and coat problems
Look out for the following signs that may indicate skin and coat problems:
- Hair loss or bald spots.
- Flaking or crusting on the skin.
- Redness or swelling.
- Itching, manifested by increased scratching.
- Unpleasant smell from fur or skin.
Diagnosis
Several steps are necessary to determine the exact cause of skin and coat problems:
- Medical history : The veterinarian will collect information about housing conditions, diet and previous health history.
- Physical examination : Inspection of the coat and skin to detect signs of infection, parasitic infestation, or other abnormalities.
- Skin swabs or biopsies : These may be needed to more accurately determine skin conditions.
- Allergy testing : If an allergic reaction is suspected.
Differential diagnosis
The following diseases should be considered in the differential diagnosis:
- Parasitic infestation such as mites, fleas or lice.
- fungal infections.
- Bacterial skin infections.
- Allergic reactions, for example to food or bedding.
- Hormonal imbalances that can cause hair loss.
Treatment options
Treatment depends on the cause of the skin and coat problems:
- Parasite control : Appropriate medication is required when infested with parasites.
- Antifungals : Special antifungal drugs are used for fungal infections.
- Antibiotics : The use of antibiotics may be necessary for bacterial infections.
- Allergy management : If you have allergies, allergy triggers should be avoided and, if necessary, anti-allergic medication should be administered.
- Grooming measures : Regular grooming and the use of mild, skin-friendly cleaning products can help.
Your guinea pig's skin and coat health plays an important role in its overall well-being. Regular check-ups and good care can help identify and treat problems early. If there are any signs of skin or coat problems, it is important to act quickly and consult a veterinarian if necessary. With your care and attention, you will help ensure that your guinea pig lives a healthy and happy life.
Parasite Infestation in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Parasitic infestation is a common disease in guinea pigs and can lead to various health problems. Early detection and effective treatment are crucial to helping your little friend.
Symptoms of parasite infestation
Symptoms of a parasite infestation can vary, but some common signs include:
- Severe itching, manifested by increased scratching.
- Visible parasites or their eggs in the fur or on the skin.
- Hair loss, especially in areas of intense scratching.
- Redness, swelling or sores on the skin.
- General restlessness or changes in behavior.
Diagnosis
Various tests are necessary to diagnose a parasite infestation:
- History : The vet will ask about previous infections, contact with other animals and housing conditions.
- Physical Exam : A thorough examination of the coat and skin for signs of parasites.
- Microscopic examination : Skin flakes or fur samples can be examined under the microscope for parasites.
- Fecal examination : To identify intestinal parasites.
Differential diagnosis
Other diseases that can cause similar symptoms should be excluded:
- Skin infections (bacterial or fungal).
- Allergic reactions, for example to food or bedding.
- Hormonal imbalances that can lead to hair loss.
Treatment options
Treatment depends on the type of parasite infestation:
- Anti-parasitic medications : Special medications against the respective parasites, such as anti-mite medications or flea medications.
- Comprehensive cage cleaning : To avoid reinfections, thorough cleaning of the cage and surrounding area is necessary.
- Treating all animals : All guinea pigs in a household should be treated to prevent the spread of parasites.
- Supportive skin care : Soothing skin lotions or shampoos can help regenerate the skin and relieve itching.
- Nutrition and strengthening the immune system : A balanced diet supports the immune system and helps the body fight infections better.
A parasite infestation can be unpleasant and harmful to your guinea pig, but with the right treatment and prevention, you can help your little friend get back to health quickly. Regular checks, good hygiene and careful observation are crucial to detect parasite infestations early and treat them effectively. With your loving care and attention, you can ensure that your guinea pig lives a healthy and happy life.
Reproductive Health Issues in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Reproductive health problems are not uncommon in guinea pigs, especially females. These problems can significantly impact both the animal's well-being and quality of life.
Symptoms of reproductive health problems
Watch out for the following signs that may indicate reproductive problems:
- Changes in behavior, such as increased aggressiveness or withdrawal.
- Visible changes in the genital area, such as swelling or discharge.
- Difficulty or pain when urinating.
- Blood in urine.
- Weight loss or loss of appetite.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing reproductive health problems requires a thorough examination by a veterinarian:
- Medical History : The veterinarian will collect information about age, reproductive history, and previous health problems.
- Physical examination : A careful examination of the genital area and palpation of the abdomen.
- Ultrasound examination : To assess the internal reproductive organs.
- Blood tests : May be necessary to identify hormonal imbalances or infections.
Differential diagnosis
It is important to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms:
- Urinary tract infections or stones.
- Digestive problems that cause pain in the abdominal area.
- Tumors or cysts that are not reproductive in nature.
Treatment options
Treatment depends on the specific diagnosis:
- Drug therapy : Hormonal treatments may be helpful in some cases.
- Surgical procedures : Surgery may be necessary for serious illnesses such as tumors or severe infections of the uterus.
- Supportive care : A balanced diet and stress-free environment support recovery.
- Sterilization : To prevent future reproductive problems, sterilization may be considered, especially for female guinea pigs.
Reproductive health problems in guinea pigs require careful observation and, if necessary, quick action. Early detection and adequate medical care are crucial to avoid serious consequences. Pay attention to the signs and seek veterinary advice immediately if you suspect anything. Through your attentive care and precautions, you will make a significant contribution to the health and well-being of your guinea pig.
Respiratory Problems in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Respiratory problems in guinea pigs are serious health concerns that require immediate attention. Early detection and treatment is critical to your little friend's health and well-being.
Symptoms of breathing problems
Watch your guinea pig for signs such as:
- Unusual breathing noises such as whistling, wheezing or wheezing.
- Accelerated or difficult breathing.
- Nasal discharge or wet nose.
- Frequent sneezing.
- General weakness or reduced activity.
- Loss of appetite or weight loss.
Diagnosis
The following steps are necessary to diagnose breathing problems:
- History : The veterinarian will collect information about symptoms, housing conditions and possible contact with other sick animals.
- Physical examination : checking the respiratory tract, listening to the lungs and chest.
- X-rays : To image the lungs and airways.
- Laboratory tests : Blood tests or nasal swabs can help identify the cause of breathing problems.
Differential diagnosis
It is important to rule out other conditions that may show similar symptoms:
- Heart problems that can cause difficulty breathing.
- Allergic reactions, for example to dust in the litter.
- Dental problems that can lead to difficulty eating and associated breathing problems.
Treatment options
Treatment for breathing problems depends on the exact cause:
- Antibiotics : For bacterial infections of the respiratory tract.
- Expectorant medications : To support breathing when there is mucus.
- Supportive Care : Ensuring a clean, dust-free environment and stress-free attitude.
- Inhalation therapy : In some cases, inhalation therapy may be helpful to open the airways.
- Nutritional management : Ensuring a balanced diet to strengthen the immune system.
Breathing problems in guinea pigs should never be ignored. Prompt and appropriate treatment is crucial. Watch for early signs of breathing difficulties and seek veterinary help immediately if suspected. With your careful care and attention, you can help ensure your guinea pig stays healthy and lives a happy life.
Urinary Problems in Guinea Pigs: A Detailed Guide
Introduction
Urinary problems can pose serious health risks in guinea pigs and require appropriate attention and care. Early detection and treatment are essential to your animal's well-being.
Symptoms of urinary problems
Watch your guinea pig for signs such as:
- Blood in urine.
- Difficulty or pain when urinating.
- Frequent urination or incontinence.
- Changes in the color or smell of urine.
- Apathy or changes in behavior.
- Loss of appetite or weight loss.
Diagnosis
The following steps are necessary to diagnose urinary problems:
- Medical history : The vet will ask for information about diet, drinking habits and previous health history.
- Physical examination : Inspection of the genital area and palpation of the bladder.
- Urinalysis : A sample of urine may be examined for signs of infection, crystals, or other abnormalities.
- Ultrasound : To image the bladder and kidneys and look for stones or other abnormalities.
- X-rays : May be necessary to identify urinary stones.
Differential diagnosis
It is important to rule out other conditions that may show similar symptoms:
- Kidney or bladder infections.
- Metabolic diseases that lead to changes in urine.
- Diseases of the reproductive system that can cause similar symptoms.
Treatment options
Treatment depends on the specific cause of the urinary problems:
- Antibiotics : For bacterial infections of the urinary tract.
- Painkillers : To relieve discomfort.
- Diet changes : A diet low in calcium can help prevent bladder stones from forming.
- Surgical procedures : In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove urinary stones.
- Adequate hydration : Make sure your guinea pig always has access to fresh, clean water.
Urinary problems in guinea pigs require careful observation and sometimes quick action. Watch for signs of discomfort or changes in the urine and seek veterinary advice immediately if suspected. With proper care and attention, you can help your guinea pig live a healthy and happy life.
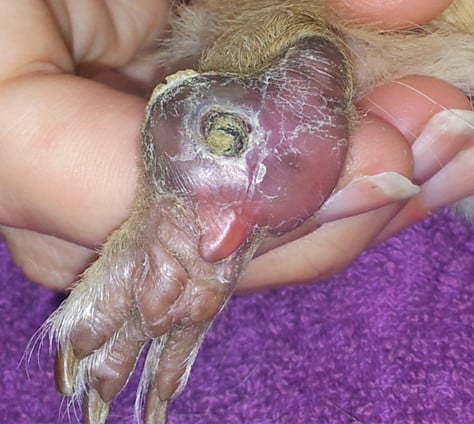
Pododermatitis - one of the often overlooked diseases in guinea pigs
Pododermatitis, often known as bumblefoot, is a condition that can occur in guinea pigs and affects the feet. This inflammatory disease is not only painful but can also lead to serious complications without proper treatment.
Causes of Pododermatitis
The main causes of pododermatitis in guinea pigs are:
- Hard or unclean surfaces: A hard, rough or dirty cage floor can lead to pressure points and wounds on the feet.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases pressure on the feet, which can promote the development of pododermatitis.
- Lack of exercise: A lack of opportunities to move can lead to poor blood circulation in the feet.
- Genetic predisposition: Some guinea pigs are genetically more susceptible to skin and foot problems.
Symptoms of pododermatitis
The symptoms of pododermatitis include:
- Swelling and redness on the soles of the feet.
- Visible sores or abscesses on the feet.
- Painful reactions when touching the feet.
- Lameness or a change in gait.
- Decreased activity and loss of appetite due to pain.
Diagnosis
To diagnose pododermatitis, the veterinarian will:
- a thorough examination of the feet to assess the severity of the condition.
- a medical history to identify possible causes.
- If necessary , take x-rays to detect bone involvement or deeper infections.
Treatment options
Treatment for pododermatitis includes:
- Wound care: Cleaning and disinfecting the affected areas.
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections.
- Painkillers: To relieve symptoms.
- Bandage: To protect the feet and promote healing.
- Adjustment of the keeping conditions: Soft bedding and regular cleaning of the cage.
- Weight management: For overweight animals.
Prevention of pododermatitis
To prevent pododermatitis (as one of the diseases in guinea pigs) it is important:
- Use a soft, clean surface in the cage.
- Avoid being overweight and ensure you get enough exercise.
- Check your guinea pigs' feet regularly for signs of pododermatitis.
Pododermatitis is a serious condition that can lead to long-term health problems without proper treatment. Early detection and treatment as well as adjustment of housing conditions are crucial for the health and well-being of your guinea pig.
(C) https://kb.rspca.org.au/knowledge-base/what-are-common-health-problems-in-guinea-pigs/
Overview of diseases in guinea pigs
FAQ: Diseases in guinea pigs
What are the most common diseases in guinea pigs?
Guinea pigs are susceptible to various diseases, including gastrointestinal diseases, respiratory infections, skin and coat problems, parasitic infestations, reproductive health problems and urinary tract diseases.
What should I do if my guinea pig is sick?
If you see any signs of illness, you should consult a veterinarian immediately. Many illnesses in guinea pigs can worsen quickly, so early diagnosis and treatment is crucial.
How do I tell if my guinea pig is sick?
Watch for changes in behavior, loss of appetite, unusual bowel movements, difficulty breathing, changes in fur or skin, lethargy, or aggressiveness. Any of these symptoms can indicate an illness.
How can I protect my guinea pig from guinea pig diseases?
A balanced diet, regular cage cleaning, avoiding stress, regular health checks and monitoring behavior changes are important measures to prevent disease.
Are skin and coat problems in guinea pigs serious?
Yes, skin and coat problems can be a sign of parasite infestation, allergies or other serious health problems. Early diagnosis and treatment by a veterinarian are therefore important.
Can people get diseases from guinea pigs?
While transmitting disease from guinea pigs to humans is rare, it is possible. Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands after handling the animal and cleaning the cage, are important.
How often should I take my guinea pig to the vet?
In addition to regular annual health checks, you should take your guinea pig to the vet if you notice any behavioral or health changes. Older animals or animals with known health problems may require more frequent visits.
What are signs of respiratory disease in guinea pigs?
Signs of respiratory illness include wheezing, coughing, nasal discharge, rapid breathing, and difficulty breathing. If you experience such symptoms, an immediate visit to the vet is advisable.
How serious are urinary tract problems in guinea pigs?
Urinary tract problems can be very serious, especially if left untreated. Symptoms such as blood in the urine, difficulty urinating, or frequent urination require immediate veterinary attention.
Are gastrointestinal problems common in guinea pigs?
Yes, gastrointestinal problems are not uncommon in guinea pigs and can be caused by dietary errors, stress, or infections. Symptoms include changes in bowel movements, bloating, weight loss and loss of appetite.
These FAQs provide a basic overview of guinea pig health. Remember that regular veterinary checks and careful observation of your guinea pig's behavior and health are essential to keeping him healthy and happy.
Which breeds of guinea pigs are particularly susceptible to which of the diseases mentioned?
Guinea pigs, regardless of their breed, can generally be susceptible to various diseases. However, there are some breed-specific tendencies in susceptibility to certain diseases:
- Long-haired breeds (e.g. Sheltie, Peruvian): These guinea pigs are more prone to coat and skin problems due to their long fur. The long fur can become matted more easily and is more susceptible to parasite infestation as well as fungal and bacterial infections.
- Rex Guinea Pig: This breed, with its characteristic ruffled coat, can be prone to skin problems, especially if skin care is not adequate.
- Skinny Guinea Pigs: As a hairless breed, skinnies are particularly susceptible to skin problems, including fungal and bacterial infections. They require special care to protect their sensitive skin.
- Brachycephalic breeds (e.g. teddy guinea pigs): These breeds with a shorter snout may be more susceptible to respiratory illnesses. Your facial structure can cause respiratory problems.
- Older guinea pigs of all breeds: With increasing age, the risk of certain diseases such as tumors, heart problems and metabolic diseases increases.
It is important to note that regardless of the breed, good care, adequate nutrition and regular veterinary checks are essential to prevent disease or detect it early. Each guinea pig is an individual, and its health can be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental conditions and lifestyle.
Summary of diseases in guinea pigs
Diseases in guinea pigs can be diverse and often require attentive care and early medical treatment. One of the most common diseases in guinea pigs is gastrointestinal diseases, which can be caused by inadequate nutrition or infections. Skin and fur problems are also common diseases in guinea pigs, often caused by parasite infestation or allergic reactions. Respiratory diseases are also important diseases in guinea pigs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses or allergens. In addition, urinary tract problems are serious illnesses in guinea pigs that can be traced back to a number of causes, such as bladder stones or infections.
Additionally, dental problems are common diseases in guinea pigs as their teeth continually grow and can cause problems if not worn down correctly. Eye diseases are also diseases in guinea pigs that can occur due to infections, injuries or genetic factors. Parasitic infections, such as mites or lice, are common diseases in guinea pigs and can cause itching, hair loss and skin inflammation. Fungal infections are also diseases in guinea pigs, which are often promoted by damp housing conditions.
Nutritional diseases in guinea pigs often occur due to an unbalanced diet, which can lead to nutritional deficiencies or digestive problems. Foot problems, such as bumblefoot, are also diseases in guinea pigs that can be caused by poor housing or obesity. Respiratory diseases, particularly pneumonia, are serious illnesses in guinea pigs and require immediate veterinary attention.
Reproductive health problems are also diseases in guinea pigs, especially females, which can lead to complications such as uterine infections. Ear infections, although less common, are also among guinea pig diseases and can be caused by bacteria or fungi. Although metabolic diseases such as diabetes are rarer, they are still serious diseases in guinea pigs.
Additionally, eye infections such as conjunctivitis are diseases in guinea pigs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or foreign bodies in the eye. Heart disease, although not as common, is a potentially serious illness in guinea pigs. Cancers, including tumors, are serious diseases in guinea pigs that can occur, especially in older animals. Abscesses, often the result of injury or infection, are also illnesses in guinea pigs.
Finally, stress and behavioral problems that can lead to health problems are also illnesses to be aware of in guinea pigs. Overall, it is important to know the signs of these diseases in guinea pigs and seek veterinary advice if suspected to ensure the well-being and health of your guinea pig.
