Fleas in dogs: detecting, preventing and combating them effectively
- Fleas in dogs: detecting, preventing and combating them effectively
- Fleas on dogs: The uninvited guests
- Causes of Fleas on Dogs
- Identifying Fleas on Dogs
- Consequences of fleas on dogs
- Preventive measures against fleas on dogs
- Treatment options for fleas on dogs
- Complications and consequences of fleas in dogs
- Behavior in case of repeated flea infestation
- Frequently asked questions about fleas on dogs
- How can I tell if my dog has fleas?
- What are the possible effects of a flea infestation on my dog?
- How can I treat a flea infestation on my dog?
- How can I prevent my dog from getting fleas?
- Can fleas be passed from my dog to me?
- Where do fleas like to sit on dogs?
- How do dogs behave when they have fleas?
- Fleas on Dogs: A Comprehensive Summary
Fleas on dogs not only cause irritation to the animal, but can also be transmitted to humans. A thorough understanding of these parasites and their life cycles is essential for their effective control and prevention.
Fleas on dogs: The uninvited guests
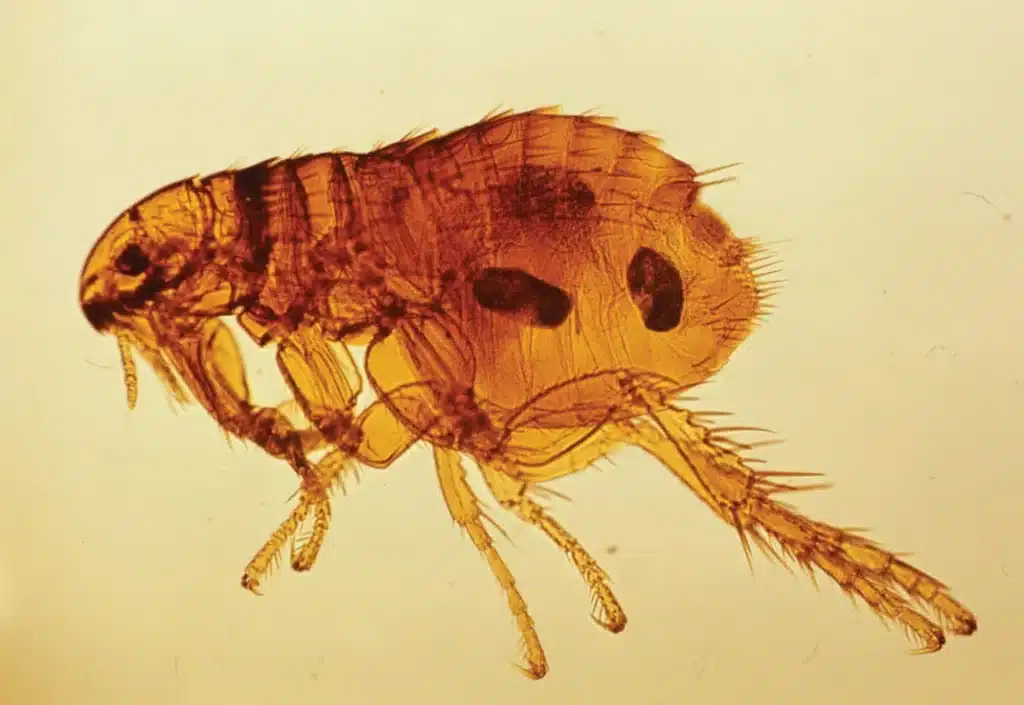
Fleas on dogs are pest insects that are known for their rapid reproduction. A single flea can quickly build up a population of hundreds. They are bloodsuckers and need this to reproduce. Due to their ability to spread quickly, flea infestations on dogs can occur frequently, causing itchy bites and even serious health problems.
The adult fleas we see are just the tip of the iceberg. The majority of the flea population consists of eggs, larvae and pupae that are found in the dog's environment. It is therefore important to involve not only the dog itself, but also its environment when treating a flea infestation.
Causes of Fleas on Dogs
Dogs can get fleas in a variety of ways. They can pick them up from other animals or from their environment where the flea eggs and larvae lurk. It is important to know that fleas are able to survive and reproduce in the favorable conditions of a home.
Identifying Fleas on Dogs
The most common signs of fleas in dogs are restlessness, frequent scratching, skin inflammation or hair loss. However, some dogs may barely show any itching despite having fleas. In such cases, a flea comb can be helpful to detect flea dirt in the fur.
Where do fleas like to live on dogs?
Fleas prefer areas on the dog that are warm, well supplied with blood and easy to access. However, they are also forced to stay in places where they are less likely to be discovered and removed. Therefore, they usually prefer the following areas:
- Back and hip area: The fur is often denser here and the dog is less able to reach this area to scratch or bite, which offers a certain level of security for fleas.
- Abdomen and groin area: These are warm, well-circulated areas that are attractive to fleas. However, they are also more vulnerable to detection and removal by the dog.
- Area around the neck and under the chin: This is another area that is difficult for the dog to reach. Flea collars are often effective precisely because they are placed in this area, which is often affected by flea infestations.
It is important to note that fleas on dogs move on the dog's body and are not just limited to these preferred areas. Therefore, when looking for fleas, it is necessary to examine the dog's entire body.
The search for fleas on dogs should be systematic and thorough. A flea comb is a useful tool for tracking down the small parasites. Often the first indication of a flea infestation is not the fleas themselves, but rather the flea droppings, which leave small, black crumbs behind. This flea feces dissolves in water to form a rusty brown or reddish dye because it contains the dog's blood digested by the flea.
How do dogs behave when they have fleas?
The symptoms of fleas in dogs can vary and depend on various factors, such as the health of the animal, the number of fleas and the duration of the infestation. However, there are some common behavioral changes and physical signs that may indicate your dog has fleas:
- Increased scratching and biting: Fleas cause intense itching in dogs. This is why dogs increasingly scratch, bite and lick certain parts of their body. The rear, belly and sides of the dog are particularly often affected.
- Restlessness and nervousness: Dogs can become restless and nervous due to the unpleasant itching. You may have difficulty relaxing or sleeping and may generally appear more restless and impatient than usual.
- Skin irritation and hair loss: If the flea infestation is severe or long-lasting, visible skin changes may occur. These include redness, scales, pustules, thickening of the skin and hair loss. Severe skin reactions can occur, especially in dogs that are allergic to flea saliva.
- Changes in eating behavior or weight loss: With severe flea infestations, dogs may also exhibit loss of appetite and weight loss, especially if the infestation persists over a long period of time and is not treated.
- Conspicuous licking or biting at certain areas: If a dog excessively licks or bites a certain area of its body, this may be an indication of a flea infestation.
Consequences of fleas on dogs
Fleas on dogs can lead to a number of health problems, including allergic reactions, skin diseases and tapeworm infections. With massive flea infestations, they can even lead to anemia, especially in puppies.
Can fleas on dogs be transmitted to people?
Fleas in dogs are parasites that are specific to certain types of hosts. The dog flea (Ctenocephalides canis) and the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis) are two of the most common flea species that infest pets. While these types of fleas actually preferentially attack dogs and cats, they are capable of jumping on and biting other species, including humans.
However, humans are not ideal hosts for these types of fleas. A flea that bites a human usually will not stay on them or establish a population. Instead, the flea will likely jump on the human, bite, and then return to the original host, in this case the dog.
Dog and cat flea bites can cause itching and skin irritation in humans. In rare cases, they can also transmit diseases or lead to secondary skin infections.
It is important to note that although fleas on dogs occasionally bite humans, they do not permanently colonize human hosts. The best way to prevent flea bites in humans is to effectively treat and prevent flea infestations in pets. This includes regular vet visits, use of flea control and prevention products, regular washing of pet beds, and regular cleaning of living quarters.
(C) https://cdn.britannica.com/90/590-050-AF13D996/Flea.jpg
Preventive measures against fleas on dogs
Prevention is the key to avoiding fleas on dogs. Here are some steps you can take to reduce the likelihood of a flea infestation:
- Regular parasite control: Use flea and tick treatments recommended by your veterinarian. These can be administered either orally or topically and provide effective protection against fleas.
- Cleaning the environment: Clean your dog's environment regularly to keep the flea population under control. This includes both the house and the garden.
- Frequent washing and combing of dog fur: Regular washing and combing of dog fur can detect and remove fleas early.
- Be careful when contacting other animals: Avoid letting your dog come into contact with animals that may have fleas.
- Regular use of flea prevention: Regular use of flea prevention products can significantly reduce the risk of flea infestation. There are many different preparations that both kill fleas and prevent them from laying eggs, including spot-on drops, tablets, collars, and sprays. To select the appropriate product, we recommend consulting your veterinarian.
- Regular grooming: Regular grooming with a flea comb can help detect fleas early and remove them before they can multiply. This is particularly important for long-haired dogs.
- Treating all pets: If there are multiple animals in the household, it is important that all animals are treated for fleas. Otherwise, an untreated animal can serve as a reservoir for fleas, causing a re-infestation.
Treatment options for fleas on dogs
If you have a flea infestation, it is important to treat both the animal and its environment. Here are some options for treatment:
- Topical medications: These are applied to the dog's skin and kill fleas as soon as they come into contact with the medication.
- Oral Medications: These pills are taken by the dog and work from within to kill fleas.
- Flea collars: These collars contain insecticides that spread through the dog's fur and kill fleas.
- Environmental sprays: These kill fleas in the dog's environment, including eggs, larvae and pupae.
- Professional pest control: In severe cases, it may make sense to call in a professional pest controller to treat the flea infestation in the dog's area.
If you have a flea infestation, always consult your veterinarian to determine the best treatment plan for your dog and his specific situation.
How do I get rid of fleas on dogs?
If you discover that your dog has fleas, you should act quickly to stop the infestation and eliminate the fleas completely. Several steps are required:
- Diagnosis: First of all, a flea infestation on your dog should be confirmed by a veterinarian. This can also determine whether the dog may also be infected with other parasites.
- Treating the Dog: After confirming the flea infestation, your veterinarian will recommend appropriate treatment for your dog. There are several options, such as oral medications, spot-on preparations, or flea collars. These agents work by killing adult fleas and, in some cases, preventing the development of flea eggs and larvae.
- Cleaning the environment: About 95% of flea infestations are in the environment and not on the dog itself. Therefore, in addition to treating the dog, it is important to thoroughly clean the area. This includes vacuuming all areas where your dog spends time, including carpets, upholstered furniture, and the dog bed. Also wash all washable items (such as dog blankets) at high temperatures.
- Insecticidal use: After cleaning, it is advisable to treat the area with a specific insecticide. This should be able to kill not only adult fleas, but also their eggs and larvae. There are various products in the form of sprays or mist that can be used for this purpose. Follow the safety instructions on the product.
- Preventive measures: To avoid a new infestation, you should take preventive measures. This includes regular use of flea preventatives, grooming the dog with a flea comb, and cleaning the area regularly.
It is important to note that treating fleas takes time and may take several weeks to completely eliminate all fleas from the environment. So stay patient and consistent in your treatment.
Finally, it should be noted that a flea infestation can not only be annoying for the dog, but can also be harmful to their health. Fleas can transmit various diseases, including flea tapeworm infection and bartonellosis (cat scratch disease). It is therefore important to always consult a veterinarian if you suspect a flea infestation.
Complications and consequences of fleas in dogs
In addition to the obvious discomfort caused by itching and restlessness, a flea infestation can cause other health problems for your dog. Some of them are:
- Allergic Reactions: Some dogs may have an allergic reaction to flea saliva, resulting in flea saliva allergy dermatitis (FAD). This condition causes extreme itching, skin inflammation and hair loss. In affected dogs, FAD usually occurs in the back half of the body.
- Bacterial infections: So-called “hot spots” can occur in dogs with flea saliva allergies. These are moist, purulent skin infections that cause intense itching and require immediate veterinary attention.
- Worm infestation: Fleas can also serve as intermediate hosts for certain types of tapeworms. If a dog swallows an infected flea, it can become infected with these worms itself.
- Anemia: A severe flea infestation can lead to anemia, especially in puppies. Fleas feed on blood, and a large flea infestation can cause a puppy to lose a significant amount of his blood.
It is therefore important to take immediate action and initiate treatment if you see signs of a flea infestation.
Behavior in case of repeated flea infestation
Repeated flea infestations can be frustrating and are often due to one or more of the following:
- Inadequate use of antiparasitic medications: Improper use of flea treatments can cause some fleas to survive and continue to multiply.
- Short treatment period: Flea infestations often require treatment over a longer period of time to ensure that all fleas and their eggs are killed.
- Untreated animals in the household: All animals in the household must be treated to prevent re-infestation.
- Inadequate environmental cleaning: It is important to thoroughly clean and disinfect the dog's environment to eliminate all fleas and eggs.
To prevent re-infestation, it is important to follow your veterinarian's instructions carefully and treat all animals in the household and the dog's environment appropriately.
Frequently asked questions about fleas on dogs
How can I tell if my dog has fleas?
Some of the most common signs that your dog has a flea infestation include restless behavior, constant scratching, bites and rashes on the skin, hair loss, and visible fleas or flea feces on the dog's fur. If you see flea poop, they are small black or dark brown crumbs that run reddish on damp paper because they are made of undigested blood.
What are the possible effects of a flea infestation on my dog?
Fleas can cause a variety of health problems in dogs, including allergic reactions to flea saliva (flea saliva allergy dermatitis), bacterial skin diseases, tapeworm infections and, in severe cases, anemia.
How can I treat a flea infestation on my dog?
To treat a flea infestation, you should consult your veterinarian. Several effective antiparasitic medications are available and can be used in a variety of ways, including oral medications, topical spot-on treatments, and insecticide collars. If the infestation is severe, it may be necessary to continue these treatments over several months to break the flea cycle.
How can I prevent my dog from getting fleas?
Regular use of flea control and prevention products, washing pet beds, and regularly cleaning living spaces can help prevent flea infestations. Good hygiene and regular vet visits are also important.
Can fleas be passed from my dog to me?
Yes, dog fleas can bite humans, but they will not permanently colonize a human host. The flea will likely jump on the human, bite, and then return to the dog. Bites from dog fleas can cause itching and skin irritation in humans. However, it is rare for them to transmit diseases to humans.
Where do fleas like to sit on dogs?
Fleas prefer areas with little hair where they can get to the skin more easily. This includes the stomach, inner thighs and the area around the base of the tail. However, fleas can be found in any part of your dog's fur.
How do dogs behave when they have fleas?
Dogs with fleas may be restless, scratch or bite themselves frequently, and have skin irritation or hair loss. They may also show signs of discomfort, such as: B. Loss of appetite or behavioral changes. However, it is important to note that not all dogs have fleas
Fleas on Dogs: A Comprehensive Summary
Fleas on dogs are a common parasitic infection that can cause significant discomfort and lead to health problems. These parasites feed on blood and multiply quickly in the environment, which can lead to a persistent infestation.
Fleas on dogs are not only a source of discomfort and stress for the animal, but can also cause serious health problems. These include allergic reactions to flea saliva, causing skin rashes and itching, as well as the transmission of tapeworms and other parasites.
Identifying fleas on dogs can be difficult because symptoms vary from animal to animal. However, common signs include excessive scratching, skin irritation, hair loss and the presence of flea feces in the dog's fur.
Treating fleas on dogs requires a targeted approach. Several antiparasitic medications are available, including oral medications, topical spot-on treatments, and flea collars. It is important to note that these treatments must be used regularly to be effective.
Preventing fleas on dogs is an important aspect of pet care. This can be accomplished through regular use of flea control products, washing pet beds, and regular cleaning of living spaces.
Fleas on dogs prefer areas with less hair where they can more easily get to the skin. These are often the stomach, inner thighs and the area around the base of the tail.
Fleas on dogs can also bite humans, but they will not permanently colonize a human host. These bites can cause itching and skin irritation, but it is rare for them to transmit disease to humans.
The behavior of dogs with fleas can vary, but they often exhibit restlessness, increased scratching or biting, and may show signs of discomfort such as loss of appetite or behavioral changes.
Ultimately, controlling fleas on dogs requires a consistent and proactive approach, including regular vet visits, appropriate treatments, and good household hygiene.
Fleas on dogs are a common problem, but one that can be effectively managed with proper care and attention. Working closely with your veterinarian is crucial to ensuring your dog remains healthy and flea-free.
