Malassezia Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Yeast Infection in Animals
- Malassezia Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Yeast Infection in Animals
- Introduction: What is Malassezia Dermatitis?
- Causes of Malassezia Dermatitis
- Symptoms of Malassezia dermatitis
- Diagnosis of Malassezia dermatitis
- Treatment of Malassezia dermatitis
- Prevention of Malassezia dermatitis
- Prognosis and long-term management
- Preventive measures for breeders and animal owners
- Interesting facts about Malassezia yeast fungi
- Malassezia dermatitis in cats
- Prevention in cats
- Frequently asked questions about Malassezia dermatitis - FAQs:
- Conclusion
- Current research on Malassezia dermatitis
- Current literature on Malassezia dermatitis
Introduction: What is Malassezia Dermatitis?
Malassezia dermatitis is a skin infection caused by an overgrowth of yeast, particularly Malassezia yeast. These yeast fungi are part of the normal skin flora and occur in small numbers in moist and warm skin areas. In healthy skin, there is a balance between yeast and the skin's defense mechanisms. When this balance is disrupted, Malassezia dermatitis can result.
Causes of Malassezia Dermatitis
Malassezia dermatitis usually occurs when the skin's defense mechanisms are weakened by another disease. These diseases include:
- Atopic dermatitis
- Food allergy
- Hormonal disorders such as hypothyroidism
- Congenital diseases such as primary seborrhea
Some breeds are particularly sensitive to Malassezia yeast fungi due to their special skin (breed disposition). Dogs can also develop an allergy to malassezia, which is accompanied by severe itching.
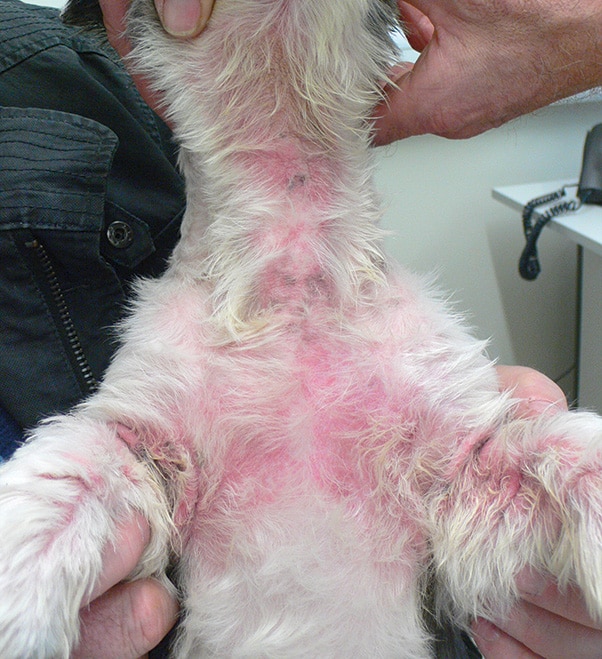
Symptoms of Malassezia dermatitis
The typical symptoms of Malassezia dermatitis are:
- Skin redness
- Flaking
- Oily skin surface
- Oily, rancid smell
The ears, underside of the neck, paws and armpits are often particularly affected. Some dogs only show red areas between the toes, while others only develop flaky skin and itching without redness and odor.
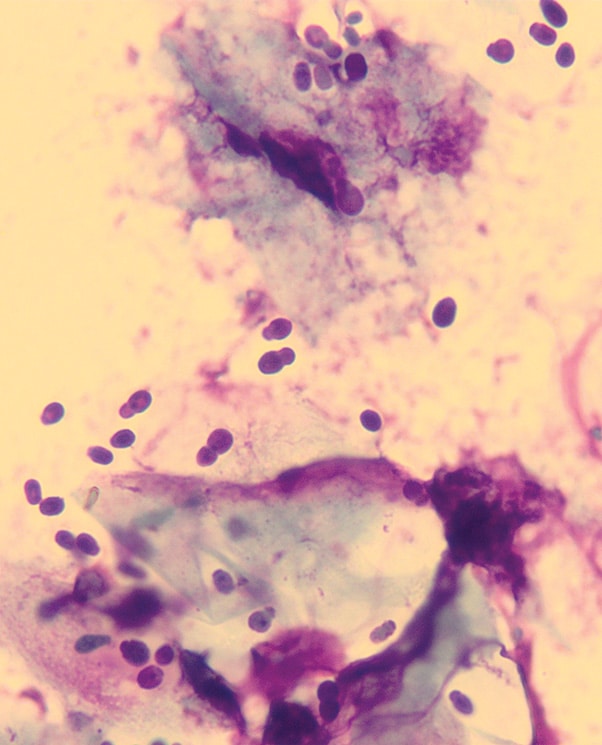
Diagnosis of Malassezia dermatitis
The diagnosis of Malassezia dermatitis is based on clinical examination and microscopic detection of the yeast fungi in ear secretions or skin swabs.
Treatment of Malassezia dermatitis
Malassezia dermatitis is treated with antifungal medications, which are administered either in tablet form or as a shampoo. For ear infections, ear drops with appropriate active ingredients are used. When using a shampoo, it is important to leave it on the skin for at least 10 minutes so that it can develop its full effectiveness.
Since Malassezia dermatitis only develops if another skin disease has paved the way, it is advisable to carry out appropriate tests to clarify the causes. If possible, the underlying condition should be treated to prevent recurrence.
Prevention of Malassezia dermatitis
To prevent Malassezia dermatitis, it is important to know the causes and risk factors and, if necessary, minimize them. This includes:
Good skin care
Regular grooming and skin cleaning can help control yeast growth. Make sure that your pet is dried thoroughly after bathing or swimming, especially in the damp and warm skin areas.
Control of allergies
If your pet suffers from allergies, it is important to control them as best as possible to reduce skin irritation and infections. This can be achieved through the use of hypoallergenic food, regular grooming or, if necessary, medication.
Treatment of underlying medical conditions
Treating conditions that increase the risk of Malassezia dermatitis, such as hormonal imbalances or congenital skin diseases, can help reduce the risk of a yeast infection.
Regular vet visits
Regular veterinary visits are important to monitor your pet's health and detect early signs of skin problems. If necessary, the veterinarian can recommend appropriate measures to minimize the risk of Malassezia dermatitis.
Prognosis and long-term management
The prognosis for animals with Malassezia dermatitis is generally good if the underlying causes are identified and treated. However, in some cases, recurrent infections may occur, requiring long-term monitoring and treatment.
Long-term management
Some animals require long-term medication or special skin care to prevent recurring infections. These can include:
- Regular use of antifungal shampoos or sprays
- Long-term medication, for example to treat allergies or hormonal disorders
- Diet management for food allergies
Collaboration with the veterinarian
Working closely with your veterinarian is crucial to monitoring your pet's condition and ensuring the best possible treatment. Regular follow-up visits allow your veterinarian to assess the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments if necessary.
Adaptation of the environment
In some cases, adjusting your pet's environment may help reduce the risk of recurring Malassezia dermatitis infections. This can include:
- Use of hypoallergenic bedding materials
- Cleaning and disinfection of sleeping places and toys
- Avoiding environmental allergens that can cause skin irritation
Preventive measures for breeders and animal owners
Breeders and pet owners can also help reduce the risk of Malassezia dermatitis in their animals. Here are some preventative measures you can take:
Early detection and treatment
Watch for signs of skin problems in your animals and seek veterinary attention early if necessary. The earlier Malassezia dermatitis is detected and treated, the better the chances of a successful recovery.
Consider genetic factors
Some dog breeds are more susceptible to Malassezia dermatitis due to genetic factors. If you are a breeder, you should pay attention to these factors when selecting breeding animals and adapt the breeding strategy if necessary.
Stress reduction
Stress can weaken your pet's immune system and increase the risk of skin infections. Make sure your animals live in a stress-free environment and offer them plenty of activity and social contact.
Caring for the immune system
A strong immune system is essential for preventing Malassezia dermatitis. Make sure your animals receive a balanced and nutritious diet and that all necessary vaccinations and deworming are carried out.
Interesting facts about Malassezia yeast fungi
Malassezia yeast fungi are normally harmless inhabitants of the skin flora in animals. However, they can be used under certain circumstances, such as: B. with weakened immune defenses or skin barriers, lead to excessive reproduction and infection. Here are some interesting facts about these microorganisms:
- Malassezia yeasts are widespread in many animal species, including dogs, cats and humans.
- There are several species of Malassezia yeast that can colonize different animal species and skin areas.
- Malassezia yeast fungi feed on fatty acids produced in the skin's sebaceous glands. This explains why they prefer to settle in oily areas of the skin.
Overall, Malassezia dermatitis is a complex disease that requires comprehensive diagnosis and treatment. Early detection, treatment of underlying causes, and appropriate prevention can minimize the risk of infection.
Malassezia dermatitis in cats
Although Malassezia dermatitis is more common in dogs, it can also occur in cats. The symptoms and causes are similar to those in dogs, but there are some differences in diagnosis and treatment in cats.
Symptoms in cats
Symptoms of Malassezia dermatitis in cats can vary, but typically they include:
- Skin redness
- Flaking
- Oily skin surface
- Unpleasant smell
- itching
Affected areas may include the ears, skin around the eyes, paws, armpits, and abdomen.
Causes in cats
The causes of Malassezia dermatitis in cats are similar to those in dogs and may include:
- Allergies (e.g. food allergies, atopic dermatitis)
- Immune system disorders
- Hormonal disorders
- Congenital skin diseases
Diagnosis and treatment in cats
Diagnosis of Malassezia dermatitis in cats is similar to that in dogs, through clinical examination and microscopic examination of skin samples. However, treatment for cats may differ from that for dogs because cats may be more sensitive to some medications.
Treatment for Malassezia dermatitis in cats may include:
- Antifungal shampoos or sprays
- Antifungal medications in tablet form or as a topical treatment
- Treating the underlying causes, e.g. B. Allergies or hormonal disorders
Prevention in cats
To reduce the risk of Malassezia dermatitis in cats, pet owners should pay attention to the following preventative measures:
- Regular grooming and skin cleaning
- Control allergies with hypoallergenic food or medication
- Treating underlying medical conditions that may increase the risk of Malassezia dermatitis
- Regular veterinary visits to monitor your cat's health
Although Malassezia dermatitis is less common in cats than dogs, it is important to recognize and treat this condition appropriately. Early diagnosis, treatment of underlying causes, and appropriate prevention measures can minimize the risk of Malassezia dermatitis in cats.
Frequently asked questions about Malassezia dermatitis - FAQs:
What is Malassezia Dermatitis?
Malassezia dermatitis is a skin condition caused by an excessive proliferation of Malassezia yeasts on the surface of the skin. These yeasts are normally harmless inhabitants of the skin flora, but can lead to infection under certain conditions, such as a weakened immune system or skin barrier. Typical symptoms include skin redness, flaking, oily skin surface, unpleasant odor and itching.
How is Malassezia dermatitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Malassezia dermatitis is based on clinical examination and microscopic examination of skin samples to detect the yeast fungi. A veterinarian may also perform tests to identify underlying causes that may have contributed to the development of Malassezia dermatitis, such as allergies, hormonal imbalances, or other skin conditions.
How is Malassezia dermatitis treated?
Treatment for Malassezia dermatitis involves the use of antifungal medications, which can be administered either in tablet form, as a shampoo, or as a topical treatment. Ear drops with appropriate active ingredients can be used for ear infections. In addition to treating the yeast infection, it is important to treat the underlying cause to prevent the condition from recurring.
How can I prevent Malassezia dermatitis in my pet?
To reduce your pet's risk of Malassezia dermatitis, practice good skin and coat care, make regular veterinary visits to monitor health, and watch for signs of skin problems. It is also important to strengthen your pet's immune system through a balanced diet and regular vaccinations and deworming. For animals prone to allergies or other skin conditions, additional measures should be taken to treat or control the underlying causes.
Conclusion
Malassezia dermatitis is a common skin disease in animals caused by an overgrowth of yeast fungi. Treatment requires identifying and controlling the underlying causes and using antifungal medications. Careful care, working with your veterinarian , and adjusting the environment can reduce the risk of recurring infections. The prognosis for animals with Malassezia dermatitis is generally good, especially if the underlying causes are successfully treated.
Current research on Malassezia dermatitis
Malassezia dermatitis is an important topic in veterinary research. Scientists and veterinarians are continually working to develop a better understanding of the causes, diagnosis and treatment of this condition. Some of the most current research areas are:
1. Genetics of Malassezia yeasts
Researching the genetics of Malassezia yeast helps to better understand the different species and strains of these fungi. By studying the genetic differences between different Malassezia species, scientists may be able to develop new treatment approaches and better understand why some animals are more susceptible to these infections than others.
2. Immune response in Malassezia dermatitis
The role of the immune system in the development and progression of Malassezia dermatitis is another important area of research. Studies are investigating how the immune system reacts to Malassezia yeasts and what factors contribute to the immune system not responding adequately to the yeasts in some animals. This research can help develop new therapeutic approaches to strengthen the immune system and improve defense mechanisms against Malassezia yeasts.
3. New therapy options
The development of new treatment options for Malassezia dermatitis is another important research goal. Scientists are studying new antifungal drugs and their effectiveness against Malassezia yeasts, as well as possible side effects and interactions with other medications. Research into new therapeutic approaches can help make the treatment of Malassezia dermatitis more effective and safer.
4. Prevention and management
Research into the prevention and management of Malassezia dermatitis is another important area to improve the quality of life of affected animals. Studies are examining how pet owners and veterinarians can best work together to identify risk factors for Malassezia dermatitis and take appropriate prevention and control measures. This includes examinations for optimal coat and skin care, controlling allergens and strengthening the immune system.
Continuing research into Malassezia dermatitis is helping to advance the understanding of this condition and develop new diagnostic and treatment options that improve the well-being of affected animals.
Current literature on Malassezia dermatitis
Here are some current literature references on Malassezia dermatitis:
- Gaitanis G, Magiatis P, Hantschke M, Bassukas ID, Velegraki A. The Malassezia genus in skin and systemic diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25(1):106-141. doi:10.1128/CMR.00021-11
- Gupta AK, Batra R, Bluhm R, Boekhout T, Dawson TL Jr. Skin diseases associated with Malassezia species. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51(5):785-798. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.12.034
- Prohic A, Jovovic Sadikovic T, Krupalija-Fazlic M, Kuskunovic-Vlahovljak S. Malassezia species in healthy skin and in dermatological conditions. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55(5):494-504. doi:10.1111/ijd.13165
- Rudramurthy SM, Honnavar P, Chakrabarti A, et al. Association of Malassezia species with dandruff. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2016;34(1):61-64. doi:10.4103/0255-0857.174104
- Nenoff P, Krüger C, Ginter-Hanselmayer G, et al. Mycology - an update part 2: dermatomycoses: clinical picture and diagnostics. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2014;12(9):749-777. doi:10.1111/ddg.12481
Please note that research is constantly evolving and there may be other current studies that have been published in the meantime. It can be helpful to search for additional articles in medical databases such as PubMed to stay up to date with the latest research.