Mouse Diseases: Your Guide to Identifying and Treating Diseases in Mice
Mice are adorable and popular pets whose care and health are of great importance. In this article, we want to give you a comprehensive overview of the most common diseases that can affect mice and how to recognize and treat them. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to ensure the well-being of your furry friends.
Signs of health: How to recognize a vital and happy mouse
Mice are charming creatures that, when healthy, can bring a lot of joy. Observing your mice is the first step to ensuring they are in great health. In this section, we will focus on the physical and behavioral indicators that indicate good health.
1. Active and curious behavior
Healthy mice are naturally curious and active. They enjoy exploring their surroundings, climbing, running and interacting with other mice as well as the people around them.
2. Shiny and clean coat
Shiny, clean and well-groomed fur is a strong indication of a mouse's health. The coat should be free of dandruff, bald spots or parasites.
3. Clear and bright eyes
The eyes of a healthy mouse should be clear, bright, and free of discharge. Watery or sticky eyes can indicate a possible health problem.
4. Clean ears and nose
The ears and nose should be clean and free of discharge. Look for any signs of redness or swelling, as these may indicate an infection.
5. Good feed and water intake
A healthy mouse should show good eating behavior and drink regularly. Watch for sudden changes in appetite or drinking behavior.
6. Regular bowel movements
The feces of a healthy mouse should be firm and well-formed. Diarrhea or constipation can be signs of health problems.
7. Normal weight and good body condition
A well-fed and not overweight mouse is usually healthy. It is advisable to check your mice's weight regularly to ensure that it is within the normal range.
8. Freedom from parasites
Check your mice regularly for signs of parasitic infestation, such as fleas, mites or lice. A parasite infestation can significantly affect the health of your mice.
9. Smooth breathing
Pay attention to your mice's breathing. It should be quiet and steady, with no wheezing, whistling or other noticeable noises.
10. Healthy skin and good muscle tone
The skin should be elastic and without redness, swelling or abscesses. Good muscle tone is also a sign of health and vitality.
11. Active interaction and sociable behavior
Mice are sociable animals and should enjoy interacting with their fellow mice. Healthy mice exhibit normal social behavior and are not aggressive or overly anxious.
(C) https://www.msdvetmanual.com/all-other-pets/mice/diseases-and-disorders-of-mice
Mouse diseases, treatment and prevention
Mice are magical companions, but like all pets, they can be exposed to various diseases. This guide is intended to give you a comprehensive understanding of the major mouse diseases, their treatment options and prevention measures.
1. Diarrhea (diarrhea) - mice diseases
Causes:
Diarrhea in mice can be caused by bacterial infections, viruses, parasites or disturbed intestinal flora.
Treatment:
Treatment may include antibiotics, antiparasitics, or other medications, depending on the cause of the diarrhea. A visit to the vet is essential to diagnose the exact cause and begin appropriate treatment.
Prevention:
Good hygiene, a balanced diet, and avoiding stressful situations can help prevent diarrhea in mice.
2. Respiratory diseases - mice diseases
Causes:
Common causes are infections caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi, as well as allergies or poor housing conditions.
Treatment:
Treatment may include antibiotics or antifungals. Adequate ventilation and clean housing environment are crucial for recovery.
Prevention:
Good ventilation, clean conditions and avoiding drafts and extreme temperature changes can prevent respiratory diseases.
3. Fungal skin infections - mouse diseases
Causes:
Fungal spores in the environment or from other animals can cause fungal skin infections.
Treatment:
Antifungal medications, both topical and oral, are the main treatment. A veterinarian should be consulted.
Prevention:
Regular cleaning and disinfection of the housing environment can reduce the risk of fungal skin infections.
4. Ulcerative dermatitis - mice diseases
Causes:
Causes can be allergies, parasite infestation or bacterial infections.
Treatment:
Treatment includes cleaning and disinfection of the affected areas, possibly accompanied by antibiotics or antiparasitic medications.
Prevention:
Good hygiene and regular checks for parasites can help prevent ulcerative dermatitis.
5. Parasitic infestation - mouse diseases
Causes:
Parasites can be transmitted through contact with infected animals or contaminated surfaces.
Treatment:
Antiparasitic drugs are the main treatment. An accurate diagnosis from a veterinarian is crucial.
Prevention:
Good hygiene, regular parasite checks and treatments can help prevent parasite infestations.
Combat injuries in mice
Mice are social animals, but like many animals, fights and arguments can occur among them, especially if they live in an environment that is perceived as stressful or if there are too many mice in a small room. Here is a comprehensive description of the battle injuries that can occur in mice and how to treat and prevent them.
1. Types of combat injuries
Bites and scratches:
These are the most common battle injuries in mice. They can vary from small scratches to deeper bite wounds.
Abscesses:
If a bite wound becomes infected, an abscess may form that is filled with pus and requires medical attention.
Hair loss:
Mice can tear out each other's fur during an argument, resulting in bald patches.
2. Treatment of combat injuries
Veterinary care:
If you have serious injuries or signs of infection, you should definitely see a veterinarian. He can clean the wounds, stitch them if necessary, and prescribe antibiotics.
Home remedies:
For minor injuries, antiseptic solutions can be used to clean the wounds. It is important to keep the wound clean and free of infection.
3. Prevention of combat injuries
Group size and environment:
Avoid overcrowding and ensure your mice have enough space to minimize stress and aggression.
Social adjustment:
Incorporate new mice into the group slowly and under supervision to reduce the likelihood of fights.
Providing hiding places and toys:
Provide enough hiding places and toys to keep your mice occupied and less likely to exhibit aggressive behavior.
Health monitoring:
Regular health checks can help detect early on any illnesses or conditions that could be affecting your mice's behavior.
Conclusion combat injuries
Combat injuries in mice can pose serious health problems and often require veterinary attention. By understanding the causes and proactively monitoring your mice's health and behavior, you can minimize the risk of battle injuries and create a safe, comfortable environment for your furry friends.
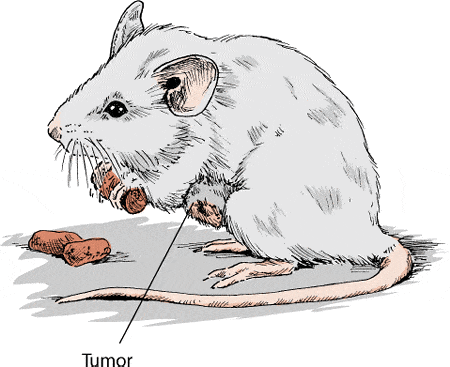
Mammary tumors in mice - mouse diseases
Mammary tumors, also known as mammary tumors, are a common health complaint in mice, particularly older female mice. These tumors can be benign or malignant. Here is a comprehensive overview of mammary tumors in mice, their diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
1. Detection of mammary tumors
Palpable masses:
You may notice a change in your mouse's breast region, often these are palpable masses or swellings along the mouse's milk ridges.
Changes in behavior:
Mice in pain or discomfort may become lethargic or show changes in their eating or drinking behavior.
External changes:
Skin redness, ulcers, or unusual discharge from the nipple can also be signs of breast tumors.
2. diagnosis
Veterinary examination:
A veterinarian can determine the type of tumor through a physical examination and possibly an ultrasound or biopsy.
3. Treatment
Surgical removal:
The most common treatment for mammary tumors in mice is surgical removal of the tumor. The earlier the tumor is discovered and removed, the better the chances of recovery.
Medical therapy:
In some cases, medications may be given to control tumor growth or relieve symptoms.
4. Prevention
Good diet and exercise:
A balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of breast cancer.
Early castration:
Early castration of female mice can significantly reduce the risk of mammary tumors.
Conclusion mammary tumors in mice
Mammary tumors in mice can pose serious health problems, but with early detection and appropriate veterinary care, the chances of recovery can be greatly improved. Good prevention, including a healthy diet and early castration, can reduce the risk of mammary tumors and contribute to the health and longevity of your mice. If you have any signs or symptoms that could indicate a mammary tumor, it is essential to consult a veterinarian immediately.
Age-related diseases in mice - mouse diseases
Mice have a relatively short life expectancy, and various health problems can arise as they age. Here is a detailed overview of some age-related diseases that mice can face, as well as their diagnosis, treatment, and possible preventive measures.
1. arthritis
Description:
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints that is common in older mice. It can cause pain and stiffness.
Symptoms:
Difficulty moving, limping, and reduced activity can be signs of arthritis.
Treatment:
Pain management through medications and supplements that promote joint health can help.
2. Cardiovascular diseases
Description:
As mice age, they can develop heart problems that can significantly impact their quality of life.
Symptoms:
Shortness of breath, reduced activity and weakness can indicate heart problems.
Treatment:
Medication to support heart function and regular veterinary monitoring are crucial.
3. Tumors and cancer
Description:
Older mice are more susceptible to developing tumors, including mammary tumors and other cancers.
Symptoms:
Palpable masses, weight loss, and behavioral changes may be signs of tumors.
Treatment:
Surgical removal and medication may be possible treatment options.
4. Kidney and liver diseases
Description:
The function of the kidneys and liver can decline with age, which can lead to various health problems.
Symptoms:
Weight loss, loss of appetite, and increased thirst can be symptoms of kidney or liver problems.
Treatment:
Diet changes and drug treatments can help relieve symptoms and support organ function.
5. Dental problems
Description:
Tooth overgrowth and tooth loss can occur in older mice, making eating difficult.
Symptoms:
Difficulty chewing, weight loss, and drooling can indicate dental problems.
Treatment:
Regular dental exams and dietary adjustments can help manage dental problems.
6. Cataracts and vision problems
Description:
Cataracts and other vision problems can occur in older mice, affecting their ability to see their surroundings clearly.
Symptoms:
Cloudy eyes and difficulty navigating can be signs of vision problems.
Treatment:
While there is no cure, environmental adjustments can help maintain your mouse's quality of life.
Conclusion age-related mouse diseases
Age-related diseases in mice can be challenging, but with proper care, regular veterinary exams, and environmental adjustments, you can help ensure your mouse lives a comfortable, healthy life as it ages. If there are any signs of health problems, it is important to consult a veterinarian in a timely manner for correct diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of mouse diseases
Mice are small but robust animals. However, when they do become ill, the symptoms can sometimes be subtle. Early detection of disease symptoms can be crucial to providing necessary care and treatment. Here are some signs and symptoms that may indicate your mouse is sick:
1. Changed behavior
Lethargy:
If your mouse is less active than usual or sleeps a lot, it could be a sign of illness.
Aggression or withdrawal:
A sick mouse may either become withdrawn or behave unusually aggressively toward other mice or people.
2. External signs
Coat condition:
A shaggy, dull or unkempt coat can be a sign of illness. Healthy mice have shiny, smooth fur.
Skin problems:
Skin irritations, abscesses, redness, or swelling may indicate skin infections or other medical conditions.
Eyes and nose:
Sticky, watery or sore eyes as well as a runny or stuffy nose are often signs of an infection.
3. Breathing
Breathing sounds:
Whistling, wheezing, or other unusual breathing sounds may indicate respiratory problems.
Rapid breathing:
An increased breathing rate can be a sign of stress or illness.
4. Eating and drinking behavior
Loss of appetite:
If your mouse suddenly stops eating or drinking, it could be a sign of a serious health problem.
Excessive drinking:
A sudden increase in thirst can be a sign of diabetes or other health problems.
5. Excretions
Diarrhea or constipation:
Changes in bowel movements, especially persistent diarrhea or constipation, can indicate serious health problems.
Urine color and consistency:
Changes in the color or consistency of urine can also indicate health problems.
6. Weight loss
Sudden or consistent weight loss can signal a serious health problem and should definitely be examined by a veterinarian.
7. Coordination and movement
Limping or difficulty moving:
If your mouse is limping or having difficulty moving, it could indicate an injury or neurological disease.
Tremors or convulsions:
Tremors, weakness, or convulsions may indicate serious health problems and require immediate veterinary evaluation.
Summary of symptoms of mouse diseases
Observing your mouse and knowing its normal behavior and appearance is crucial to detecting signs of disease early. If you experience one or more of the above symptoms, you should consult a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Your attentive care can help maintain your mouse's well-being and provide him with a better quality of life.
Transmissible diseases from mice to other animals or humans
Mice are adorable little creatures, but like many animals, they can carry pathogens that are potentially transmittable to other animals or people. Below is a list and description of the diseases that can be transmitted by mice:
1. Hantaviruses
Description:
Hantaviruses can be transmitted to humans through contact with mouse feces, urine or saliva. They can cause serious illnesses such as Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), which is a serious respiratory illness.
Prevention:
Avoid contact with mice and thoroughly clean areas where mice may live. Wear gloves and masks when cleaning areas where mice have been active.
2. Salmonella
Description:
Salmonella can be transmitted through contact with contaminated mouse feces. The infection can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, fever and abdominal cramps.
Prevention:
Good hygiene practices, such as washing hands thoroughly and cleaning surfaces, can help reduce the risk of Salmonella infection.
3. Rickettsial pox
Description:
Rickettsial pox is transmitted through a mite bite, and mice are often host animals for these mites. Symptoms can include fever, headache and a rash.
Prevention:
Controlling mice and mites in your environment and avoiding areas where mice are active can help reduce the risk of rickettsial pox infection.
4. Leptospirosis
Description:
Leptospirosis is caused by bacteria that can be spread through the urine of infected animals such as mice. People can become infected when they come into contact with contaminated water or soil.
Prevention:
Avoid contact with mouse urine and wear gloves and other protective clothing when handling mice or entering potentially contaminated areas.
5. Rat Bite Fever
Description:
Rat-bite fever can be transmitted through the bite or scratch of an infected mouse or through contact with an infected animal's saliva while eating or drinking.
Prevention:
Avoid contact with mice, especially if you are unsure whether they are healthy. If you must handle mice, wear gloves and other protective clothing.
Conclusion Transmissibility of mouse diseases
Although mice can be lovely companions, it is important to be aware of the health risks they can pose to humans and other animals. With proper preventive measures and some understanding of the potential illnesses, you can protect yourself and your loved ones while enjoying the company of your furry friends. If disease transmission is suspected, it is advisable to seek medical or veterinary attention immediately.
Summary of mouse diseases
Mouse diseases can present with a variety of symptoms and it is essential to detect these early to enable adequate treatment. The range of mouse diseases ranges from diarrhea and respiratory diseases to skin problems and parasite infestation. Not only can mouse diseases affect the health of your furry friends, but they can also sometimes be transmitted to humans and other animals.
Some mouse diseases, such as those caused by hantaviruses or salmonella, can cause serious health problems in humans. Early detection of mouse diseases by observing behavioral changes, loss of appetite, changes in fur condition or breathing problems is crucial.
A regular veterinary examination can help identify mouse diseases early and create appropriate treatment plans. Treatment for mouse diseases can range from antibiotics to antiparasitics to special diets and environmental changes, depending on the type of mouse diseases.
Prevention of mouse diseases through good hygiene, regular cleaning and a balanced diet is also important to minimize the risk of mouse diseases. By better understanding mouse diseases and their symptoms, you can actively contribute to the health and prosperity of your mice and build better relationships with your furry companions.
Awareness of the possible routes of transmission of mouse diseases to humans is also crucial to protecting both your family and your animals from the potential risks of mouse diseases.
- Mouse Diseases: Your Guide to Identifying and Treating Diseases in Mice
- Signs of health: How to recognize a vital and happy mouse
- Mouse diseases, treatment and prevention
- Combat injuries in mice
- Mammary tumors in mice - mouse diseases
- Age-related diseases in mice - mouse diseases
- Symptoms of mouse diseases
- Transmissible diseases from mice to other animals or humans
- Summary of mouse diseases
