- Ovarian Cysts in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
- Introduction
- What are ovarian cysts in guinea pigs?
- Symptoms & Signs of Ovarian Cysts in Guinea Pigs
- Diagnosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
- Differential diagnosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
- Treatment of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
- What is the prognosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs?
- Are there breed-specific clusters?
- Can you prevent ovarian cysts in guinea pigs?
- Summary Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
Ovarian Cysts in Guinea Pigs: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Ovarian cysts are a common disease in guinea pigs caused by hormonal imbalances. In this article, we provide a comprehensive overview of the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for ovarian cysts in guinea pigs.
What are ovarian cysts in guinea pigs?
Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs are a relatively common health disorder caused by hormonal irregularities and require special attention. These cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in the ovaries of guinea pigs. They can be of different sizes and vary in their activity in terms of hormone production.
Causes and development of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
The exact cause of ovarian cyst development in guinea pigs is not yet fully understood. However, it is believed that hormonal imbalances play a central role. A key component is the inadequate release of luteinizing hormone (LH) by the adenohypophysis, a part of the pituitary gland. This hormonal dysregulation causes the normal processes in the ovary to be disrupted, causing the follicles to fail to rupture as they should and instead turn into cysts.
Types of Ovarian Cysts in Guinea Pigs
There are mainly two types of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs:
- Follicular cysts : They form when the Graafian follicles fail to rupture. These cysts are usually filled with a clear fluid.
- Lutein cysts : They develop from corpus luteum structures and may be more hormonally active than follicular cysts.
Symptoms & Signs of Ovarian Cysts in Guinea Pigs
Of course, it is important to know exactly the symptoms and signs of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs in order to take appropriate measures in a timely manner. Here is a comprehensive overview of the different symptoms:
1. Visible changes to the body structure:
- Abdominal enlargement : One of the most noticeable signs of ovarian cysts is an increase in abdominal circumference. This may be due to the size of the cysts that fill the abdominal cavity.
- Weight changes : Despite having an enlarged abdomen, guinea pigs can lose weight because the cysts can affect other organs.
2. Changes in coat condition:
- Alopecia (hair loss) : Hormonally active cysts can cause uneven or extensive hair loss, especially on the sides and back.
3. Behavioral changes:
- Hypersexual Behavior : Some guinea pigs exhibit increased sexual interest or behavior due to the hormonal imbalances.
- Lethargy or restlessness : Changes in behavior such as increased lethargy or, conversely, restlessness can also be indicators of the presence of ovarian cysts.
4. Health problems:
- Sterility : Ovarian cysts can affect fertility, which can lead to infertility.
- Uterine changes : These include endometrial hyperplasia (thickening of the lining of the uterus) and, in some cases, neoplasia (abnormal growth of tissue).
- Bone marrow suppression : In some guinea pigs, ovarian cysts can impair the function of the bone marrow, which can lead to various blood count changes.
5. Indigestion:
- Changes in eating behavior : Although guinea pigs continue to eat, they are no longer able to eat as much food due to the mass taken up by the cysts, which can lead to weight loss.
- Digestive problems : Digestive disorders may occur due to the displacement of the intestinal organs by the cysts.
Diagnosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
Diagnosing ovarian cysts in guinea pigs requires a detailed examination that varies depending on the type of cyst. Here is a comprehensive overview of the diagnostic methods, differentiated according to the different types of cysts:
1. Diagnosis of follicular cysts
Follicular cysts are the most common type of ovarian cyst in guinea pigs and occur when Graafian follicles fail to rupture and fill with fluid.
Investigation methods:
- Palpation : Careful palpation of the abdominal cavity may lead to the identification of enlarged, fluid-filled structures.
- Ultrasound : An ultrasound scan provides a detailed view of the ovaries and can help clearly identify the cysts. Follicular cysts appear as clear, fluid-filled sacs.
- Blood tests : Hormonal tests can help identify the presence of hormonal imbalances associated with follicular cysts.
2. Diagnosis of lutein cysts
Lutein cysts arise from the corpus luteum and are often more hormonally active than follicular cysts. They can have a greater impact on the guinea pig's behavior and overall health.
Investigation methods:
- Ultrasound : Ultrasound is also a key technique here. Lutein cysts may have a different echotexture than follicular cysts, which may help in differentiation.
- Hormonal blood tests : Because lutein cysts often show increased hormonal activity, blood tests for hormones such as estrogen and progesterone can be informative.
3. Further diagnostic procedures
In addition to the specific diagnostics depending on the type of cyst, there are also general methods that are used to diagnose ovarian cysts:
- X-rays : They can be useful for examining the effects of large cysts on other abdominal organs.
- Biopsy : In rare cases, a biopsy may be necessary to differentiate between cystic and neoplastic (tumor-like) changes.
Importance of early detection
Early diagnosis is crucial to initiate appropriate treatment and maintain the guinea pig's quality of life. If you suspect ovarian cysts, you should consult veterinarian
Diagnosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs involves a combination of clinical examination, imaging, and laboratory tests. The exact approach depends on the type of cysts. Early and accurate diagnosis is the key to successful treatment and the animal's well-being.
Differential diagnosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
When making the differential diagnosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs, it is important to consider other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. Here is an overview of possible differential diagnoses and how they can be distinguished from ovarian cysts:
1. Gastrointestinal disorders
- Symptoms : Digestive problems, changes in eating behavior, weight loss.
- Differentiation : Gastrointestinal disorders usually do not cause enlargement of the ovaries. Imaging procedures such as X-rays or ultrasound can contribute to the diagnosis.
2. Tumors or neoplasms
- Symptoms : abdominal swelling, behavioral changes, sometimes hair loss.
- Differentiation : The type of growth and the structure of the mass are different in tumors than in cysts. Imaging procedures and biopsies are crucial for diagnosis.
3. Ascites (abdominal dropsy)
- Symptoms : swelling of the abdomen, possibly difficulty breathing.
- Differentiation : Ascites causes a fluid-filled abdominal cavity, in contrast to the solid or semi-solid masses of ovarian cysts. Ultrasound examinations are very helpful here.
4. Kidney or bladder problems
- Symptoms : Changes in urination, feeling unwell, possibly visible changes in the abdominal region.
- Differentiation : The location and type of symptoms can help distinguish kidney or bladder problems from ovarian cysts. Ultrasound and urinalysis are useful in such cases.
5. Hormonal disorders
- Symptoms : Behavioral changes, changes in coat condition.
- Differentiation : Hormonal testing can help differentiate between primary hormonal disorders and those caused by ovarian cysts.
Importance of thorough examination
It is important that a veterinarian perform a thorough examination to make the correct diagnosis. This may require a combination of different diagnostic methods, including physical examination, imaging, and laboratory tests.
Differential diagnosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs is an important step in ruling out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. An accurate diagnosis is crucial to ensure effective treatment and ensure the guinea pig's well-being.
Treatment of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
Treatment for ovarian cysts in guinea pigs varies depending on the type and severity of the cysts. Here is a comprehensive explanation of the treatment options:
1. Treatment of follicular cysts
Follicular cysts are fluid-filled cysts that arise from unfertilized follicles.
Treatment options:
- Drug therapy : Hormonal treatments may be used to regulate ovarian function and prevent further cysts from growing.
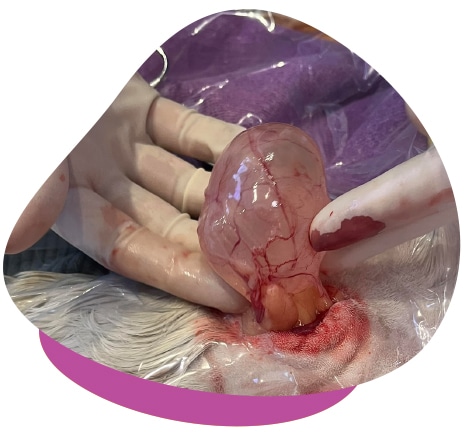
- Surgical removal : In severe cases, surgical removal of the cysts may be necessary. This is especially the case if the cysts are large and affecting the animal.
- Supportive care : A balanced diet and stress reduction can help improve the animal's well-being.
2. Treatment of lutein cysts
Lutein cysts tend to be more hormonally active and can be more challenging.
Treatment options:
- Hormone therapy : Special hormone preparations can be used to reduce the hormonal activity of the cysts.
- Surgical removal : As with follicular cysts, surgery may be necessary, especially if the cysts lead to serious health problems.
- Monitoring and management : Regular veterinary checks are important to monitor the development of the cysts and adjust treatment accordingly.
3. General treatment approaches
Regardless of the type of cysts, there are some general treatment approaches that can be used for guinea pigs with ovarian cysts:
- Pain management : Pain medications may be given to relieve discomfort.
- Nutritional management : A healthy, balanced diet is important to strengthen the immune system and support the animal's well-being.
- Regular monitoring : Regular veterinary examinations are crucial to monitor the animal's health and adjust treatment if necessary.
Importance of individualized treatment
Each guinea pig is unique and therefore treatment should be tailored to the specific needs and health status of the individual animal. Working closely with a veterinarian is essential to develop the best treatment strategy.
Treating ovarian cysts in guinea pigs requires a differentiated approach that takes into account the type of cysts, the severity of symptoms, and the individual needs of the animal. A combination of medical and supportive measures can effectively promote the health and well-being of the guinea pig.
When do the cysts need to be operated on?
The decision to surgically remove ovarian cysts in guinea pigs depends on various factors. Here are some important considerations to take into account when deciding to have surgery:
1. Size and type of cysts:
- Large cysts : When the cysts are so large that they interfere with the guinea pig's daily life, for example by putting pressure on other organs.
- Hormonally active cysts : Cysts that exhibit significant hormonal activity, causing serious health problems.
2. Symptoms and health status:
- Severe Discomfort : When the guinea pig is obviously in pain or severe discomfort.
- Impairment of quality of life : If the animal's quality of life is significantly impaired by the cysts, e.g. through behavioral changes or unwillingness to eat.
3. Response to other treatments:
- When drug treatments or other non-surgical measures are unsuccessful or do not provide relief from symptoms.
4. Risks of surgery:
- Health suitability for surgery : The guinea pig's general health must be good enough to tolerate anesthesia and surgery.
- Risk-benefit assessment : The potential risks of surgery must be carefully weighed against the possible benefits.
5. Veterinarian's recommendation:
- Close consultation with the veterinarian is crucial. The veterinarian can make a professional recommendation based on the examination and the animal's medical history.
The decision to operate on ovarian cysts in guinea pigs should be made individually and in close consultation with a qualified veterinarian. It depends on the size and type of cysts, the animal's health and symptoms, and response to other forms of treatment. Careful consideration of the risks and benefits is essential.
What is the prognosis of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs?
The prognosis for guinea pigs with ovarian cysts depends on several factors, including the type and size of the cysts, the timing of diagnosis, and the treatment method chosen. Here is an overview of the various aspects of the forecast:
1. Early detection and treatment
- Favorable prognosis : When ovarian cysts are detected and treated early, the prognosis is often favorable. Early intervention can prevent disease progression and improve the animal's quality of life.
- Importance of Regular Checkups : Regular veterinary exams are crucial for early detection of ovarian cysts.
2. Type and size of cysts
- Minor Cysts : Smaller cysts, especially those that do not cause significant hormonal changes, can often be well managed.
- Large or hormonally active cysts : These usually require more intensive treatment and the prognosis depends on the animal's response to treatment.
3. Treatment approach
- Drug treatment : In animals that respond well to hormonal therapies, the prognosis is often positive.
- Surgical procedures : Surgical removal of cysts can provide a permanent solution, but like any surgical procedure, it carries certain risks.
4. General health of the animal
- Good general health : Guinea pigs that are otherwise healthy tend to have a better prognosis.
- Comorbidities : Existing health problems may affect the prognosis and require more comprehensive treatment.
5. Long-term monitoring and care
- Regular monitoring : Continuous monitoring by a veterinarian is important to monitor the animal's health and respond to changes.
- Species-appropriate housing and care : Good care, including a balanced diet and a stress-free environment, supports the well-being of the guinea pig.
The prognosis for guinea pigs with ovarian cysts can vary, but with early and appropriate treatment and regular veterinary monitoring, a positive outcome is often possible. The individual needs and health status of the animal play a decisive role in the prognosis.
Are there breed-specific clusters?
Regarding ovarian cysts in guinea pigs, there is currently no clear evidence that certain breeds show an increased susceptibility to this disease. Ovarian cysts appear to occur equally in guinea pigs of different breeds. However, it is important to note that genetic factors may play a role, meaning that a higher prevalence could occur in some lines or families of guinea pigs.
The development of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs is more related to other factors such as age, hormonal imbalances and possibly environmental conditions. For example, older females are more susceptible to this disease.
It is always advisable to pay attention to the individual health of each guinea pig, regardless of their breed. Regular health checks and careful observation of behavioral and physical changes are crucial for early detection and treatment of ovarian cysts. If you have any concerns about your guinea pig's health, it is always a good idea to consult a veterinarian.
Can you prevent ovarian cysts in guinea pigs?
Preventing ovarian cysts in guinea pigs can be challenging because the exact causes are often not fully understood. However, there are some general guidelines that can help minimize risk and promote your guinea pigs' overall well-being:
1. Species-appropriate posture and stress reduction:
- Social interaction : Guinea pigs are social animals and need contact with other animals.
- Appropriate environment : A spacious, clean and safe living space helps reduce stress.
2. Balanced nutrition:
- Healthy diet : A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports the immune system and overall health.
- Sufficient hay and fresh water : These staple foods are essential for the health of guinea pigs.
3. Regular health checks:
- Veterinary checks : Regular checkups by a veterinarian can help detect health problems early.
- Introspection : Watch for signs of discomfort or behavioral changes in your animals.
4. Early castration:
- Some breeders and veterinarians are discussing early castration of female guinea pigs as a preventative measure against ovarian cysts. However, this should always be done in consultation with an experienced veterinarian.
5. Pay attention to genetic factors:
- Since genetic predispositions can play a role, breeding selection should be carried out carefully.
While there is no guaranteed method for preventing ovarian cysts in guinea pigs, species-appropriate housing, a healthy diet, regular health checks, and stress management can minimize the risk and promote the animals' overall well-being. Working closely with a veterinarian is also important to discuss individual prevention strategies.
Summary Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs
Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs are a common condition caused by hormonal imbalances. Early detection of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs is crucial for effective treatment. When it comes to ovarian cysts in guinea pigs, there are different types, mainly follicular cysts and lutein cysts. Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs can cause a variety of symptoms, such as abdominal swelling and behavioral changes. Diagnosing ovarian cysts in guinea pigs usually requires a combination of physical examination and imaging tests.
Treatment for ovarian cysts in guinea pigs depends on the type and severity of the cysts. Hormonal therapy may be necessary for ovarian cysts in guinea pigs, particularly lutein cysts. Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs can also be removed surgically in some cases. Proper care and regular veterinary checkups are important for guinea pigs with ovarian cysts.
The prognosis for guinea pigs with ovarian cysts depends on various factors. Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs can be treated effectively if detected early. Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs often require long-term monitoring and management. A balanced diet and a stress-free environment are beneficial for guinea pigs with ovarian cysts.
Overall, awareness of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs is critical to the health and well-being of these animals. Regularly checking for signs of ovarian cysts in guinea pigs and working closely with the veterinarian can help improve the affected animals' quality of life. Ovarian cysts in guinea pigs are a serious condition, but are manageable with appropriate treatment and care.
