- Mediterranean Diseases in Dogs: Prevention, Symptoms and Treatment
- Introduction
- What are Mediterranean diseases in dogs?
- Occurrence of these Mediterranean diseases in dogs
- Symptoms of Mediterranean Diseases in Dogs
- Diagnosis of Mediterranean Diseases in Dogs
- Treating Mediterranean Diseases in Dogs
- Prognosis for individual Mediterranean diseases in dogs
- How to prevent Mediterranean diseases in dogs?
- Can Mediterranean diseases in dogs be transmitted to people or other animals?
- Summary of Mediterranean diseases in dogs
Mediterranean Diseases in Dogs: Prevention, Symptoms and Treatment
Introduction
Mediterranean diseases in dogs are a growing health risk, not only in southern countries, but increasingly in Germany too. These diseases, caused by parasites such as ticks and mosquitoes, can cause serious health problems in dogs. In this article you will learn everything about the prevention, symptoms and treatment of these diseases.
What are Mediterranean diseases in dogs?
Mediterranean diseases include various diseases that are mainly transmitted by parasites such as mosquitoes and ticks. The most famous include:
1. Babesiosis (canine malaria)
Babesiosis, often referred to as canine malaria, is caused by the parasite Babesia canis, which is transmitted primarily by ticks. This disease affects the dog's red blood cells, causing symptoms such as fever, pale mucous membranes, jaundice, dark-colored urine and anemia. If left untreated, babesiosis can be fatal, but if detected early and treated with special antiparasitic drugs, the chances of recovery are good.
2. Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is caused by the bacterium Ehrlichia and is a tick-borne disease. The bacteria infect the white blood cells and can cause symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, vomiting, swelling of the lymph nodes, nosebleeds and weight loss. Treatment usually involves long-term antibiotic therapy. Effective tick protection is the best prevention.
3. Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is caused by the parasite Leishmania and is transmitted through the bite of infected sand flies. This disease affects various organs, including the liver, spleen and bone marrow. Typical symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, skin lesions, excessive claw growth, weight loss and hair loss around the eyes. There is no cure for leishmaniasis, but it can be controlled with medication. As a preventive measure, protection against mosquito bites is crucial.
4. Dirofilariasis (heartworm disease)
Dirofilariasis, caused by the heartworm Dirofilaria immitis, is transmitted through mosquito bites. The larvae migrate into the blood vessels and eventually into the dog's heart, where they can grow into adult worms. Symptoms include shortness of breath, chronic cough, weight loss and dysfunction of the heart and other organs. In severe cases, surgical removal of the worms may be necessary. Regular deworming and mosquito repellent have a preventative effect.
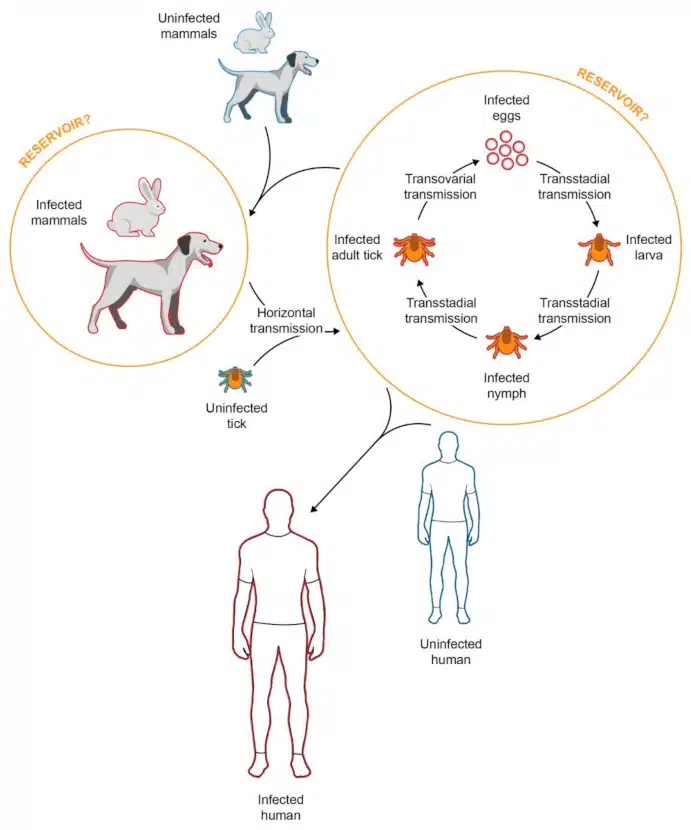
(C) https://www.mdpi.com/2414-6366/6/4/172
Occurrence of these Mediterranean diseases in dogs
1. Babesiosis (canine malaria)
Babesiosis is particularly widespread in southern European countries, but can also be found in some areas of Central and Eastern Europe:
- Southern Europe : Italy, Spain, Greece and Portugal have a high distribution.
- Eastern Europe : It is also known to occur in countries such as Hungary and Romania.
- Central and Northern Europe : In recent years there have been increasing cases in Germany, France and even some Scandinavian countries.
2. Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis also occurs mainly in warm, Mediterranean regions, but has also spread to other parts of Europe:
- Mediterranean : Countries such as Italy, Spain and Greece.
- Expansion of the distribution area : With the spread of the brown dog tick, also in countries such as Germany and France.
3. Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is typical of the Mediterranean region, but there are also reports of cases in areas further north:
- Classic distribution areas : Greece, Italy, Spain, Portugal and Turkey.
- More northern regions : In recent years there has been an increase in cases in southern France and other parts of Europe, possibly due to climatic changes and the increasing mobility of dogs.
4. Dirofilariasis (heartworm disease)
Dirofilariasis is a disease that originally comes from warmer climates, but is increasingly occurring in temperate areas:
- Southern Europe : High distribution in countries such as Italy, Spain and Greece.
- Northern and Central Europe : Increasing cases in Germany, France and even some parts of the Netherlands and Switzerland.
Important to know
The occurrence of these diseases is no longer limited to the classic Mediterranean regions. Due to global warming and the increasing travel activity of pets, the pathogens and their vectors (ticks, mosquitoes) are increasingly spreading to northern regions of Europe. Therefore, it is important to learn about the risks in your specific place of residence or travel destination and take appropriate precautions.
Symptoms of Mediterranean Diseases in Dogs
Symptoms of the individual Mediterranean diseases in dogs:
1. Babesiosis (canine malaria)
Babesiosis, often referred to as canine malaria, is caused by the parasite Babesia canis and presents with the following symptoms:
- Fever : A sudden increase in temperature is one of the first signs.
- Pallor of the mucous membranes : This indicates anemia (anemia).
- Dark colored urine : Due to destruction of red blood cells.
- Jaundice : Yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Loss of appetite and fatigue : General weakness and lack of interest in activities.
2. Ehrlichiosis
Tick-borne Ehrlichiosis causes a variety of symptoms including:
- Fever and general malaise : Often the first sign of infection.
- Swelling of the lymph nodes : especially in the neck area.
- Shortness of breath and cough : Due to the infection of the lungs.
- Bleeding tendency : Like nosebleeds, due to the impairment of blood platelets.
- Weight loss and vomiting : A sign of advanced disease.
3. Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis, transmitted by sand flies, has a variety of symptoms depending on which organs are affected:
- Skin changes : Ulcers, dry skin and hair loss, especially around the eyes.
- Swollen lymph nodes : Often one of the first signs.
- Weight loss despite normal appetite : Due to the impairment of the internal organs.
- Excessive Claw Growth : A unique symptom of this disease.
- Lameness or pain in joints : Due to inflammation.
4. Dirofilariasis (heartworm disease)
Dirofilariasis, caused by heartworm, often only becomes apparent in advanced stages with symptoms such as:
- Chronic cough : Especially after exertion.
- breath : Difficulty breathing due to heart and lung damage.
- Weakness and lethargy : Due to reduced blood circulation.
- Weight loss : Even with normal eating behavior.
- Collapse : In severe cases when the heart is severely compromised.
Important to know
Symptoms can vary and are not always immediately noticeable. Some dogs show only mild symptoms or no symptoms at all until the disease is well advanced. Therefore, regular prevention and protection against parasites such as ticks and mosquitoes is essential. If any of these diseases are suspected, a veterinarian be consulted immediately as early diagnosis and treatment can be life-saving.
Diagnosis of Mediterranean Diseases in Dogs
The diagnostic methods for the different Mediterranean diseases that can affect dogs:
1. Diagnosis of Babesiosis (Canine Malaria)
Babesiosis is most often diagnosed through blood tests. This involves looking for the pathogen, Babesia canis, in the blood:
- Blood smear : This looks for Babesia parasites in the red blood cells under the microscope.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) test : This method is very accurate and can detect Babesia DNA in the blood.
- Serology tests : These tests look for antibodies to Babesia in the dog's blood.
2. Diagnosis of Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is also primarily diagnosed through blood tests:
- Complete blood count (CBC) : This looks for signs of infection, such as low blood platelet counts or anemia.
- Serology tests : These tests detect antibodies against the Ehrlichia bacterium.
- PCR test : This test can specifically detect Ehrlichia DNA in the dog's blood.
3. Diagnosis of leishmaniasis
Diagnosing leishmaniasis can be complex because it affects a variety of organs:
- Serology tests : These tests look for antibodies to Leishmania.
- Bone marrow or lymph node biopsy : This involves taking tissue samples and examining them microscopically for Leishmania parasites.
- PCR test : Again, a PCR test can be used to identify the DNA of the Leishmania parasite.
4. Diagnosis of Dirofilariasis (Heartworm Disease)
Dirofilariasis is most often diagnosed through tests that specifically look for heartworms:
- Antigen tests : These blood tests look for antigens produced by adult female heartworms.
- Microfilaria test : This looks for heartworm larvae in the blood.
- X-ray and ultrasound : These imaging tests can be used to confirm the presence of heartworms in the heart and pulmonary arteries.
Important to note
If you suspect any of these diseases, it is important to act quickly and get veterinarian Many of these tests require specialized laboratory facilities and expertise. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to your dog's health and well-being.
Treating Mediterranean Diseases in Dogs
The treatment methods for the different Mediterranean diseases that can affect dogs.
1. Treatment of Babesiosis (Canine Malaria)
When it comes to babesiosis, rapid and targeted treatment is crucial:
- Antiparasitic medications : Medications such as imidocarb dipropionate are used to combat the Babesia parasites.
- Supportive care : Fluid therapy and blood transfusions may be necessary, especially in severe cases of anemia.
- Other medications : Anti-inflammatory medications or medications to support liver function are also sometimes given.
2. Treatment of Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is usually treated with antibiotics:
- Antibiotics : Doxycycline is the most commonly used antibiotic and is usually given over several weeks.
- Supportive treatment : Depending on the severity of symptoms, additional support such as fluid therapy or anti-inflammatory medications may be necessary.
3. Treatment of leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis requires comprehensive and long-term treatment:
- Antiparasitic medications : Medications such as allopurinol and miltefosine are used to reduce the parasite burden.
- Supportive care : Depending on the organs affected, additional medications or nutritional supplements may be necessary.
- Long-term treatment : Leishmaniasis often requires lifelong treatment and regular follow-up.
4. Treating Dirofilariasis (Heartworm Disease)
Treatment of dirofilariasis depends on the stage of the disease:
- Drug treatment : Drugs such as melarsomine are used to kill adult worms. This treatment must be carefully monitored.
- Supportive therapy : Cardiac medications, anti-inflammatory medications, and rest are important to prevent complications during treatment.
- Prevention of new infections : Monthly preventative medications are necessary to prevent new infections.
Important to know
Each of these diseases requires individualized treatment tailored to your dog's specific condition and needs. Early detection and treatment are crucial for treatment success. Regular check-ups at the vet and preventative measures against parasites are also of great importance to protect your dog's health and prevent the spread of these diseases.
Prognosis for individual Mediterranean diseases in dogs
1. Prognosis for babesiosis (canine malaria)
The prognosis for dogs suffering from babesiosis depends heavily on the time of diagnosis and when treatment begins:
- Early detection and treatment : With early detection and adequate treatment, the prognosis is usually good.
- Late diagnosis : If diagnosed late, especially if severe anemia has already occurred, the prognosis may be worse.
2. Prognosis for Ehrlichiosis
The prognosis for Ehrlichiosis varies depending on the stage of the disease and the dog's general health:
- Acute phase : In the acute phase, the prognosis is usually positive if treated promptly.
- Chronic phase : As the disease progresses into a chronic phase, treatment may become more difficult and the prognosis becomes more cautious.
3. Prognosis for leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis can be a very serious disease, and the prognosis depends on various factors:
- Early diagnosis and treatment : With early diagnosis and consistent treatment, the dog's quality of life can often be well maintained.
- Advanced cases : If the disease is advanced, particularly if major organs are affected, the prognosis may be less favorable.
4. Prognosis for dirofilariasis (heartworm disease)
The prognosis for dogs with dirofilariasis depends heavily on the extent of the infestation and the stage of the disease:
- Mild to moderate infection : For mild to moderate infection, the prognosis after treatment is usually good.
- Severe infection : If the infestation is severe, particularly if the heart and lungs are affected, the prognosis can be serious.
Important to note
For all of these diseases, early detection and treatment is crucial for a better prognosis. Regular veterinary checks and preventive measures against parasites are therefore essential. Additionally, at the first signs of illness, it is important to consult a veterinarian immediately to discuss the best treatment options and improve the dog's prognosis.
How to prevent Mediterranean diseases in dogs?
Explaining the preventative measures for each Mediterranean disease is very important to best protect your dog.
1. Prevention of Babesiosis (Canine Malaria)
Babesiosis is transmitted by ticks, so effective tick protection is crucial:
- Regular use of tick repellents : Spot-on preparations, collars, or oral medications that kill or repel ticks.
- Checking and removing ticks : Regular coat checks and prompt removal of ticks reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoiding risk areas : Areas with a high tick density should be avoided if possible.
2. Prevention of Ehrlichiosis
Since Ehrlichiosis is also transmitted by ticks, measures similar to those for babesiosis are effective:
- Effective tick protection : Use of preparations that specifically work against the vector tick.
- Regular coat checks : Daily checks of fur and skin for ticks, especially after walks in nature.
- Design of the living area : Avoid tall grass and piles of leaves near the living area to keep ticks away.
3. Prevention of leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is transmitted by sand flies, so protection against mosquito bites is crucial:
- Mosquito repellents : Spot-on preparations or collars that repel mosquitoes.
- Avoiding Mosquito Peaks and Areas : Use caution especially in the evening hours and in areas with high mosquito populations.
- Protective measures in the house : Use fly screens and avoid open windows in the evenings.
4. Prevention of Dirofilariasis (Heartworm Disease)
Dirofilariasis requires regular prevention because the disease is serious:
- Monthly preventive medications : These medications kill the larval stages of the heartworm, preventing it from developing into the adult form.
- Annual heartworm testing : Regular testing at the vet to ensure early detection.
- Mosquito repellent : Since dirofilariasis is transmitted by mosquitoes, mosquito repellents are also helpful.
General tips
- Regular veterinary examinations : Regular check-ups at the vet help to detect and treat parasite infestations at an early stage.
- Awareness and information : Educate yourself about the risks and signs of these diseases, especially if you are traveling to high-risk areas or adopting a dog from these areas.
By combining these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of infection with these diseases and preserve the health of your faithful companion.
Can Mediterranean diseases in dogs be transmitted to people or other animals?
1. Babesiosis (canine malaria)
- Transmission to other animals : Babesiosis can be transmitted to other dogs and, in some cases, cats, usually through tick bites.
- Transmission to humans : Transmission of babesiosis to humans is rare but possible, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. However, the strain that infects dogs is usually not the same one that infects humans.
2. Ehrlichiosis
- Transmission to other animals : Other pets such as cats can also contract Ehrlichiosis, although this is less common than in dogs.
- Transmission to humans : There are human forms of Ehrlichiosis that can be transmitted by the same ticks. However, the specific pathogen strains usually differ between dogs and humans.
3. Leishmaniasis
- Transmission to other animals : Leishmaniasis can also affect cats and, in rare cases, other animals. However, dogs are the main hosts.
- Transmission to humans : Humans can also become infected with leishmaniasis, particularly in regions where the disease is endemic. However, transmission does not occur directly from dog to person, but rather through the bite of infected sand flies.
4. Dirofilariasis (heartworm disease)
- Transmission to other animals : Dirofilariasis mainly affects dogs, but can also occur in cats, foxes and, in rare cases, humans.
- Transmission to humans : Cases of dirofilariasis in humans are rare and usually only occur when an infected mosquito bites a human rather than a dog. The disease is usually less severe in humans than in dogs.
Important to note
Although the risk of direct transmission of these diseases from dogs to humans is typically low, it is important to educate yourself about the risks in your area and take preventive measures for both your pets and yourself, especially in areas in which these diseases are widespread. Good protection against ticks and mosquitoes is of great importance for both your pet's health and your own health.
Summary of Mediterranean diseases in dogs
Mediterranean diseases in dogs are a group of diseases that are particularly widespread in the Mediterranean regions, but are also increasingly occurring in other parts of Europe. These Mediterranean diseases in dogs include babesiosis, Ehrlichiosis, Leishmaniasis and Dirofilariasis. Mediterranean diseases in dogs are typically transmitted by vectors such as ticks and mosquitoes. Mediterranean diseases in dogs can present with different symptoms depending on the disease. The diagnosis of Mediterranean diseases in dogs is usually done through special blood tests that target specific pathogens.
When treating Mediterranean diseases in dogs, a combination of drug therapy and supportive care is often necessary. Mediterranean diseases in dogs often require long-term treatment, especially for chronic diseases such as leishmaniasis. Prevention of Mediterranean diseases in dogs primarily involves protection against tick and mosquito bites. Mediterranean diseases in dogs can also be transmitted to humans in some cases, although this is relatively rare and requires specific conditions.
Mediterranean diseases in dogs are endemic in many countries around the Mediterranean, but are spreading due to climatic changes and pet mobility. Mediterranean diseases in dogs represent a significant health risk that should be taken seriously and actively managed. The best protection against Mediterranean diseases in dogs is to take preventative measures and have regular veterinary checks. Mediterranean diseases in dogs can be well managed with timely diagnosis and treatment to maintain the dog's quality of life and health.
Mediterranean diseases in dogs are an important aspect of animal health that concerns both pet owners and veterinarians. The increasing prevalence of Mediterranean diseases in dogs requires increased attention and knowledge of these diseases among dog owners. In conclusion, Mediterranean diseases in dogs is a complex issue that requires comprehensive understanding and active prevention.
