- Basic information about hamster diseases
- Causes of hamster diseases
- Prevent and treat hamster diseases
- 16 typical hamster diseases - causes, symptoms & treatment
- Graphical summary of hamster diseases
- Which hamster diseases are contagious to whom?
- How do sick hamsters behave?
- How do I recognize parasites in hamsters?
- How do you recognize mites in hamsters?
- Summary of hamster diseases
Basic information about hamster diseases
Hamsters are adorable little creatures, but they can also be susceptible to various diseases. Some common illnesses that can affect hamsters are colds, diarrhea, skin diseases and tumors. Healthy living and disease prevention can be promoted through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a clean, safe home.
- Colds: Hamsters can catch colds very easily. It is therefore important to avoid drafts, cold and wet conditions and to provide them with a warm, dry place to live.
- Diarrhea: Diarrhea can occur in hamsters due to improper diet or infections. It is important to provide them with fresh and clean water and a balanced and healthy diet to avoid this.
- Skin diseases: Hamsters can suffer from various skin diseases, such as fungal infections or parasites. Regularly cleaning the cage and monitoring for signs of skin problems can help prevent skin diseases.
- Tumors: Older hamsters can develop tumors. Early detection through regular health checks can help improve treatment options.
It is always advisable to consult a veterinarian . Regular checkups can also help identify and treat potential health problems early. Make sure your little friend always has access to fresh water and healthy food, and make sure his environment is clean and safe. This means your hamster can live a long, happy and healthy life!
Causes of hamster diseases
Hamsters can get sick for a variety of reasons, and it's important to be aware of the causes to keep them as healthy as possible. Here are some detailed causes of hamster diseases:
1. Unfavorable environmental conditions:
Hamsters are sensitive to extreme temperatures and drafts. Cold and damp conditions can lead to colds and respiratory illnesses. A clean, dry and draft-free cage is essential.
2. Poor nutrition:
An unbalanced diet can lead to various health problems such as diarrhea, obesity and nutritional deficiencies. A balanced diet with enough protein, vitamins and minerals is important.
3. Stress:
Stress can be caused by insufficient sleep, loud noises, or other animals and can weaken the immune system, making hamsters more susceptible to illness.
4. Bacterial and Viral Infections:
Bacteria and viruses can be transmitted through contaminated food, water or contact with sick animals, which can lead to a variety of illnesses.
5. Parasites:
Mites, fleas and other parasites can cause skin diseases and itching. Regular cleaning of the cage and a clean environment can help prevent parasite infestation.
6. Tumors and cancers:
These can be triggered by genetic predisposition or environmental factors. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
7. Dental problems:
Hamsters' teeth grow continuously. If not worn properly, they can cause feeding problems.
8. Age and Genetics:
Older hamsters or those with genetic predispositions may be more susceptible to certain diseases.
To avoid illness, it is important to pay attention to the hamster's needs, keep his home clean, provide him with a balanced diet, and perform regular health checks. veterinarian be consulted immediately Here's how you can help your hamster live a long and healthy life!
Prevent and treat hamster diseases
It is extremely important to both prevent and effectively treat hamster diseases to ensure our little friend lives a happy and healthy life. Here are some tips on how to prevent and treat illness:
Disease prevention:
- Balanced diet: Offer your hamster a varied and balanced diet with fresh fruit, vegetables, high-quality hamster food and sufficient fresh water.
- Clean cage: Keep the cage clean to reduce the risk of infections. Change bedding and hay regularly and remove leftover fresh food every day.
- Stress reduction: Avoid loud noises, sudden movements and other stressors. A quiet, safe environment is important for your hamster's well-being.
- Regular vet visits: Regular health checks can help detect and treat illnesses early.
- Exercise and activity: Make sure your hamster gets enough exercise and doesn't get bored to avoid obesity and behavior problems.
Treatment of diseases:
- Veterinary care: veterinary care immediately . Early diagnosis and treatment can be crucial.
- Medication: Your veterinarian may prescribe medications to treat infections, parasites, or other conditions.
- Supportive Care: In some cases, your hamster may need additional care, such as extra warmth or special food, to help him recover.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, such as tumors, surgical intervention may be necessary.
- Adjusting Living Conditions: You may need to adjust your hamster's environment to prevent further illness, for example by eliminating drafts or adjusting its diet.
Remember to always monitor your little friend's needs and watch for any signs of illness or discomfort. With love, care and attention you can help your hamster live a long, healthy and happy life!
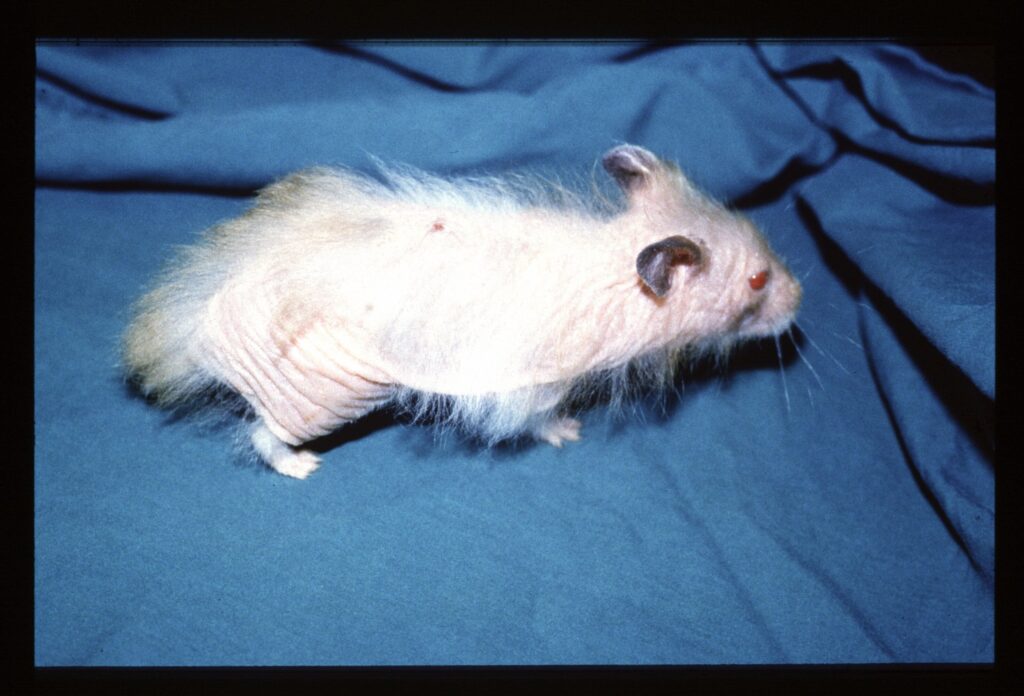
(C) https://www.veterinary-practice.com/article/demodicosis-in-the-hamster
16 typical hamster diseases - causes, symptoms & treatment
Here are 16 typical hamster diseases with their respective causes, symptoms and treatment options:
1. Colds:
- Causes: drafts, temperature fluctuations, moisture
- Symptoms: sneezing, nasal discharge, apathy
- Treatment: Warmth, rest, veterinary advice
2. Diarrhea:
- Causes: Wrong diet, bacteria, stress
- Symptoms: Loose stools, loss of appetite, abdominal pain
- Treatment: Rehydration, diet, medication as determined by a veterinarian
3. Wet Tail:
- Causes: stress, bacteria
- Symptoms: Wet around tail area, diarrhea, loss of appetite
- Treatment: Antibiotics, painkillers, plenty of fluids
4. Abscesses:
- Causes: Bacterial infections, injuries
- Symptoms: swelling, pus
- Treatment: Antibiotics, surgical opening and cleaning of the abscesses
5. Tumors:
- Causes: Genetic predisposition, age
- Symptoms: lumps, weight loss, behavioral changes
- Treatment: Surgery, Medication, Supportive Care
6. Dental problems:
- Causes: Insufficient abrasion, malnutrition
- Symptoms: Longer teeth, weight loss, salivation
- Treatment: teeth correction, adjustment of diet
7. Diabetes:
- Causes: genetics, nutrition
- Symptoms: Frequent drinking and urination, weight loss
- Treatment: Diet adjustment, insulin, blood sugar monitoring
8. Skin diseases:
- Causes: parasites, allergies, fungal infections
- Symptoms: itching, skin redness, hair loss
- Treatment: medication, environmental management, skin care
9. Heart diseases:
- Causes: age, genetics
- Symptoms: shortness of breath, weakness, weight loss
- Treatment: medication, diet adjustment, regular check-ups
10. Respiratory infections:
- Causes: bacteria, viruses, dust
- Symptoms: sneezing, shortness of breath, nasal discharge
- Treatment: Antibiotics, painkillers, clean environment
11. Heatstroke:
- Causes: Overheating, high ambient temperatures
- Symptoms: panting, apathy, collapse
- Treatment: cooling, hydration, veterinary care
12. Ear infections:
- Causes: bacteria, fungi, mites
- Symptoms: head tilt, itching, discharge
- Treatment: ear cleaning, medication, parasite control
13. Kidney problems:
- Causes: old age, infections, poisoning
- Symptoms: Increased drinking and urination, weight loss
- Treatment: Diet adjustment, medication, regular monitoring
14. Inflammation of the uterus (pyometra):
- Causes: Hormonal disorders, bacterial infections
- Symptoms: discharge, loss of appetite, weakness
- Treatment: antibiotics, surgery
15. Eye infections:
- Causes: Foreign bodies, bacteria, injuries
- Symptoms: Watery eyes, redness, pus
- Treatment: eye wash, antibiotics, eye ointments
16. Intestinal obstruction:
- Causes: Swallowing indigestible materials
- Symptoms: Constipation, bloated stomach, apathy
- Treatment: Surgery, medications to promote bowel function, fluid intake
If you suspect your hamster is sick, you should see a veterinarian as soon as possible for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. A well-informed owner and loving care can make a significant contribution to ensuring the well-being of the hamster!
Graphical summary of hamster diseases
Which hamster diseases are contagious to whom?
Some hamster diseases can be contagious, either to other hamsters or even to humans. Here are some examples:
1. Contagious to other hamsters:
- Wet Tail: Very contagious to other hamsters, especially when stressed.
- Respiratory infections: Can be easily transmitted from one hamster to another.
- Fungal infections: Transmissible through contact or shared environments.
- Parasitic infestation: Mites, fleas and other parasites can be passed between hamsters.
2. Contagious to humans:
- Salmonellosis: Some hamsters can carry salmonella in their digestive tract, which can be transmitted to humans through contact with hamster feces.
- Ringworm: This is a fungal infection that can be transmitted to humans, usually through direct skin contact.
3. Contagious to other animals:
- Parasites: Some parasites can be passed between hamsters and other pets.
Protective measures:
- Hygiene: Regular hand washing after contact with the hamster or its cage can minimize the risk of disease transmission.
- Quarantine: New hamsters should initially be kept separately to ensure they do not transmit diseases.
- Vet visits: Regular check-ups can help detect and treat illnesses early.
It is important to be aware that while some diseases are contagious, many hamster diseases are not transmittable. Good care, attention and regular veterinary visits can help minimize the risk of disease and protect the health of both hamster and owner.
How do sick hamsters behave?
A sick hamster may exhibit various behavioral changes and symptoms. Here are some things to look for to determine if your hamster might be sick:
1. Behavioral changes:
- Withdrawal: A sick hamster may spend more time hidden or in its den and be less active.
- Changed eating behavior: Reluctance to eat or reduced appetite can indicate an illness.
- Aggressiveness or Irritability: Some hamsters may become irritable or aggressive when they feel uncomfortable.
2. Physical symptoms:
- Weight loss: Sudden or steady weight loss can be a warning sign.
- Changed posture: A sick hamster may sit curled up or with fluffed fur.
- Difficulty breathing: Rapid or noisy breathing may indicate a respiratory disease.
- Changes in fur: Shaggy, sticky or lost fur can be a sign of skin diseases.
3. Changes in the cage:
- Unclean cage: If the hamster isn't keeping his cage as clean as usual, it could be a sign that he's not feeling well.
- Irregular bowel movements: Diarrhea or constipation can indicate digestive problems.
4. Miscellaneous:
- Lethargy: Lack of energy and lack of interest in your surroundings are often signs of malaise.
- Limping or difficulty moving: Could indicate injury or joint problems.
What to do:
If you are concerned that your hamster is sick, you should have him examined by a veterinarian as soon as possible. Many hamster diseases can be successfully treated if they are detected early. And of course, it's important to give your little friend lots of love and care, especially when he's not feeling well!
How do I recognize parasites in hamsters?
It can be challenging to detect parasites in a hamster because they are often small and difficult to see. However, here are some signs and symptoms that may indicate a parasite infestation:
1. Changed behavior:
- Scratching and biting: If your hamster scratches or bites itself frequently, this could be a sign of parasites.
- Restlessness and Stress: An infested hamster may be restless and show signs of stress.
- Decreased Activity: A hamster that is not feeling well may become lethargic and withdrawn.
2. Physical symptoms:
- Hair loss and skin changes: Redness, dandruff, pustules or bald spots can be signs of parasite infestation.
- Weight loss: Despite eating normally, an infested hamster may lose weight.
- Changes in feces: Diarrhea or changes in the color and consistency of feces can indicate parasites.
3. Direct visibility:
- Visible Parasites: Some parasites such as mites or fleas may be visible upon close inspection, but they are often microscopic.
What you can do:
- Visit to the vet: If you suspect parasites, you should have your hamster examined by a veterinarian to receive an accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendation.
- Hygiene: Keep the cage clean to prevent parasite infestation and remove feces and remains of fresh food every day.
- Preventive examinations: Regular checks at the vet can help detect parasites and other diseases at an early stage.
Through careful observation and regular care, you can help prevent parasites from settling in your hamster in the first place. However, if there are signs of an infestation, it is important to act quickly and seek professional advice to quickly nurse your little friend back to health!
How do you recognize mites in hamsters?
Mites are small parasites that can cause skin problems in hamsters. It's not always easy to detect a mite infestation early, but here are some clues that can help you determine whether your hamster may be affected:
1. Skin and fur changes:
- Hair loss: A typical sign of mite infestation is hair loss, especially around the eyes, ears and on the legs.
- Skin redness and flaking: The hamster's skin may appear red, inflamed, and flaky.
- Crusting: Crusts can form on the skin.
2. Changed behavior:
- Itching: A hamster with mites will scratch and bite itself frequently due to the intense itching.
- Restlessness and insomnia: The hamster may become restless and have difficulty sleeping due to the discomfort.
3. Direct visibility:
- Visible Mites: In some cases, mites or their eggs may be visible upon close inspection, especially if there is a heavy infestation.
Diagnosis and treatment:
- Veterinary Examination: If you suspect mites, you should have your hamster examined by a veterinarian as soon as possible. A swab or skin biopsy may be necessary for diagnosis.
- Drug treatment: The veterinarian may recommend appropriate treatment, such as antiparasitic medications.
Prevention:
- Cleanliness: Regular cleaning of the cage and surrounding area can help prevent mite infestations.
- Proper bedding: Use appropriate, dust-free bedding to avoid skin irritation.
- Contact with other animals: Avoid your hamster's contact with other animals that may be infected.
If you notice one or more of these symptoms in your hamster, it is important to act immediately and have your hamster examined by a veterinarian to ensure its comfort and health.
Summary of hamster diseases
Hamsters are adorable and often hardy pets, but like all animals, they can suffer from various hamster diseases. One of the most common hamster diseases is the common cold, which can be triggered by drafts, temperature fluctuations or wet conditions. It is important to pay attention to coughing, sneezing, or nasal discharge as these symptoms may indicate a cold.
Diarrhea is another of the common hamster diseases that can be caused by improper diet or bacterial infections. Acting quickly is crucial to prevent dehydration and further complications.
Wettail, one of the most serious hamster diseases, is often characterized by severe diarrhea and requires immediate veterinary attention as it can be fatal. Skin diseases caused by parasites, fungal infections or allergies are also common hamster diseases and can cause itching, redness and hair loss.
Dental problems are also common hamster diseases. Hamsters have ever-growing teeth, and if these are not worn down naturally, they can cause problems. Tumors, especially in dwarf hamsters, are unfortunately not uncommon and can pose a serious threat.
Diabetes is another of the hamster diseases that commonly occurs in dwarf hamsters. It is important to pay attention to symptoms such as increased drinking and urination. Respiratory diseases can be caused by bacteria, viruses or dust and can cause symptoms such as a runny nose and difficulty breathing.
Mite infestation is one of the itchy hamster diseases characterized by frequent scratching and skin irritation. Internal parasites can also cause various hamster diseases and should be checked through regular veterinary examinations.
Eye infections are also hamster diseases and can be caused by bacteria, injuries or foreign bodies in the eye. Ear infections are another hamster illness that are often caused by bacteria or fungi and can show signs such as tilted head.
In conclusion, early detection and treatment of hamster diseases is crucial to ensure the well-being and life expectancy of our little friends. A balanced diet, a clean environment and regular health checks are essential to prevent and treat hamster diseases.
Preventative measures such as regular cage cleaning and proper hygiene also help reduce the risk of hamster diseases. If an illness is suspected, a veterinarian should be consulted immediately for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. It is important to recognize the signs of hamster illnesses in order to act quickly and avoid possible complications. The health of our hamsters should always be our top priority to ensure they live a happy and healthy life.
