- Introduction: Relieving Joint Pain in Dogs - Pain Relievers for Dogs
- Different types of painkillers
- Importance of veterinary diagnosis
- Diagram: Treating Joint Problems in Dogs with Dog Pain Relievers
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in detail
- Opioids in detail - painkillers for dogs
- Introduction to Steroids - Pain Relievers in Dogs
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) under the microscope - painkillers in dogs
- Trocoxil: A special feature in pain therapy for dogs
- Can you give dogs medical preparations?
- How metamizole works - painkillers in dogs
- Galiprant®: An advanced alternative - painkillers for dogs
- Librela®: Revolution in pain management - painkillers for dogs
- How opioid analgesics work - painkillers in dogs
- Gabapentin and Pregabalin: How they work - Painkillers in dogs
- Phen-Pred: How it works - painkillers for dogs
- How glucocorticoids (cortisone) work - painkillers in dogs
- What should be taken into account during long-term treatment with all of the painkillers mentioned? - Painkillers for dogs
- Summary of painkillers for dogs
Introduction: Relieving Joint Pain in Dogs - Pain Relievers for Dogs
If your dog suffers from osteoarthritis or other joint problems, pain medications can play a crucial role in relieving his discomfort. Finding the right medication is essential to improving your pet's quality of life while minimizing potential side effects.
The relevance of painkillers in dogs for joint problems
Dog pain medications are often the first choice for relieving discomfort and pain in dogs with osteoarthritis and other joint diseases. Not only do they help minimize pain, but they also improve the animal's mobility and general well-being.
Different types of painkillers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are one of the most commonly prescribed types of pain relievers for dogs with joint problems. They reduce inflammation and effectively relieve pain.
Opioids - painkillers for dogs
Opioids are powerful painkillers that are prescribed for severe pain. They are generally only used for severe, chronic pain.
Steroids - pain relievers for dogs
Steroids are anti-inflammatory medications that can reduce swelling and relieve pain. However, they should only be used under close veterinary supervision as they can cause side effects.
Complementary Therapies - Pain Relievers in Dogs
Natural supplements and physical therapy treatments can also help relieve pain and discomfort. Glucosamine and chondroitin are popular supplements that can support joint health.
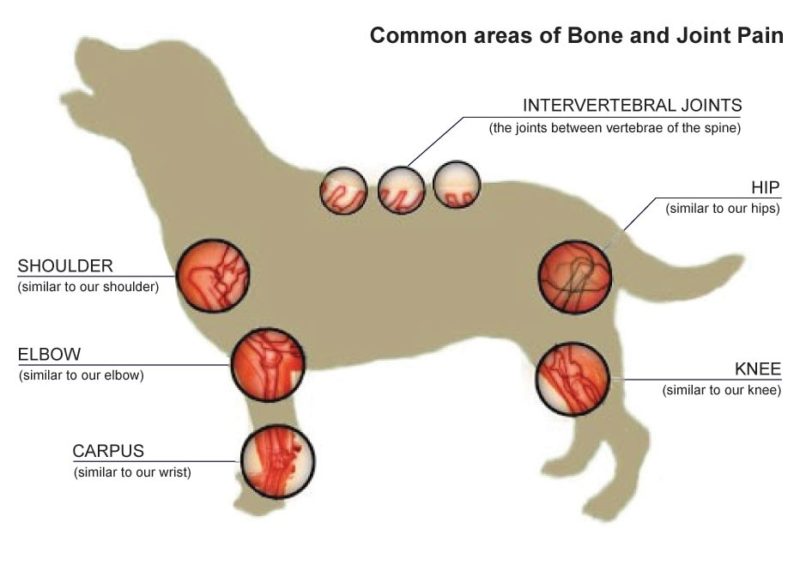
Importance of veterinary diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis from a veterinarian is essential to finding the appropriate treatment and pain medication for your dog. The veterinarian will assess the dog's health and recommend the optimal treatment option.
How does the vet determine the dog's pain level?
The veterinarian takes care to determine the dog's pain level. This includes close observation, a comprehensive clinical examination and sometimes specialized tests.
Observation and behavior analysis
First, the veterinarian observes the dog and analyzes its behavior. Dogs who experience pain often exhibit behavioral changes such as aggressiveness, withdrawal, loss of appetite, or increased panting. Changes in movement, such as limping or a stiff gait, can also indicate pain.
Clinical examination
Through a thorough clinical examination, including palpation of the body, the veterinarian can attempt to identify the exact source of the pain. Tender or swollen areas, reactions to touch and pressure help determine the location and level of pain.
Specialized tests
Sometimes additional tests such as blood tests, x-rays, or ultrasound are necessary to accurately identify the cause of the pain and to more accurately assess the pain level.
Pain scales
Some veterinarians also use specialized canine pain scales to objectively assess pain levels. These scales assess various parameters such as response to touch, mobility and general behavior to provide an assessment of pain levels.
All of these methods allow the veterinarian to make an informed diagnosis and initiate appropriate pain therapy with pain medications in dogs to ensure the dog's well-being.
Diagram: Treating Joint Problems in Dogs with Dog Pain Relievers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in detail
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, abbreviated as NSAIDs, are medications primarily used to treat pain and inflammation. They are particularly effective for conditions such as osteoarthritis in dogs, where inflammation and pain are the main complaints.
How NSAIDs work - painkillers in dogs
NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of enzymes involved in the production of pain and inflammatory mediators. This allows them to both relieve pain and reduce inflammation, making them a valuable option for dogs with joint problems.
application areas
NSAIDs are primarily used to treat chronic pain conditions such as osteoarthritis, but also for acute pain, for example after operations or injuries. Their use can significantly improve the animal's quality of life by allowing them to move with less pain.
possible side effects
Although NSAIDs are very effective, it is important to use them under veterinary supervision as they can also cause side effects. These include gastrointestinal problems such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, kidney damage and liver problems. Your veterinarian will weigh the risk of these side effects against the pain relief benefits and determine an appropriate dosage.
Dosage and administration
The dosage of NSAIDs is crucial and must be individually adapted to the respective animal. It is essential not to exceed the recommended dose and to administer the medication exactly according to the veterinarian's instructions. Overdose or improper administration may increase the risk of side effects.
Conclusion: responsible use of NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are an effective way to control pain and inflammation in dogs with joint disease. However, it is of the utmost importance to use them responsibly and under constant veterinary supervision to protect and promote the dog's health and well-being.
(C) https://tevavetclinic.co.za/2020/06/05/understanding-arthritis-in-dogs-and-cats/
Opioids in detail - painkillers for dogs
Opioids are a group of medications used to relieve severe to very severe pain. They are particularly effective and are often prescribed when other painkillers such as NSAIDs are not sufficient.
How do opioids work?
Opioids bind to specific receptors in the central nervous system and thus block pain transmission. This mode of action allows them to effectively control pain, even if it is very intense.
Areas of application in dogs
In dogs, opioids are often used after surgery or for chronic pain conditions such as cancer when other painkillers are not effective enough. They are a valuable option to improve the quality of life of dogs in severe pain.
Side effects and precautions
Like all medications, opioids also have side effects. These may include respiratory depression, sedation, constipation and vomiting. It is extremely important to use opioids only under close veterinary supervision and to closely follow the prescribed dose and administration schedule to minimize the risk of side effects and overdose.
Dosage and administration
The dosage of opioids must be precise and tailored to the individual dog. Overdoses can lead to serious health problems, so it is important to strictly follow the veterinarian's instructions.
Conclusion: Responsible use of opioids
Opioids are powerful medications that can provide effective pain relief. Your responsible use can help to significantly improve the well-being and quality of life of dogs with severe and chronic pain. However, responsible handling, strict monitoring and correct dosage are crucial to ensure the animal's safety and avoid unwanted side effects.
Introduction to Steroids - Pain Relievers in Dogs
Steroids are a diverse class of medications commonly used in veterinary medicine to treat inflammation, allergies, and certain autoimmune diseases. They can be very effective in dogs at reducing swelling and inflammation and modulating the immune system.
How do steroids work?
Steroids work by modulating the activity of certain immune system cells and molecules to reduce inflammation. They can also help suppress the immune system, preventing excessive immune reactions such as those found in autoimmune diseases.
Areas of application for dogs
Steroids are used in dogs in a variety of situations, such as to control inflammation, allergic reactions, skin conditions, and certain joint conditions such as osteoarthritis. They can also be used in the treatment of some autoimmune diseases and cancers.
possible side effects
Although steroids can be effective, they also have a high potential for side effects, especially with long-term use. These include increased thirst and urine production, weight gain, thinning of the skin, and increased risk of infection. Therefore, it is important to use steroids under close veterinary supervision and to use the lowest effective dose.
Administration and dosage
The dosage and administration of steroids must be tailored precisely to the individual dog and its health status. Overdoses and improper administration can increase the risk of side effects, so following veterinary instructions is essential.
Conclusion: Responsible use of steroids
Steroids can be very effective in treating a variety of conditions in dogs. However, their responsible and supervised use is crucial to protecting the dog's health. It is essential to use steroids only as directed and under careful veterinary observation to ensure safe and effective treatment and to minimize side effects.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) under the microscope - painkillers in dogs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are a class of medications used primarily to relieve pain and inflammation. They are particularly useful for conditions such as osteoarthritis and other inflammatory conditions. Below are some common NSAID preparations used in veterinary medicine.
1. Meloxicam
Meloxicam is a common NSAID and is often used to treat pain and inflammation in dogs. It is known for its pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory effects and has a comparatively low risk of side effects.
2. Carprofen
Carprofen is also a popular NSAID in veterinary medicine. It is often used postoperatively or for chronic pain conditions such as osteoarthritis. Carprofen offers good tolerability and effectiveness in controlling pain and inflammation.
3. Deracoxib
Deracoxib is another NSAID designed specifically for dogs. It is primarily used for postoperative pain and chronic pain conditions. It is characterized by its selective inhibition of COX-2 enzymes, which reduces the risk of side effects.
4. Firocoxib
Firocoxib is a selective NSAID used to control pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis and other painful conditions in dogs. It offers long-lasting effects and a low risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
possible side effects
While NSAIDs are very effective at controlling pain, they also have the potential for side effects, including gastrointestinal problems, kidney problems, and liver damage. Therefore, it is important to use NSAIDs only under veterinary supervision and at the recommended dose.
Conclusion: NSAIDs in veterinary medicine
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are essential medications in veterinary medicine for treating pain and inflammation in dogs. There are various preparations that can be selected depending on the condition and individual needs of the dog. Responsible use under veterinary supervision is essential to ensure the health and well-being of the animal and to minimize side effects.
Trocoxil: A special feature in pain therapy for dogs
Trocoxil is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) specifically designed to treat chronic inflammatory diseases such as osteoarthritis in dogs. What makes Trocoxil so special is its unique formulation and administration schedule.
Long lasting effect
One of the outstanding features of Trocoxil is its ability to work for a longer period of time. A single dose of Trocoxil can remain effective for up to a month, unlike other NSAIDs that must be administered daily. This is particularly beneficial for dog owners as it facilitates compliance and administration management.
Selective COX-2 inhibition
Trocoxil works by selectively inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), meaning it specifically reduces the production of inflammatory mediators without unduly affecting the gastrointestinal tract. This selective effect minimizes the risk of side effects and makes Trocoxil a safe option for long-term therapy of chronic diseases.
Controlled release
The formulation of Trocoxil allows for a controlled release of the active ingredient, which explains its long-lasting effect. This controlled release ensures that the active ingredient is gradually released into the body, maintaining a constant therapeutic concentration without putting strain on the organs.
Precautions and Administration
Trocoxil should only be administered under close veterinary supervision. It is crucial not to exceed the recommended dose and to have regular check-ups to monitor the dog's health. In this way, possible side effects can be identified and addressed at an early stage.
Conclusion: Trocoxil and its uniqueness
Trocoxil represents a specialty in pain and inflammation therapy in dogs because of its specific mode of action, controlled release and long-lasting effect. This uniqueness makes it a practical and efficient option for veterinarians and dog owners to manage chronic pain and inflammation in dogs , and thus significantly improves the quality of life of the affected animals.
Can you give dogs medical preparations?
Be careful with human medicine - painkillers for dogs
It is very important to exercise great caution when considering using human medicines on dogs. Many medications that are safe for humans can be toxic to dogs, causing serious health problems or even death.
Consultation with the veterinarian
Before giving a dog any human medicine, it is important to consult a veterinarian. The veterinarian can assess the safety and dosage of the medication and decide whether it is appropriate for the specific dog and its health condition.
Different metabolism
Dogs have different metabolisms than humans, and their bodies process medications differently. What is safe and effective for humans may be toxic for dogs. Examples include chocolate and onions, which are safe for humans but toxic to dogs.
Risks and side effects
Some human medicines can cause serious side effects in dogs, such as kidney failure, liver damage, gastrointestinal ulcers or blood clotting disorders. It is essential to be aware of and consider potential risks before administering medications that are not specifically designed for animals.
Conclusion: Veterinary advice is essential
The use of human medicinal products on dogs is risky and should only be done under strict veterinary supervision. The differences in metabolism between humans and dogs, the possible risks and side effects require professional assessment and monitoring to ensure the dog's health and well-being. If you are unsure or have any concerns, it is always best to seek the advice of a veterinarian before taking any action that could harm the dog.
How metamizole works - painkillers in dogs
Metamizole is a non-opioid pain reliever used to relieve severe pain, fever, and cramps. It works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, substances that cause inflammation, pain and fever. In addition, metamizole has antispasmodic properties, meaning it can relieve spasms.
Use on dogs
Metamizole may be used in dogs under veterinary supervision in certain cases, particularly when other pain medications are not effective or are not tolerated.
possible side effects
Although metamizole can be effective when used and dosed correctly, there are also potential side effects that can occur in dogs, including:
- Allergic reactions: These may include skin rashes, itching, or difficulty breathing.
- Gastrointestinal complaints: These include nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
- Blood count changes: There may be a reduction in the number of white blood cells (agranulocytosis) or all blood cells (pancytopenia), which increases the risk of infection.
- Kidney and liver damage: Long-term use can affect kidney and liver function.
Precautions and monitoring
Because of the potential side effects, metamizole should only be administered under close veterinary supervision and control. It is important to follow the recommended dosage closely and monitor the dog for signs of side effects. If there are any signs of intolerance or if the condition worsens, a veterinarian should be contacted immediately.
Conclusion: Use metamizole carefully
Metamizole can be an effective option for pain and seizure relief in dogs in certain situations, but it also carries risks. Careful consideration, precise dosage and regular monitoring are essential to ensure the dog's well-being and minimize risks. Whenever you use medication, especially those with potent effects and possible side effects, veterinary advice and support is essential.
Galiprant®: An advanced alternative - painkillers for dogs
Galiprant® (Grapiprant) is a relatively new drug that is considered a safe and effective alternative to classic NSAIDs. It belongs to the class of piprant antagonists and is used to treat pain and inflammation in dogs with osteoarthritis.
Mechanism of action
In contrast to conventional NSAIDs, which inhibit COX enzymes and thereby reduce the formation of prostaglandins, Galiprant® selectively blocks the prostaglandin E2 receptor (EP4). This leads to a reduction in pain and inflammation without affecting the gastrointestinal tract, kidney or liver to the extent that classic NSAIDs can.
Advantages of Galiprant®
- Gastrointestinal tolerance: Galiprant® is known for its lower negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract compared to conventional NSAIDs.
- Kidney Protection: The selective mode of action provides better protection for the kidneys, an important concern, especially in older dogs.
- Liver protection: Galiprant® is considered to be gentler on the liver compared to many classic NSAIDs.
Application and dosage
Galiprant® is available in tablet form and the dosage is based on the dog's weight. Accurate dosage and monitoring by a veterinarian are essential to ensure the dog is receiving the correct amount and to monitor for possible side effects.
possible side effects
Although Galiprant® is generally well tolerated, side effects such as vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite and lethargy may occur. It is important to monitor and report any behavioral or health changes while using Galiprant®.
Conclusion: Worth considering
For dogs suffering from osteoarthritis for which classic NSAIDs are not an option or are not well tolerated, Galiprant® may be an effective and safer alternative. It combines pain relief and anti-inflammatory properties with an improved safety profile, making it an attractive option for the long-term treatment of chronic pain conditions in dogs. Nevertheless, close veterinary supervision and advice is essential to ensure the dog's well-being and achieve the best possible treatment outcome.
Librela®: Revolution in pain management - painkillers for dogs
Librela® represents an innovative and groundbreaking solution in pain management in dogs. It is a preparation that uses monoclonal antibodies to effectively protect dogs from pain and inflammation, especially in osteoarthritis.
How Librela® works
Librela® works through the use of monoclonal antibodies that specifically block nerve growth factor (NGF). NGF is a protein that plays a central role in the development of pain. By blocking NGF, pain and inflammation can be effectively reduced without putting any strain on the organs.
Advantages and possible uses
- Targeted effect: Librela® offers precise and specific pain control that targets directly at the source of pain.
- Long-lasting effects: A single injection can last up to a month.
- Tolerability: Librela® shows a favorable safety profile and is generally well tolerated.
- Use for chronic pain: It is particularly suitable for dogs with chronic pain conditions such as osteoarthritis.
Application and veterinary supervision
Librela® is injected once a month by the veterinarian. It is important to have the treatment administered and monitored by a qualified veterinarian to ensure correct use and early detection of any side effects.
possible side effects
As with all medications, side effects may occur when using Librela®, including local injection site reactions, allergies, or other adverse reactions. It is therefore crucial to closely monitor the dog after administration and report any abnormalities to the vet.
Conclusion: A breakthrough in veterinary medicine
Librela® is an innovative and promising treatment option for dogs with chronic pain and inflammation. With its targeted and long-lasting effect, it offers an excellent alternative to conventional painkillers, especially if they do not work sufficiently or are not tolerated. As always, careful veterinary advice and care is required to meet each dog's individual needs and to optimally promote their well-being.
How opioid analgesics work - painkillers in dogs
Opioid analgesics are potent medications used to relieve moderate to severe pain. They work by binding to specific proteins called opioid receptors, which are found on the surface of nerve cells. This binding leads to the activation of receptors and alters the perception of pain in the brain and spinal cord, and can also influence the emotional response to pain.
Uses of opioids
Opioid analgesics are often used to treat acute pain, such as after surgery, or chronic pain conditions, such as cancer pain. In veterinary medicine, opioids can help animals better manage pain after surgery or chronic pain.
Possible side effects of opioids
Although opioids are effective, they also have a high risk of side effects and abuse. Here are some possible side effects of opioid analgesics:
- Respiratory depression: Slow or shallow breathing may occur, which can be potentially life-threatening.
- Constipation: Opioids can cause significant digestive problems, particularly constipation.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some animals may react to opioids with nausea and vomiting.
- Dependence and tolerance: With prolonged use, animals may develop tolerance and dependence and withdrawal symptoms may occur.
- Sedation and fatigue: Many animals become drowsy or lethargic after receiving opioids.
Important considerations when using opioids
Because of the potential risks and side effects, it is important to use opioids with caution and under close veterinary supervision. Correct dosage and regular evaluations are essential to ensure that the animal is safe and that the medication is effective.
Conclusion: An important part of pain therapy
Despite the risks, opioids remain an essential part of veterinary pain management, especially when other painkillers are not sufficient. Through careful use and monitoring, opioids can help significantly improve the well-being of animals in moderate to severe pain.
Are opioids addictive?
Yes, using opioids can actually lead to addiction. This is a very important topic, so I would like to go into it in more detail here.
Risk of dependence on opioids
Opioids have a high potential for developing addiction in both humans and animals. They act on the brain's reward system and can produce a feeling of well-being or euphoria. With repeated use, the body may adapt to the presence of the medication and tolerance may develop. This means that over time, increasingly higher doses are needed to achieve the same pain-relieving effect.
Dependence and withdrawal in animals
Animals can also develop physical dependence, and withdrawal symptoms may occur if the drug is stopped abruptly. These may include restlessness, increased sensitivity to pain, gastrointestinal problems and behavioral changes. Therefore, it is important to carefully monitor the use of opioids under veterinary supervision and, if necessary, gradually reduce the dose to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Responsible use of opioids
Responsible use of opioids involves careful consideration of the risks and benefits, careful dosing and monitoring, and close consideration of the animal's individual needs and health. Should long-term treatment with opioids be necessary, an appropriate pain management protocol must be established to protect the animal's health and well-being and to avoid dependence and overdose.
Conclusion: With consideration and care
Although opioids can effectively relieve pain, their use is not without risks. It is essential to use them with the utmost caution and only under close veterinary supervision. Awareness and understanding of the risk of addiction to opioids is the first step to using these powerful medications responsibly and ensuring the safety and well-being of our animals.
Gabapentin and Pregabalin: How they work - Painkillers in dogs
Gabapentin and pregabalin are anticonvulsants and are often used to treat neuropathic pain, epilepsy and anxiety disorders. They bind to the alpha-2-delta subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels in the central nervous system, which leads to a reduction in the release of various neurotransmitters such as glutamate. The result is a reduction in pain transmission and a calming effect on the nervous system.
Side effects of gabapentin and pregabalin
Gabapentin
- Dizziness and tiredness: These are the most common side effects and can occur especially at the start of treatment.
- Weight gain: Some patients report an increase in body weight with gabapentin treatment.
- Ataxia: This is a movement disorder that can affect coordination.
Pregabalin
- Dizziness: Similar to gabapentin, pregabalin can also cause dizziness at the beginning of therapy.
- Drowsiness: Tiredness and sleepiness may occur frequently.
- Headache and dizziness: These symptoms may occur occasionally.
Both medications can also cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and diarrhea. Because gabapentin and pregabalin affect the central nervous system, it is important not to stop treatment abruptly as this may result in withdrawal symptoms.
Application in animals
In veterinary medicine, gabapentin and pregabalin are used primarily to control chronic pain, particularly neuropathic pain. It is important to manage the administration of these medications strictly according to the veterinarian's instructions to avoid overdoses and unwanted side effects. When treating animals, regular check-ups are crucial to adjust the dose and achieve the best possible effect.
Conclusion
Gabapentin and pregabalin may play an important role in pain management, both in humans and animals, particularly in neuropathic pain. However, correct use and monitoring are crucial to ensure the well-being of the patient, whether human or animal, and to minimize side effects.
Phen-Pred: How it works - painkillers for dogs
Phen-Pred is a combination of the active ingredients phenylbutazone and prednisolone.
- Phenylbutazone is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and has anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving and antipyretic effects.
- Prednisolone is a corticosteroid and has strong anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects.
This combination can be used in dogs to treat inflammation and pain caused by various conditions such as arthritis.
Side effects of Phen-Pred
Phenylbutazone
- Gastrointestinal problems: May cause gastrointestinal irritation, including ulcers and bleeding.
- Kidney problems: Long-term use can cause kidney damage.
Prednisolone
- Immunosuppression: May weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to infections.
- Weight gain and increased thirst: May occur frequently, as can increased hunger.
- Hormonal disorders: Long-term use can lead to hormonal disorders, which can lead to symptoms such as Cushing's syndrome.
Application and monitoring
The use of Phen-Pred requires careful dosing and monitoring by the veterinarian to minimize the risk of side effects. It is important to carefully follow the dosage instructions set by the veterinarian and have regular check-ups to monitor the animal's health and adjust the dose if necessary.
Conclusion
Phen-Pred can be effective in relieving pain and inflammation in dogs, but close monitoring and veterinary attention is essential due to the potential side effects. It is crucial to immediately report any symptom that occurs to the veterinarian and to be careful and responsible when using Phen-Pred to ensure the animal's well-being and health.
How glucocorticoids (cortisone) work - painkillers in dogs
Glucocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids that act on the glucocorticoid receptor. They are known for their anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties. Here are some of the main effects of glucocorticoids:
- Anti-inflammatory: They inhibit inflammatory reactions in the body and can thus relieve swelling, redness and pain.
- Immunomodulation: They modulate and suppress the activity of the immune system, which can be useful in autoimmune diseases and allergic reactions.
- Metabolism: They influence the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in the body.
Side effects of glucocorticoids
While glucocorticoids are effective for many conditions, they can also cause a number of side effects, especially with long-term use. Here are some of the possible side effects:
- Osteoporosis: They can promote bone loss and increase the risk of fractures.
- Weight gain and fat distribution: They can lead to increased appetite and changes in fat distribution, especially on the face, neck and stomach.
- Skin changes: Thin skin, bruising and striae (stretch marks) may occur.
- Psychological effects: They can cause mood swings, sleep disorders and, in severe cases, even psychotic reactions.
- Blood sugar: They can increase blood sugar levels and increase the risk of diabetes mellitus.
Application and monitoring
Due to the potent effects and possible side effects of glucocorticoids, careful monitoring by a doctor or veterinarian is important. They are usually prescribed only when other treatment options are not effective or not tolerated, and at the lowest effective dose to minimize the risk of side effects.
Conclusion
Glucocorticoids are powerful medications with a wide range of effects and possible side effects. They play an important role in the therapy of inflammatory and immune reactions, but require precise dosage, monitoring and care by healthcare professionals to ensure the safety of the patient, be it human or animal.
What should be taken into account during long-term treatment with all of the painkillers mentioned? - Painkillers for dogs
Regular veterinary checks for painkillers in dogs
Regular veterinary monitoring is essential to accurately check the dog's health and identify possible side effects at an early stage. Blood tests and other diagnostics can help monitor the function of the liver, kidneys and other organs.
Correct dosage of painkillers for dogs
The correct dosage of medication is crucial. An overdose can lead to serious health problems. It is important to strictly adhere to the dose recommended by the veterinarian and to administer the medication as prescribed.
Observation of side effects of painkillers in dogs
Dog owners should carefully monitor their dog for signs of side effects, such as changes in behavior, loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, or yellowing of the skin or gums. If side effects are suspected, a veterinarian should be consulted immediately.
Supportive care for painkillers in dogs
A balanced diet, regular exercise and other supportive measures can help improve the dog's well-being during long-term treatment. Supplements like omega-3 fatty acids can also help reduce inflammation and support joint health.
In-depth communication with vet about pain medication for dogs
Open and regular communication between dog owner and veterinarian is important to discuss concerns, observations and possible concerns regarding treatment. This allows therapy to be customized based on the dog’s needs and response.
Conclusion: Careful monitoring and care during long-term treatment
Long-term treatment with pain medications requires careful monitoring and judicious care to minimize the risk of side effects and optimize the dog's quality of life. Regular veterinary checks, adherence to dosage recommendations, observation of possible side effects and supportive care measures are crucial for the success of long-term therapy with painkillers in dogs.
Summary of painkillers for dogs
The use of painkillers in dogs is an essential topic for every dog owner concerned about the well-being of their four-legged friend. Painkillers for dogs are needed to relieve the suffering of animals with various illnesses, such as osteoarthritis, joint problems or after operations. There are a variety of canine pain medications, each with their own mechanisms of action, benefits, and possible side effects.
One of the most common painkillers in dogs are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which inhibit the production of inflammatory substances. Dog pain relievers, such as NSAIDs, are particularly effective at reducing swelling, inflammation, and pain. However, despite their effectiveness, these painkillers can also cause gastrointestinal problems in dogs and should therefore be used with caution.
Another relevant painkiller in dogs are opioids, which are used for severe pain. These dog pain relievers act directly on the central nervous system and can provide effective pain relief when used correctly. However, because there is a risk of addiction, the administration of these painkillers to dogs is strictly monitored.
Corticosteroids, also known as steroids, are also important painkillers in dogs. They have an anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effect. Although these painkillers provide quick relief from inflammation and pain in dogs, they come with a number of possible side effects, especially with long-term use.
There are also specialized painkillers for dogs such as gabapentin and pregabalin, which are specifically used to treat neuropathic pain. Careful administration and monitoring of these pain medications in dogs are essential to avoid overdose and adverse reactions.
Metamizole is also an effective painkiller in dogs that has antipyretic and antispasmodic effects. While it is a useful pain reliever in dogs for various conditions, it should be used with caution due to potential side effects.
Innovative preparations such as Galiprant and Librela also represent interesting options for painkillers in dogs. These offer alternative mechanisms of action and may be useful in dogs that are allergic to other canine painkillers.
When using painkillers on dogs, it is important to always consider the dog's individual needs and health conditions. The selection and dosage of painkillers for dogs should always be made in consultation with a veterinarian to ensure safe and effective pain control.
It should also be noted that administering human medicine preparations as painkillers to dogs involves risks and should therefore only be done under the guidance of a veterinarian.
In conclusion, canine pain medications play an essential role in ensuring the well-being of our four-legged friends, and careful selection, use and monitoring of canine pain medications is of utmost importance to minimize the risk of side effects and complications.
In addition, regular check-ups at the vet be carried out to monitor the dog's health and, if necessary, adjust the painkiller therapy (painkillers for dogs). It is important to strictly adhere to the recommended dosage of painkillers in dogs and not to exceed the treatment duration in order to avoid possible overdoses or long-term effects with painkillers in dogs. In the event of any unwanted side effects or changes in the dog's behavior, a veterinarian should be consulted immediately. Proper use of dog pain medication can help dogs relieve pain and enjoy a better quality of life.
