- Feline osteochondrodysplasia (OCD): A review
- Introduction
- What is Osteochondrodysplasia?
- Genetic basis
- Osteochondrodysplasia in various cat breeds
- Symptoms and expression
- Diagnosis of Feline Osteochondrodysplasia (OCD)
- Differential diagnosis
- Treatment of Feline Osteochondrodysplasia (OCD)
- Preventive measures of osteochondrodysplasia in cats (OCD)
- Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about osteochondrodysplasia in cats
- Summary in cats
Feline osteochondrodysplasia (OCD): A review
Introduction
Osteochondrodysplasia, a hereditary disease that occurs in Scottish Fold cats, among others, is an important issue for cat lovers and breeders. In this article you will learn everything you need to know about this disease, its symptoms, genetic causes and possible treatment approaches.
What is Osteochondrodysplasia?
Osteochondrodysplasia (OCD) is a genetic disorder that affects bone and cartilage development. In Scottish Fold cats, this mutation results in the characteristic folded ears and various skeletal changes.
Genetic basis
The disease is caused by a mutation in the TRPV4 gene, which is normally responsible for tissue homeostasis and cell differentiation. OCD is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that inheriting a defective allele from one parent is enough to cause the disease.
The genetic basis and inheritance of osteochondrodysplasia (OCD) in cats is a fascinating but complex topic. To fully explain this, let’s delve deep into the world of genetics.
Basics of genetics
Our genetic material, DNA, consists of a long sequence of nucleotides organized in the form of genes. These genes carry the instructions for the development and function of all living things. Genetic mutations, i.e. changes in the DNA sequence, can lead to different physical and physiological characteristics or diseases.
Genetic causes of osteochondrodysplasia
Osteochondrodysplasia is a mutation in a specific gene. In cats, especially the Scottish Fold, a mutation in the TRPV4 gene is responsible. This gene plays an important role in the development and maintenance of bone and cartilage tissue.
Inheritance mode
OCD is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. This means that only one parent needs to carry the mutated gene to pass the disease on to the offspring. In genetics, "autosomal" means that the affected gene is located on one of the non-sex-linked chromosomes. “Dominant,” in turn, means that only one copy of the mutated gene (from one parent) is sufficient to cause the disease.
Consequences of dominant inheritance
When it comes to an autosomal dominant disorder like OCD, there are some important points to consider:
- High probability of inheritance : Each child of an affected cat has a 50% chance of inheriting the mutated gene and therefore developing the disease.
- Variability of expression : Even if the mutated gene is inherited, the severity of the disease can vary from animal to animal.
- No gender-specific difference : Since inheritance is autosomal, males and females are equally affected.
Importance for breeding
Knowing the mode of inheritance of OCD is particularly important for breeders. Since the disease is caused by a single mutated allele, animals carrying the mutated gene should be excluded from breeding. Genetic testing can help identify carriers of the mutated gene.
Understanding the genetic basis and inheritance of osteochondrodysplasia is crucial to minimizing the occurrence of the disease and ensuring the welfare of cats. Through responsible breeding practices and awareness of the genetic risks, breeders and cat owners can help reduce animal suffering and improve their quality of life.
Osteochondrodysplasia, a genetic disorder that primarily affects bone and cartilage development, is not limited to the Scottish fold in the animal world. It also occurs in other cat breeds, but with different manifestations and symptoms.
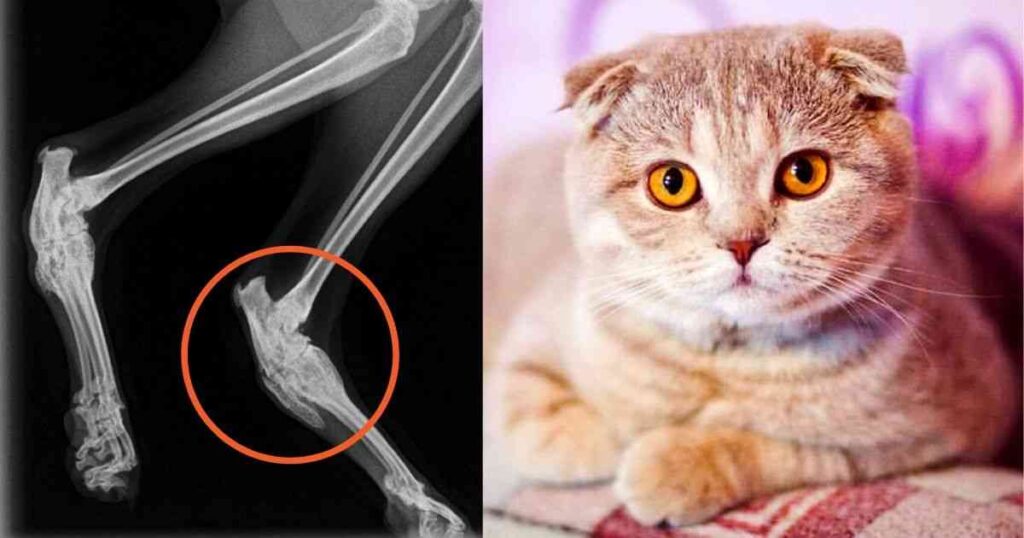
(C) https://www.walkervillevet.com.au/blog/scottish-fold-health-problems/
Osteochondrodysplasia in various cat breeds
- Maine Coon : This large and robust breed can develop a form of osteochondrodysplasia, which manifests itself as abnormal growth and structure of the bones. This can lead to joint problems and, in some cases, movement disorders.
- Devon Rex : In Devon Rex, osteochondrodysplasia can be associated with another genetic disorder, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Symptoms may include changes in bone structure, particularly in the legs and facial area.
- Munchkin : This breed is known for its short legs, a trait caused by a form of osteochondrodysplasia. For some Munchkin cats, this can cause spine and joint problems.
- Scottish Fold : The ears typical of the breed are an expression of OCD.
Symptoms and expression
Symptoms of osteochondrodysplasia can vary depending on breed. In general, the following signs can be observed:
- Deformities in the limbs
- Abnormal growth of bones
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Movement restrictions
- Skeletal deformities
The symptoms of osteochondrodysplasia (OCD) in cats are diverse and can manifest themselves in different degrees. Here I explain in detail what signs can occur with this genetic disease.
Typical symptoms of osteochondrodysplasia
- Altered bone structure : One of the most noticeable features of OCD is the altered bone and cartilage structure. This often manifests itself in deformed or abnormally grown bones.
- Folded Ears : In Scottish Folds, the breed most commonly affected by OCD, the characteristic folded ears are a direct symptom of the condition.
- Limb abnormalities : Cats with OCD often display shortened or deformed limbs. This can limit mobility and lead to an unusual gait.
- Pain and Stiffness : The abnormal bone and cartilage structures can lead to pain and stiffness in the joints, especially in the hips, shoulders and elbows.
- Restricted movement : Due to the pain and stiffness in the joints, affected cats tend to move less, which can lead to further deterioration of muscles and joint function.
- Altered spinal structure : In some cats, OCD causes a change in the structure of the spine, resulting in reduced flexibility and possibly pain.
- Lameness : In severe cases, lameness can occur, especially if the joints are severely affected.
Early detection and diagnosis
Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and the cat's well-being. Veterinarians use a combination of clinical examination, x-rays, and genetic testing to diagnose OCD.
Importance of vet visits
Regular veterinary visits are important to monitor the development of the disease and intervene early. This can help slow the progression of symptoms and improve the cat's quality of life.
Although osteochondrodysplasia is a serious and lifelong condition, early diagnosis and careful care can help significantly improve the welfare of affected cats. As a cat owner, it is important to pay attention to your pet's health and well-being and to consult a veterinarian .
Diagnosis of Feline Osteochondrodysplasia (OCD)
Diagnosing osteochondrodysplasia (OCD) in cats is a multi-step process aimed at identifying the specific symptoms and characteristics of this condition. Here I explain in detail how veterinarians typically go about diagnosing OCD in cats.
Initial observations
The diagnostic process often begins with the cat owner's observations. Behavioral changes such as reduced activity, visible stiffness when walking or signs of pain can be the first signs of an illness.
Clinical examination
If OCD is suspected, the veterinarian a thorough clinical examination. He pays particular attention to:
- Limbs and Joints : Inspect for deformity, swelling, or signs of pain.
- Mobility : Checking mobility and possible limitations.
- General Health : Assessment of the cat's general health and nutritional status.
Imaging procedures
Imaging procedures are used for a more precise diagnosis:
- X-ray : X-rays can reveal changes in the bones and joints that are typical of OCD.
- Computed tomography (CT) : CT scans provide more detailed images of bone structure and can be helpful in complex cases.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) : MRI is less commonly used but can be useful to evaluate soft tissue structures surrounding affected joints.
Genetic testing
Because OCD has a genetic cause, genetic testing can help confirm the diagnosis. These tests look for specific mutations in the cat's genome that are responsible for the disease.
Differential diagnosis
The vet will also consider other medical conditions that may cause similar symptoms, such as arthritis or other genetic conditions. This is an important step in ensuring the correct diagnosis is made and the appropriate treatment is given.
Final steps
After all examinations are completed, the veterinarian will combine the results to make a comprehensive diagnosis. This enables targeted treatment and advice for further care of the cat.
Diagnosing OCD in cats requires a combination of clinical observation, imaging tests, and genetic testing. Detecting the disease early and taking appropriate measures can help improve the cat's well-being and enable it to live as normal and pain-free a life as possible. As a cat owner, it is important to pay attention to signs of OCD and to consult a veterinarian immediately if you suspect it.
Treatment of Feline Osteochondrodysplasia (OCD)
Treating osteochondrodysplasia (OCD) in cats requires a comprehensive approach because it is a genetic disease that cannot be cured, only managed. Here I explain in detail what treatment methods are available to make the lives of cats with OCD as comfortable as possible.
Pain management
Because OCD is often associated with pain, pain management is a central part of treatment. Various methods are used here:
- Medication : Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and pain. It is important to only use these medications under veterinary supervision as they can cause side effects.
- Supplements : Dietary supplements containing glucosamine and chondroitin can have a supportive effect by helping to maintain the health of cartilage tissue.
physical therapy
Physical therapy can play an important role in maintaining mobility and reducing pain. This includes:
- Gentle exercises : Light range of motion exercises help keep the joints supple.
- Massage : Massage can help relieve tension and promote blood circulation.
- Hydrotherapy : Swimming or exercise in water offers a gentle way to strengthen muscles without putting strain on joints.
Adjustments in the home
Adjustments in the home can make it easier for a cat with OCD to move and stay active:
- Ramps and steps : Ramps and small steps help make climbing onto furniture or into the litter box easier.
- Soft berths : Soft, comfortable berths provide relief for aching joints.
- Easily accessible feeding and watering points : These should be placed so that the cat does not have to bend or stretch too much.
Surgical options
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve severe deformity or unbearable pain. However, this should be discussed individually with the veterinarian as every operation carries risks.
Supportive care
In addition to these treatment methods, loving and attentive care is crucial:
- Regular veterinary checks : Regular visits to the vet are important to monitor the cat's health and adjust treatment if necessary.
- Weight management : Excess weight can put additional stress on joints, so it's important to maintain a healthy weight.
- Emotional support : Love and care are essential for the cat's emotional well-being.
Osteochondrodysplasia in cats requires careful and comprehensive treatment to improve the quality of life of affected animals. Through a combination of medical treatment, physical therapy, home modifications, and supportive care, cat owners can help their four-legged friends live as comfortable and pain-free lives as possible.
Preventive measures of osteochondrodysplasia in cats (OCD)
Preventive measures play a critical role in preventing the spread and impact of osteochondrodysplasia (OCD) in cats. Here I go into detail about the various preventive steps that can be taken by both breeders and cat owners to minimize the risk and suffering from this genetic condition.
Responsible breeding
- Genetic testing : Breeders should perform genetic testing to identify carriers of the gene responsible for OCD. Cats that carry the mutated gene should be excluded from breeding.
- Selection of breeding partners : Careful selection of breeding partners is crucial to avoid spreading the disease. Breeders should be fully informed about the genetic history of the breeding animals.
- Education and information : Breeders should educate potential buyers about the risks of OCD and the importance of genetic testing.
For cat owners
- Conscious breed selection : Prospective buyers should be aware that certain breeds, such as the Scottish Fold, have an increased risk of OCD. Choosing a different breed may reduce the risk of developing OCD.
- Regular veterinary exams : Regular check-ups with the vet are important to detect early signs of OCD or other health problems.
- Healthy diet and exercise : A balanced diet and regular exercise contribute to the cat's overall health and can help reduce the risk of joint diseases.
- Gathering information : Educating yourself about the breed and possible health risks can help cat owners make informed decisions for the health and well-being of their animals.
General health promotion
- Weight control : Being overweight can increase the stress on the joints, increasing the risk of joint disease. It is therefore important to ensure that your cat has a healthy body weight.
- Stress reduction : A stress-free environment can promote the cat's overall health and help keep their immune system strong.
Final thoughts
Responsible actions by both breeders and cat owners can reduce the occurrence and spread of osteochondrodysplasia. The health and well-being of the cats are always our top priority. Preventive measures are an important step in minimizing cat suffering and allowing them to live a healthy and happy life.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about osteochondrodysplasia in cats
What is Feline Osteochondrodysplasia (OCD) and How to Recognize It?
Osteochondrodysplasia is a genetic disease that occurs primarily in Scottish Fold cats. It affects the development of bones and cartilage, which can lead to deformations. Typical signs include folded ears, shortened or deformed limbs, joint pain, stiffness and restricted movement. The exact diagnosis is made through clinical examinations and imaging procedures at the vet.
Can osteochondrodysplasia in cats be cured?
There is currently no cure for osteochondrodysplasia as it is a genetic disease. Treatment therefore focuses on managing symptoms to improve the cat's quality of life. This includes pain management, physical therapy, adjustments to the cat's living environment and, in some cases, surgical procedures.
How is osteochondrodysplasia inherited and can it be prevented?
OCD is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that inheriting a single mutated gene from one parent is enough to cause the disease. Prevention is possible by excluding affected animals from breeding. Genetic testing can help identify carriers of the mutated gene. Potential cat owners should research the breed and its genetic history.
What Role Does Diet Play in Treating OCD in Cats?
A balanced diet is important for the cat's overall health. For cats with OCD, a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and other anti-inflammatory nutrients can help reduce inflammation and support joint health. Obesity should be avoided as it puts additional stress on the joints.
As the owner of a cat with OCD, how can I improve their quality of life?
As an owner, you can do a lot to make the life of your cat with OCD more comfortable. This includes regular veterinary checks, an adapted diet, providing a comfortable and accessible environment (e.g. ramps, soft berths) and lots of loving attention. It is also important to pay attention to signs of pain or discomfort and, if necessary, to consult the vet early on.
Summary in cats
Feline osteochondrodysplasia is a genetic disorder that occurs primarily in Scottish Fold cats. Osteochondrodysplasia in cats affects the development of bones and cartilage, leading to deformities and joint problems. Diagnosing osteochondrodysplasia in cats requires a thorough examination by a veterinarian. Osteochondrodysplasia in cats often presents with folded ears, shortened limbs, and joint pain. A cure for osteochondrodysplasia in cats is not yet possible because it is a genetic disease. Treatment of osteochondrodysplasia in cats aims to relieve symptoms and improve the cat's quality of life.
Osteochondrodysplasia in cats is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Cats with osteochondrodysplasia require specialized care and treatment. Osteochondrodysplasia in cats can be monitored through regular veterinary checks. A balanced diet is important for cats with osteochondrodysplasia. Osteochondrodysplasia in cats often requires adjustments to the cat's living environment. Pain management is a central component in the treatment of osteochondrodysplasia in cats. Physical therapy may be helpful for cats with osteochondrodysplasia.
Osteochondrodysplasia in cats requires an understanding of the genetic basis. Osteochondrodysplasia in cats can be identified through genetic testing. When it comes to osteochondrodysplasia in cats, avoiding excess weight is important. Osteochondrodysplasia in cats can severely impact the lives of affected animals. Breeders need to be aware of the risks of osteochondrodysplasia in cats. Responsible breeding practices can reduce the incidence of osteochondrodysplasia in cats. Osteochondrodysplasia in cats presents a challenge for veterinarians and cat owners.
Education about osteochondrodysplasia in cats is important to raise awareness. Osteochondrodysplasia in cats requires lifelong care and attention. Love and care are essential for cats with osteochondrodysplasia. Overall, osteochondrodysplasia in cats requires comprehensive understanding and careful treatment to ensure the well-being of affected cats.
