- Paraphimosis in Dogs: Comprehensive Prevention and Treatment Guide
- Introduction
- What is paraphimosis?
- Causes of paraphimosis
- Breed-specific predispositions to paraphimosis
- Comprehensive explanation of the symptoms of paraphimosis
- Diagnosis of Paraphimosis in Dogs
- Differential diagnosis
- Treatment options for paraphimosis
- When to take your dog to the vet
- Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about paraphimosis in dogs
- Summary Paraphimosis in dogs
Paraphimosis in Dogs: Comprehensive Prevention and Treatment Guide
Introduction
Paraphimosis in dogs is a serious health problem that needs to be recognized and treated in a timely manner. In this article you will learn everything you need to know about this disease - from the causes and symptoms to effective treatment methods.
What is paraphimosis?
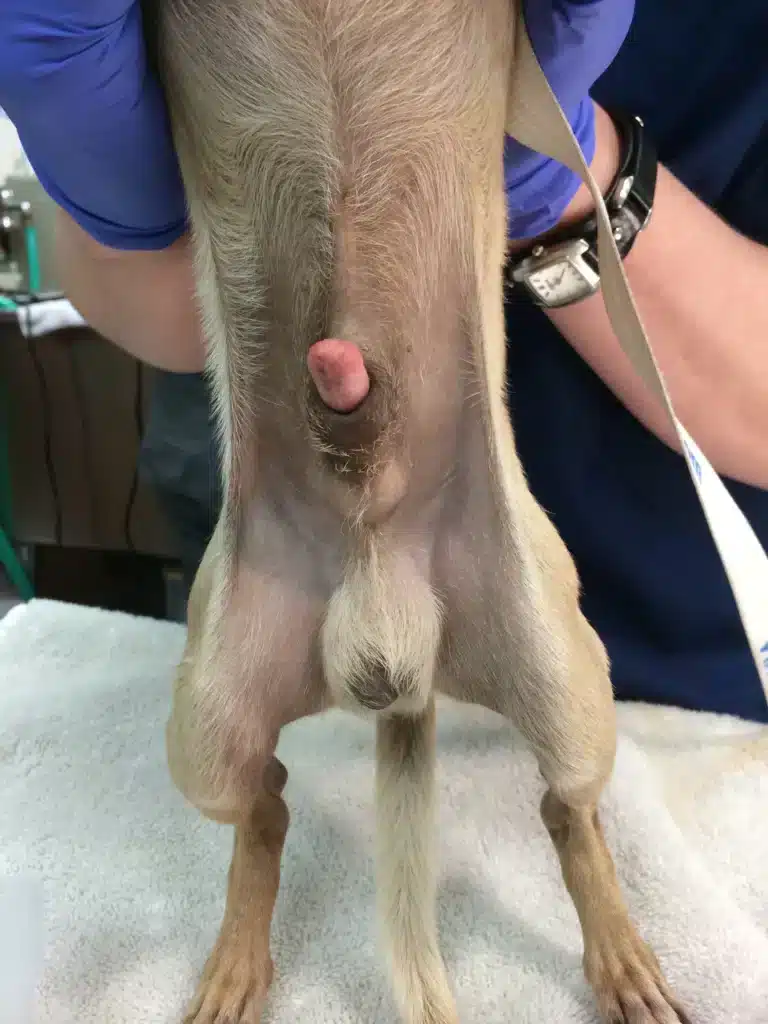
Paraphimosis is a medical condition in male dogs in which the foreskin of the penis can no longer be retracted over the glans. This causes pain, swelling and can have serious health consequences.
(C) https://tailsofasheltervet.files.wordpress.com/2014/03/photo-1.jpg
Causes of paraphimosis
Various factors can trigger paraphimosis, including:
- Anatomical peculiarities: A foreskin opening that is too narrow or a shortened foreskin.
- Traumatic events: Injuries or scarring of the penis.
- Diseases: Infections, tumors or priapism (persistent, painful erection).
Breed-specific predispositions to paraphimosis
1. Brachycephalic breeds
- Example: Pug, French Bulldog
- Reason: These breeds often have narrow preputial openings, which can increase the risk of paraphimosis.
2. Breeds with a tendency to be overweight
- Example: Labrador Retriever, Beagle
- Reason: Being overweight can put additional strain on the genital region and increase the risk of paraphimosis.
3. Small breeds
- Example: Dachshund, Chihuahua
- Reason: Anatomical peculiarities in small breeds can also lead to problems with the foreskin.
Important points for owners of predisposed breeds
- Regular checks: Pay particular attention to your dog's genital health.
- Weight Management: Keep your dog within a healthy weight range to avoid pressure on the genitals.
- Vet Advice: Discuss specific preventative measures with your veterinarian , especially if you own a susceptible breed.
Although some breeds are more susceptible to paraphimosis, any dog can experience this condition. Attentive care and regular veterinary checks are crucial to minimize risks and ensure your dog's health.
Comprehensive explanation of the symptoms of paraphimosis
1. Visible changes to the penis
- Swelling of the glans: One of the most noticeable changes is the significant swelling of the glans.
- Color change: The glans can take on a dark red to blue-purple color, indicating poor blood circulation.
2. Dog's pain reactions
- Expressions of pain: Dogs with paraphimosis often show pain reactions such as yelping, whining or licking the affected area.
- Restless behavior: Affected dogs may behave restlessly, change positions frequently, and have difficulty sitting or lying down.
3. Problems urinating
- Difficulty urinating: The dog may have difficulty urinating or may not be able to pass urine at all.
- Frequent licking: Attempts to lick the area may be a sign of difficulty urinating.
4. General behavioral changes
- Disturbed general behavior: Loss of appetite, lethargy or a general change in behavior can also be symptoms.
- Aggressive behavior: Pain-related irritability can cause the dog to react more aggressively than normal.
5. Physical changes
- Dry penile lining: Without timely treatment, the lining of the penis can dry out and lead to further complications.
Important things to do
If you see any of these symptoms, it is crucial to act quickly and veterinary attention. Early intervention can prevent serious complications and will go a long way in relieving your dog's symptoms.
Diagnosis of Paraphimosis in Dogs
Clinical examination
- Visual Inspection: A veterinarian will often begin with a thorough visual examination of the affected area.
- Palpation: The veterinarian can use palpation to determine the extent of the swelling and possible hardening.
anamnese
- History: Information about the dog's previous injuries, symptoms, and general behavior is helpful in making the diagnosis.
Further investigations
- Blood tests: May be done to detect inflammation or infection.
- Ultrasound: May be helpful in assessing the internal structure of the penis.
Differential diagnosis
Differentiation from other diseases
- Phimosis: This is where the penis cannot be pulled out of the foreskin, unlike paraphimosis where it cannot be retracted.
- Priapism: A persistent, painful erection not associated with sexual arousal.
- Penile and foreskin infections: These can cause similar symptoms such as swelling and redness.
Importance of accurate diagnosis
The correct diagnosis is crucial as it determines the treatment plan. Confusing it with other illnesses could lead to ineffective or even harmful treatment.
A comprehensive diagnosis that takes into account both clinical examinations and the dog's history is essential for the correct identification and treatment of paraphimosis. Differentiation from similar diseases through differential diagnosis is an important step in ensuring targeted and effective treatment.
Treatment options for paraphimosis
Conservative treatment methods
- Cooling compresses: Cold compresses can help reduce swelling.
- Manual reduction: Gently pushing the penis back into the foreskin, often using lubricants or local anesthetics.
- Drug therapy: Anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving medications may be administered to relieve symptoms.
Surgical interventions
- Foreskin incision: In severe cases, a surgical incision may be necessary to expand the foreskin and retract the penis.
- Phallopexy: In some cases, surgical fixation of the penis to the foreskin is performed to prevent recurrence.
- Amputation: In extreme cases where there is irreversible damage, amputation may be necessary.
Aftercare
- Regular checks: After treatment, regular veterinary checks are important to monitor the healing process.
- Home care: Keep the genital area clean and dry to avoid infection.
Preventive action
- Weight control: Being overweight can increase the risk of paraphimosis, so good weight control is important.
- Hygiene: Regular cleaning and drying of the foreskin can have a preventative effect.
Treatment for paraphimosis in dogs depends on the severity of the disease. While mild cases can often be treated with conservative methods, more severe cases may require surgical intervention. Good aftercare and preventive measures are crucial to prevent the disease from recurring and to ensure your dog's health.
When to take your dog to the vet
1. First signs of paraphimosis
- Noticeable Changes: If you notice that your dog's foreskin or penis is swollen, red or discolored, you should contact a veterinarian immediately.
- Pain reactions: If your dog shows signs of pain or discomfort in the genital area, this is a clear indication that a visit to the vet is necessary.
2. Problems urinating
- Difficulty urinating: A dog that has difficulty urinating or can no longer urinate needs urgent veterinary attention.
- Frequent licking of the genital area: This may be an indication of pain or discomfort during urination.
3. Behavioral changes
- Changed general behavior: Lethargy, loss of appetite, or general behavioral changes that indicate pain or discomfort are also reasons to see the vet.
- Aggressive or unusual behavior: If your dog is more aggressive or withdrawn than usual, it could be a sign of pain or a serious health problem.
4. Visible injuries or abnormalities
- Obvious Injuries: Any visible injury or abnormality in the genital area requires a veterinary examination.
- Long-lasting symptoms: If symptoms such as swelling or redness persist for more than a day, it is advisable to consult a veterinarian.
5. Previous medical conditions
- Known previous illnesses: Dogs that have had similar problems in the past should be taken to the vet immediately if symptoms recur.
It is better to be careful and consult a veterinarian at the first signs of irregularities in your dog's genital area. Quick action can often prevent serious complications and contributes significantly to your dog's health and well-being. A veterinarian can make an accurate diagnosis and determine the best treatment plan for your dog.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about paraphimosis in dogs
What exactly is paraphimosis in dogs?
Paraphimosis is a condition in which the dog's glans can no longer be retracted into the foreskin. This causes pain, swelling and can have serious health consequences such as poor circulation or infection.
How do I recognize paraphimosis in my dog?
Typical signs of paraphimosis include swelling and redness of the glans, the dog expressing pain, difficulty urinating and changed behavior such as restlessness or aggressiveness. In advanced cases, the glans can also take on a dark red to blue-violet color.
How is paraphimosis in dogs treated?
Treatment depends on the severity of the disease. Mild cases can often be treated with cooling compresses and gentle manual reduction. In more severe cases, anti-inflammatory medications, surgery to expand the foreskin, or even phallopexy are required. Early treatment is crucial to avoid complications.
Can paraphimosis recur in dogs?
Yes, there are cases where paraphimosis can recur, especially if the underlying causes are not addressed. Regular veterinary checks, good hygiene and weight management are important preventive measures to prevent recurrence.
How can I prevent paraphimosis in my dog?
Preventative measures include maintaining a healthy weight, regularly checking and cleaning the genital area, and promptly treating any injuries or infections in the area.
For dogs prone to paraphimosis, regular veterinary monitoring and advice can be particularly helpful. These answers should help you develop a better understanding of paraphimosis in dogs and take appropriate steps to prevent and treat it. However, if you have any concerns or symptoms, it is always advisable to consult a qualified veterinarian.
Summary Paraphimosis in dogs
Paraphimosis in dogs is a serious condition that requires special attention. When paraphimosis occurs in dogs, it is important to act quickly to avoid long-term damage. Treatment for paraphimosis in dogs depends on the severity of the disease. When diagnosing paraphimosis in dogs, a thorough examination by a veterinarian is essential. Paraphimosis in dogs can cause significant pain and discomfort. Early detection of paraphimosis in dogs is crucial for successful treatment. The symptoms of paraphimosis in dogs should never be ignored.
Prevention of paraphimosis in dogs includes regular checkups and good hygiene. If paraphimosis in dogs is suspected, a veterinarian should be consulted immediately. Treatment options for paraphimosis in dogs vary from conservative measures to surgical procedures. Paraphimosis in dogs may be more common in some breeds, so breed-specific knowledge is important. Adequate follow-up care is crucial to prevent recurrence of paraphimosis in dogs.
The prognosis for paraphimosis in dogs is usually good if treated early. Pet owners should be well informed about the risks and signs of paraphimosis in dogs. Education about paraphimosis in dogs is an important part of preventive health care. Chronic cases of paraphimosis in dogs may require long-term treatment and management. Paraphimosis in dogs can lead to serious complications in some cases.
The importance of veterinary care for paraphimosis in dogs cannot be overemphasized. Paraphimosis in dogs represents not only a physical but also an emotional burden on the animal. A comprehensive treatment strategy is essential to effectively treat paraphimosis in dogs. Finally, owner attention and care is crucial to ensure the well-being of dogs with paraphimosis.
